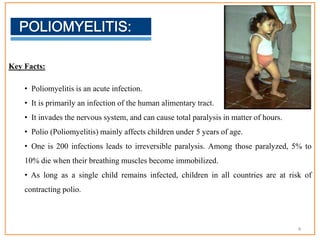
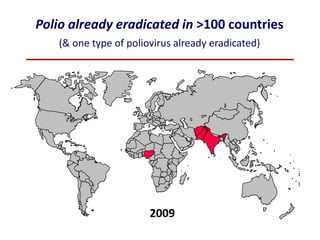
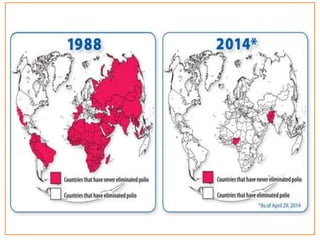
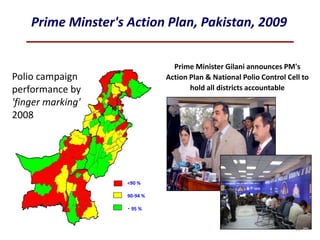
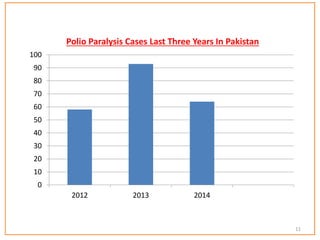
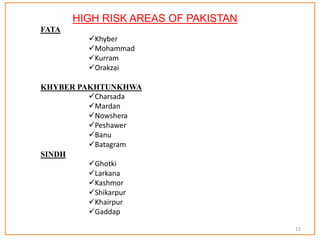
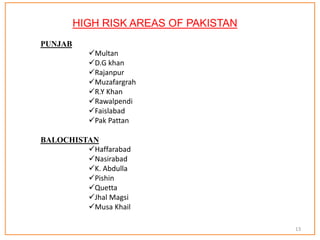
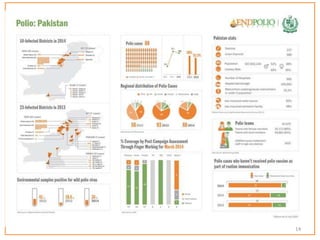
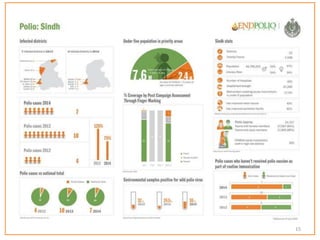
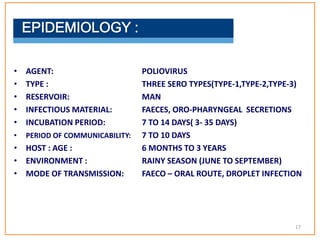
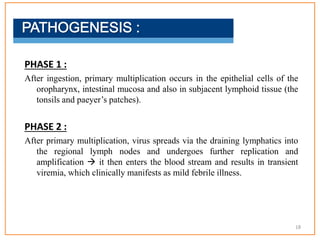
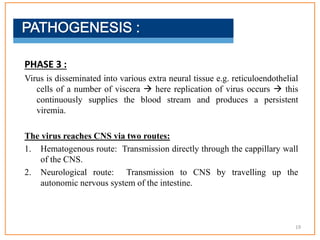
This document provides information about poliomyelitis (polio). It begins by defining the objectives of the document, which are to define polio, explore its history and pathogenesis, describe the types and clinical manifestations, discuss management, and explain the nurse's role in prevention. It then provides key facts about polio, statistics on outcomes of paralysis, highlights from the history of polio research, global eradication efforts and statistics on cases in Pakistan. The document discusses the virus, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations including paralysis, management including rest and ventilation, and the nurse's role in vaccination and education.