This document provides information on portal frame design, including three types of portal frames:
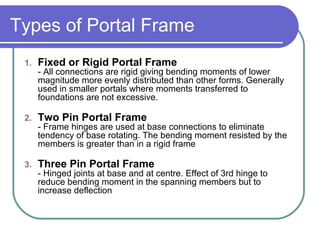
1) Rigid portal frame with all rigid connections
2) Two pin portal frame with hinged connections at the base
3) Three pin portal frame with hinged joints at the base and center
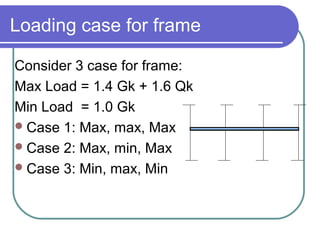
It also discusses factors that influence wind loading, three loading cases to consider, and methods for analyzing and designing portal frames.