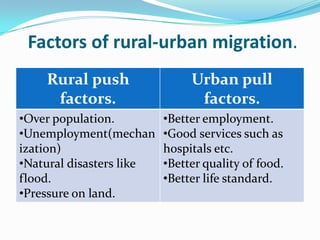
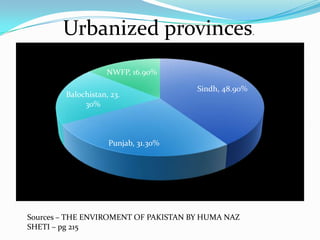
This document discusses migration and population growth in Pakistan. It defines types of migration as in-migration, out-migration, and internal migration. It identifies factors pushing people from rural to urban areas, such as overpopulation and unemployment, and pulling them to cities, like better jobs and services. Rapid urbanization is straining infrastructure and increasing problems like pollution, crime, and unsustainable population growth that can harm Pakistan's economy and environment if not addressed through education, family planning, and balancing resources and population.