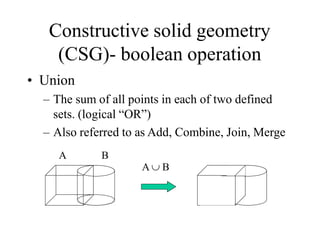
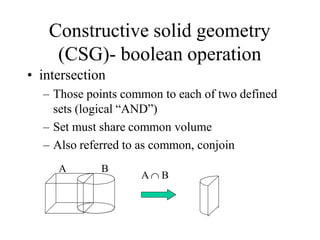
This document discusses solid modeling and its advantages over previous modeling techniques. It describes solid modeling as providing a complete, valid, and unambiguous geometric representation of physical objects by classifying points as inside or outside. It then outlines four main solid model representation schemes, focusing on Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) which represents objects as combinations of primitive solid shapes combined using Boolean operations like union, intersection, and difference to construct a complete solid model.