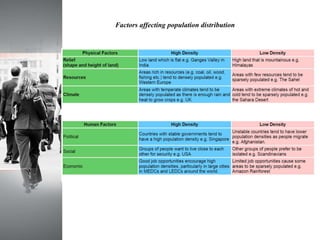
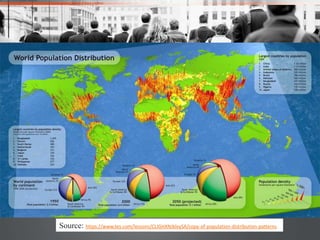
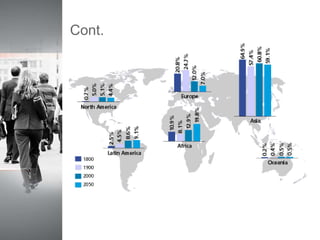
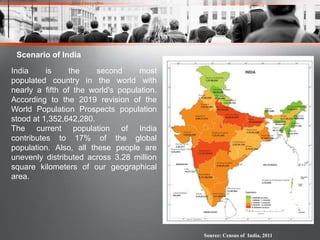
The document discusses factors that affect population distribution and provides examples. It notes that population distribution refers to the spatial arrangement of a population in a region, while density refers to proportional concentration. Key factors determining distribution include physical characteristics like climate, landforms, resources as well as human factors such as politics, economics and social organization. India is provided as a case study, with data showing it has the second largest population in the world at over 1.3 billion people distributed unevenly across its land area. The conclusion emphasizes understanding population patterns and their relationship to environmental variables is important for predicting future growth and developing sustainable policies.