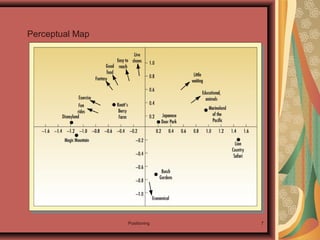
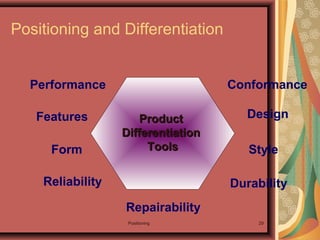
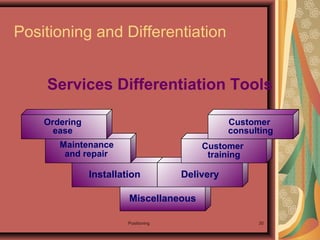
1. Positioning involves designing a company's offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in customers' minds.
2. There are various positioning strategies such as attribute, benefit, user, and competitor positioning. Nestle successfully positioned Maggi noodles as a snack item for children between meals based on careful study.
3. Right positioning is critical for success, as wrong positioning strategies like underpositioning, overpositioning, confused positioning, and doubtful positioning can negatively impact sales.