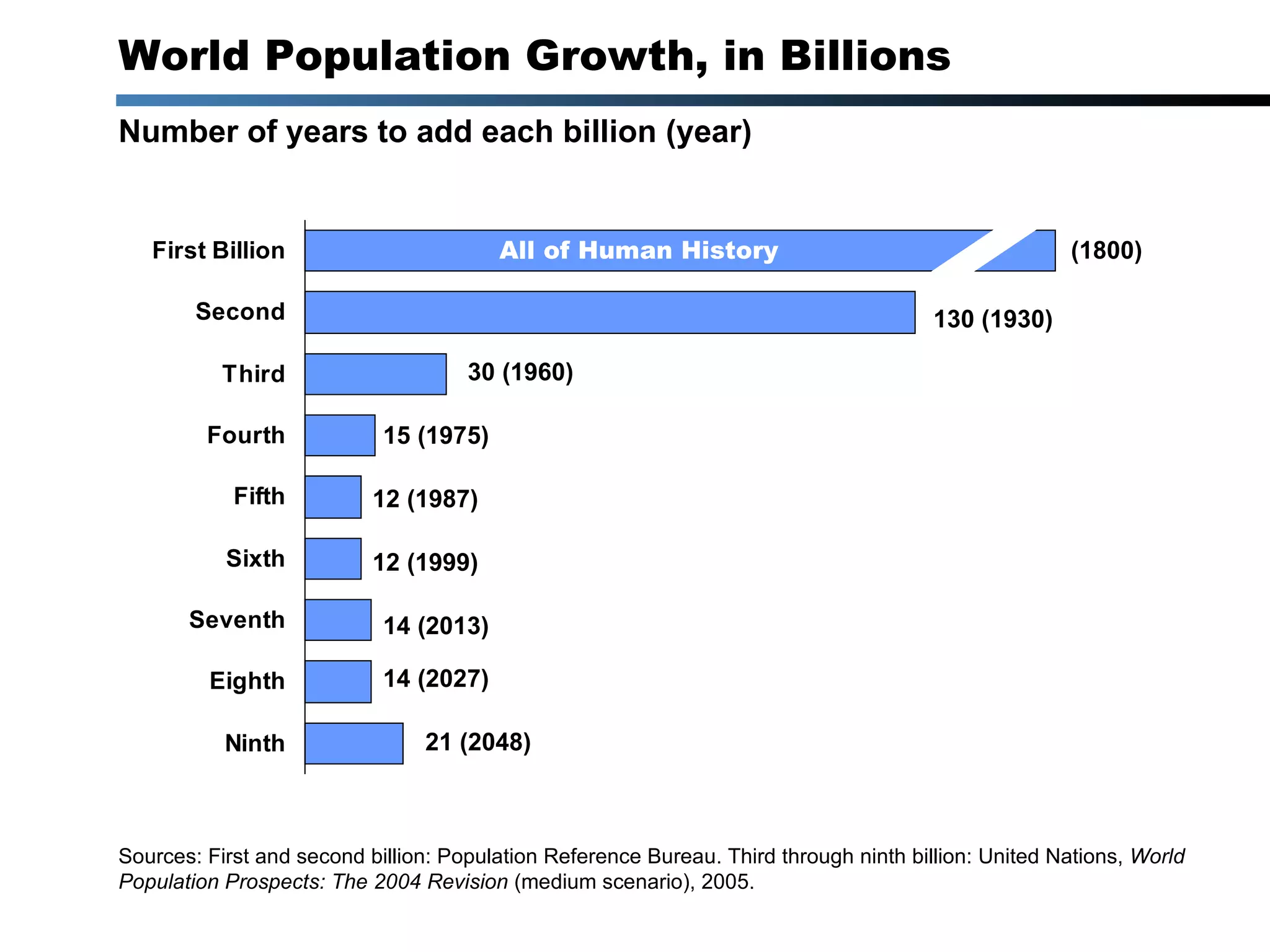
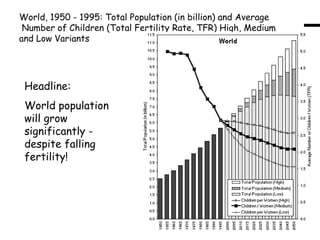
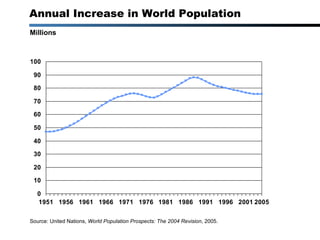
1) The world population will continue growing significantly despite falling fertility rates, reaching 9 billion by 2027 and over 10 billion by 2048.
2) Most of this population growth will occur in developing countries in Asia, Africa, and South America. India will surpass China as the world's most populous country.
3) The top 10 countries contributing to population growth over the next 30 years are India, China, Pakistan, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Indonesia, United States, Bangladesh, DR Congo, and Iran. Western Asia and Africa south of the Sahara will see the highest growth rates.