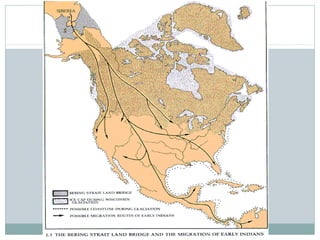
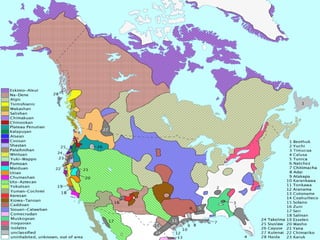
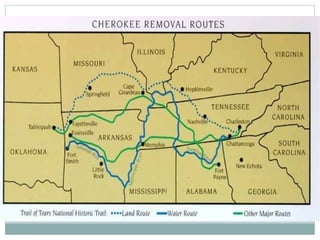
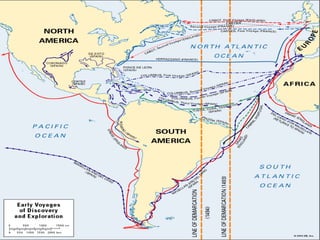
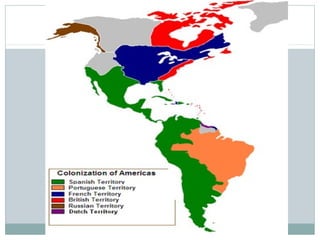
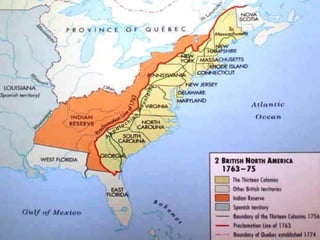
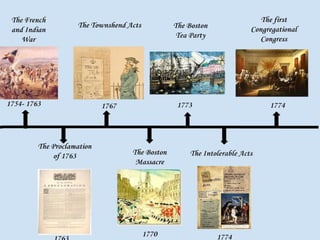
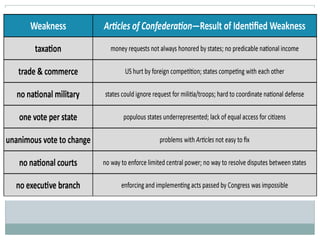
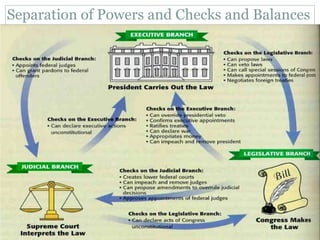
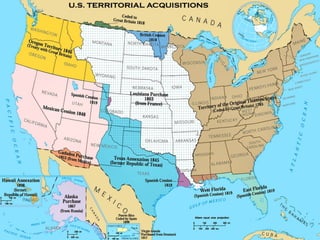
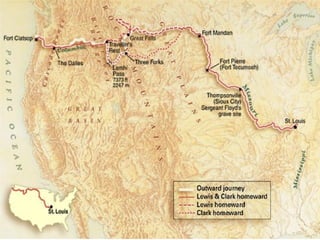
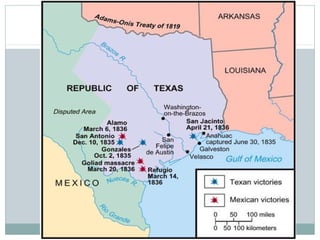
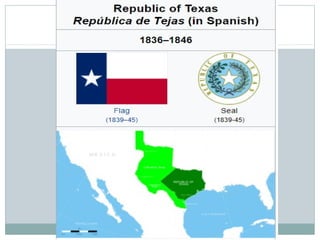
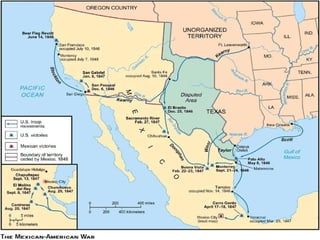
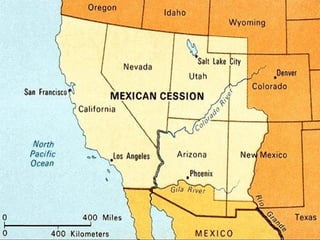
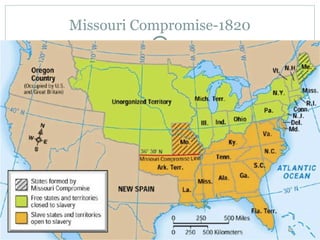
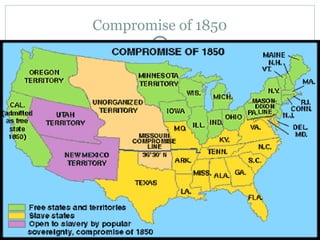
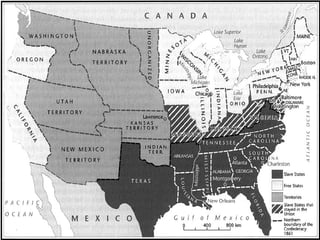
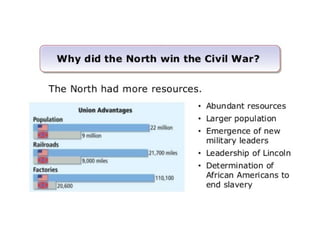
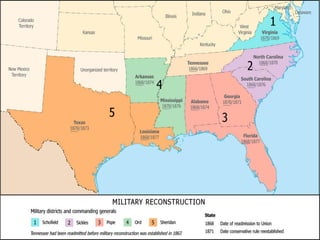
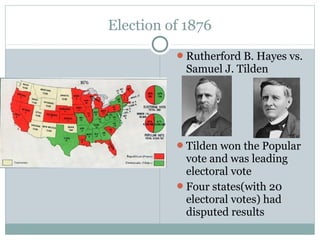
This document provides guidance on studying for an exam on key events that shaped US history from Native American arrival through Reconstruction. It lists the main topics to focus on for each event, including the time period, explanation of what happened, key people, impact on the US, and important terms. Some of the major events it identifies are Native American populations in North America, European exploration and colonization, the Revolutionary War, the US Constitution, westward expansion, the Civil War, and Reconstruction. It also includes discussion questions about these topics and the structures and powers of the US government established by the Constitution.