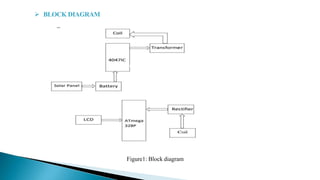
The project aims to design a wireless power transfer system for electric vehicles using solar energy. A solar panel will generate DC power that will charge a battery bank. A wireless power transfer module using electromagnetic induction will transfer power from a transmitter coil at the charger to a receiver coil on the electric vehicle. Sensors will monitor the battery voltage and an LCD will display the status. The system has advantages like reduced infrastructure costs and reliability. Challenges include increased complexity and slower charging times. Potential applications are electric vehicle charging and use in devices, robots, and to reduce pollution. The expected result is wireless charging of electric vehicles using solar power.