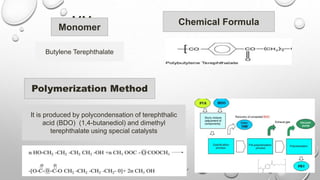
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polymer that is part of the polyester family. It has good electrical resistance, toughness, and surface finish, making it useful in the electrical and electronics industries. PBT can be made flame retardant and resistant to chemicals and water. It is produced through polycondensation of terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol. PBT can be injection molded or extruded and has applications in electrical components, automotive parts, and other industrial uses due to its properties and processability.