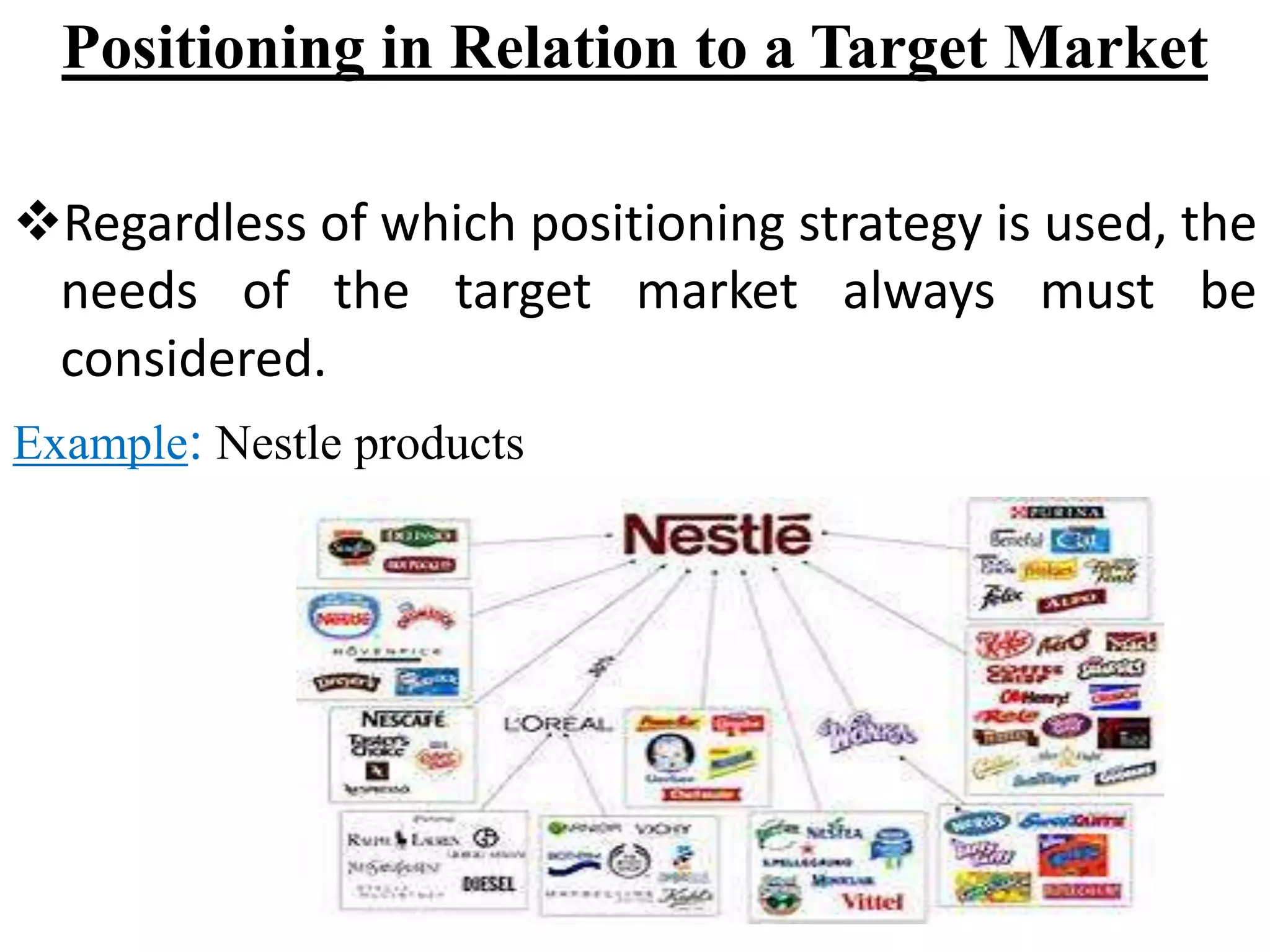
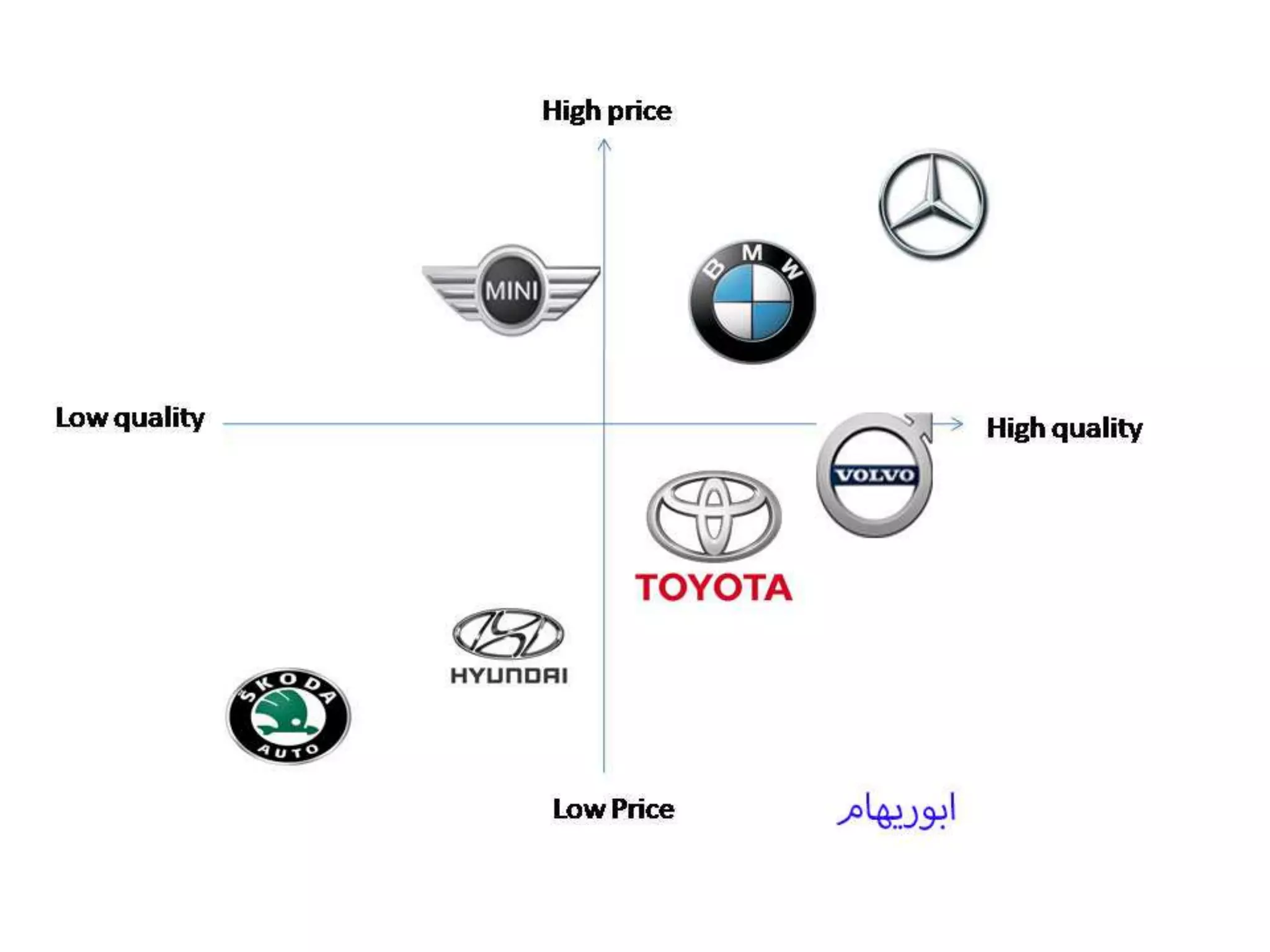
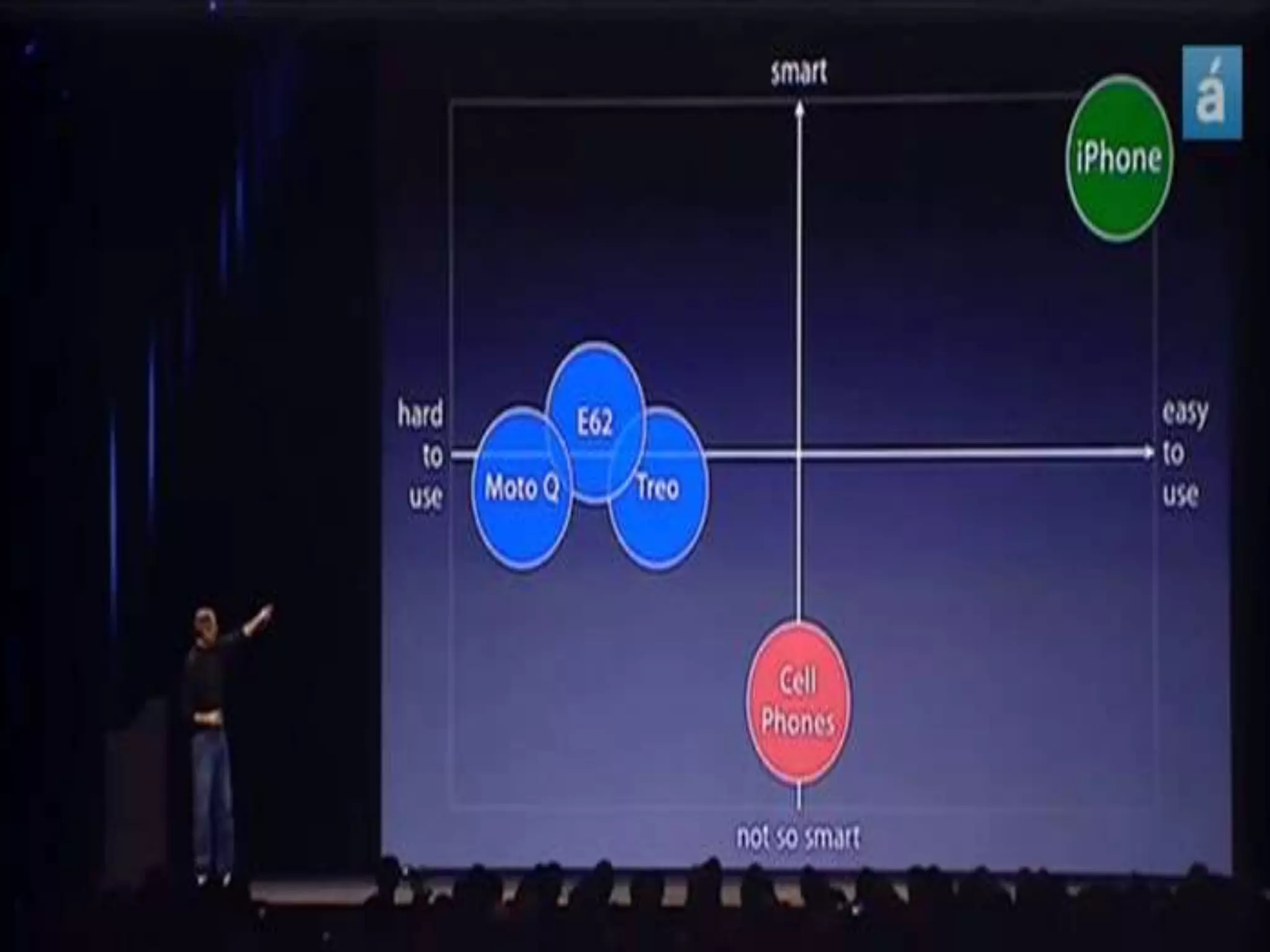
Positioning involves placing a brand in customers' minds in a way that occupies a distinctive place in the target market. It is defined as what is done to the mind of the customer rather than what is done to the product. Effective positioning differentiates a brand in a way that delivers a valued, distinctive, superior, preemptive, and affordable benefit to buyers. Principles of positioning include being first to market or creating a new category. Positioning errors can occur if a brand is under positioned, over positioned, confused, or doubtful in customers' minds. Strategies include positioning by attributes, benefits, use, competitors, product category, quality, price, or target market. Perceptual mapping involves understanding customers' ideal product