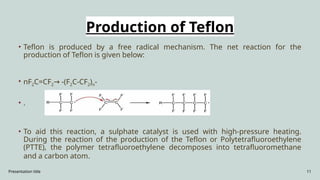
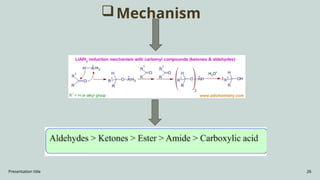
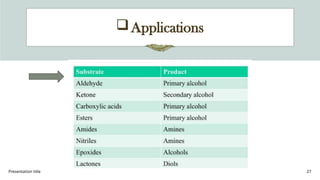
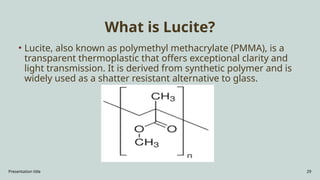
The document presents an overview of various industrial polymers including nylon-6, teflon, polystyrene, polyethylene, lithium aluminum hydride (lialh4), and lucite. It details their history, preparation methods, properties, and applications across industries such as textiles, automotive, and electronics. Each polymer is described in terms of its chemical characteristics and practical uses, highlighting their significance in modern manufacturing and product design.