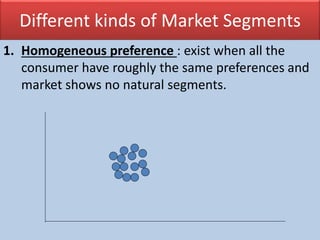
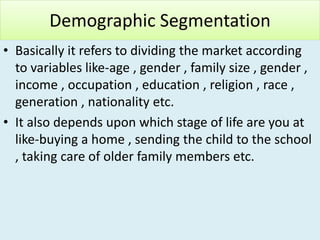
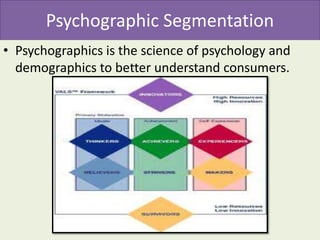
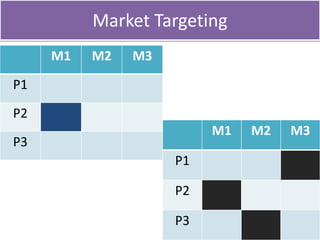
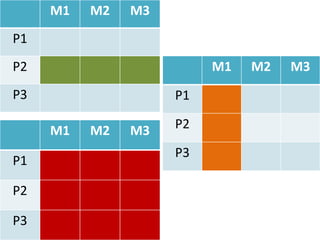
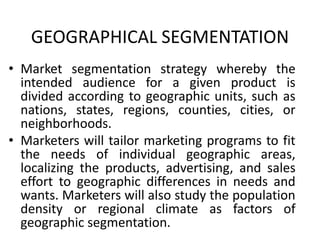
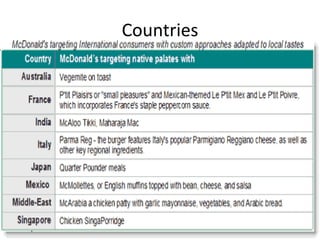
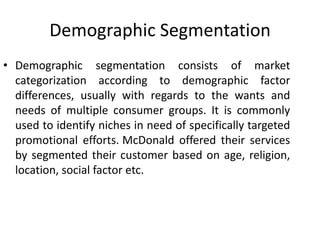
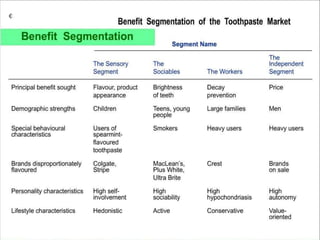
Market segmentation refers to dividing a market into distinct subgroups of customers with distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviors who might require separate products or marketing mixes. Hindustan Unilever (HUL) segments the market based on demographic, psychographic, and lifestyle factors. Some key segments targeted by HUL include break, impulse, and take-home segments defined by consumer needs and product usage occasions. McDonald's segments markets geographically, tailoring its products, advertising, and operations to local needs and customs in different countries, regions, and neighborhoods.