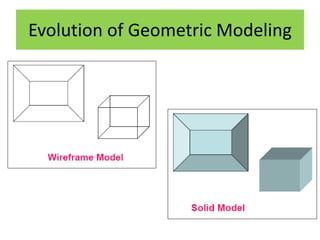
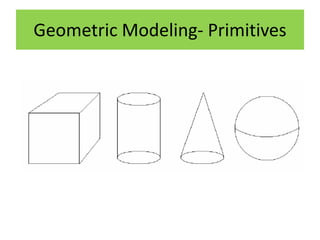
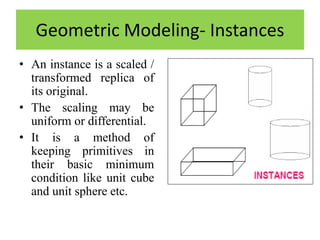
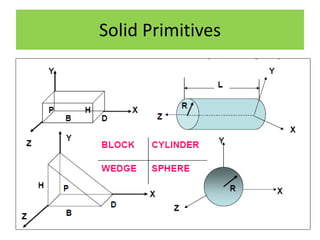
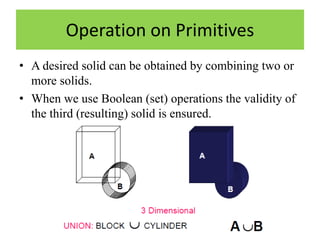
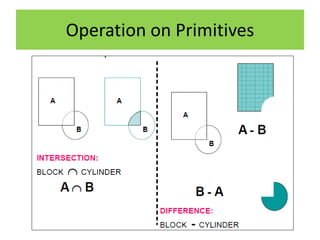
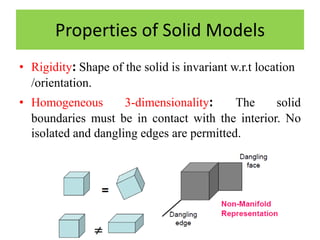
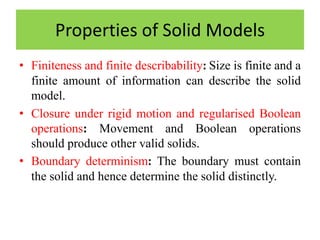
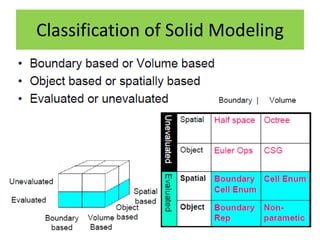
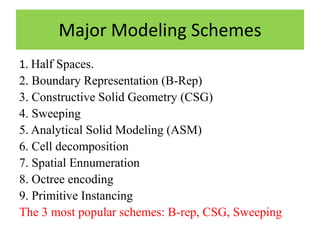
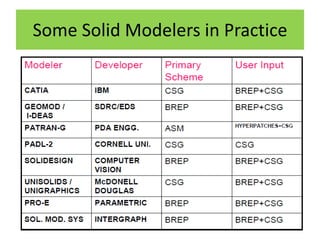
Solid models provide more complete representations of objects than surface or wireframe models by including topological information about connectivity in addition to geometric information. Solid models allow for accurate design and further automation in manufacturing. They represent objects fully using primitives that can be combined through Boolean operations. Major solid modeling schemes include boundary representation, constructive solid geometry, and sweeping which use primitives, instances, and operations on primitives to build valid solid models.