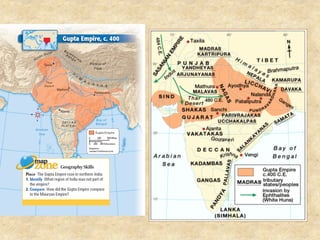
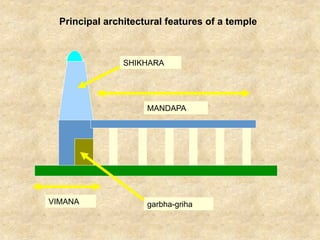
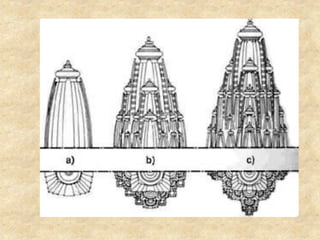
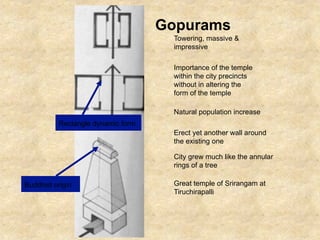
This document discusses Indian temple architecture from ancient times through the Gupta period. It notes that Gupta period temples were derived from earlier rock-cut prototypes, having wider spacing between columns in the middle and features like flat roofs and modest sizes. Key architectural elements of Hindu temples are described like the vimana, mandapa, and shikhara. Sculpture flourished during this time on a massive scale, though structures relied more on piling blocks than technical design. Gopurams, large entrance towers, came to mark the importance of temples within southern Indian cities.