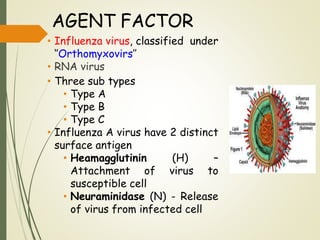
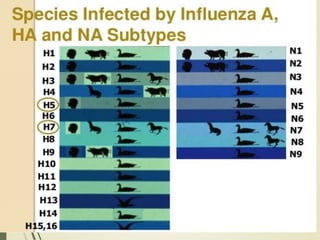
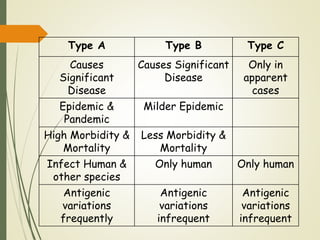
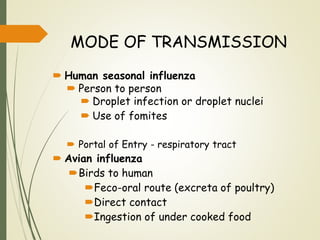
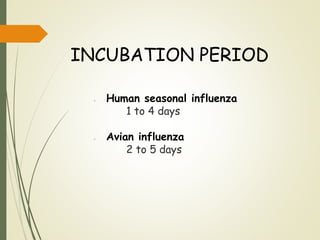
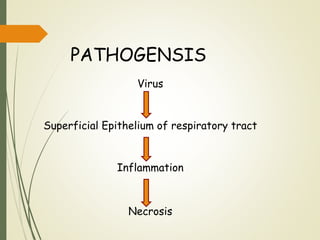
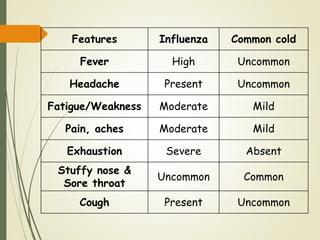
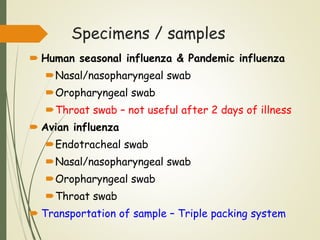
The document discusses influenza, also known as seasonal flu. It is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses that causes symptoms like fever, cough, and muscle pain. Influenza occurs seasonally as well as sporadically, and can sometimes cause pandemics every 10-40 years when the virus undergoes major antigenic changes. Influenza viruses are classified into types A, B, and C. Type A is responsible for epidemics and pandemics. The document outlines the epidemiology, transmission, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of influenza. Vaccination is recommended for high-risk groups to reduce complications.