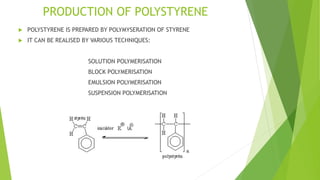
Polystyrene is produced from styrene, which was first distilled from tree resin in 1839. It is prepared through the polymerization of styrene, which can be done through various techniques like solution polymerization. Polystyrene has good thermal insulation properties and is used in many applications like building insulation, food packaging, toys, and more. It is chemically inert but dissolves in some organic solvents and is flammable.





![PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Polystyrene has good thermal and electrical insulation properties
Density of EPS 16–640 kg/m3[15]
Young's modulus (E) 3000–3600 MPa
Tensile strength (st) 46–60 MPa
Elongation at break 3–4%
Notch test 2–5 kJ/m2
Glass transition temperature 100 °C[16]
Vicat B 90 °C[17]
Linear expansion coefficient (a) 8×10−5 /K
Specific heat (c) 1.3 kJ/(kg·K)
Water absorption (ASTM) 0.03–0.1
Decomposition X years, still decaying](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polystyrene-170204121900/85/Polystyrene-7-320.jpg)


