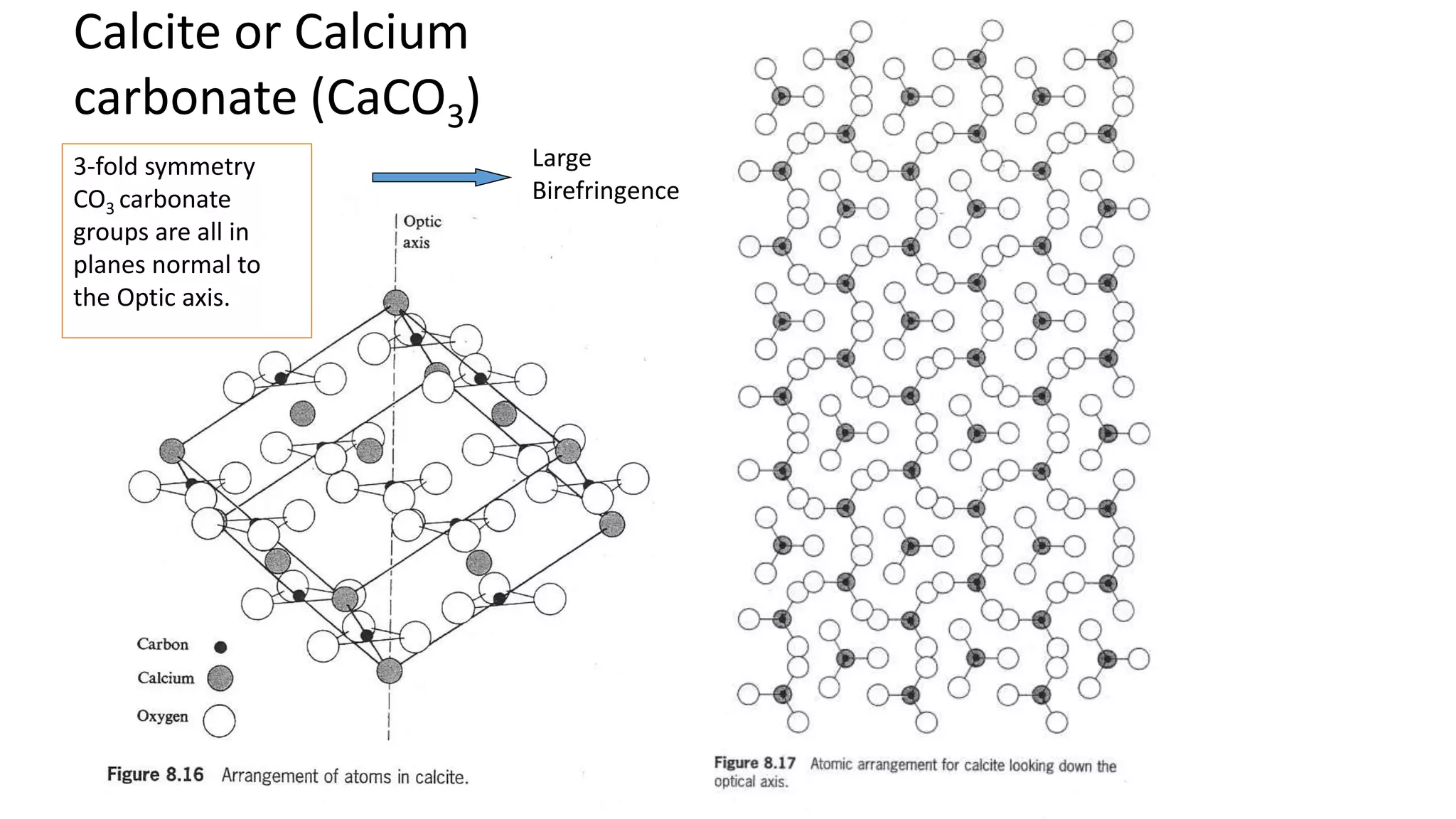
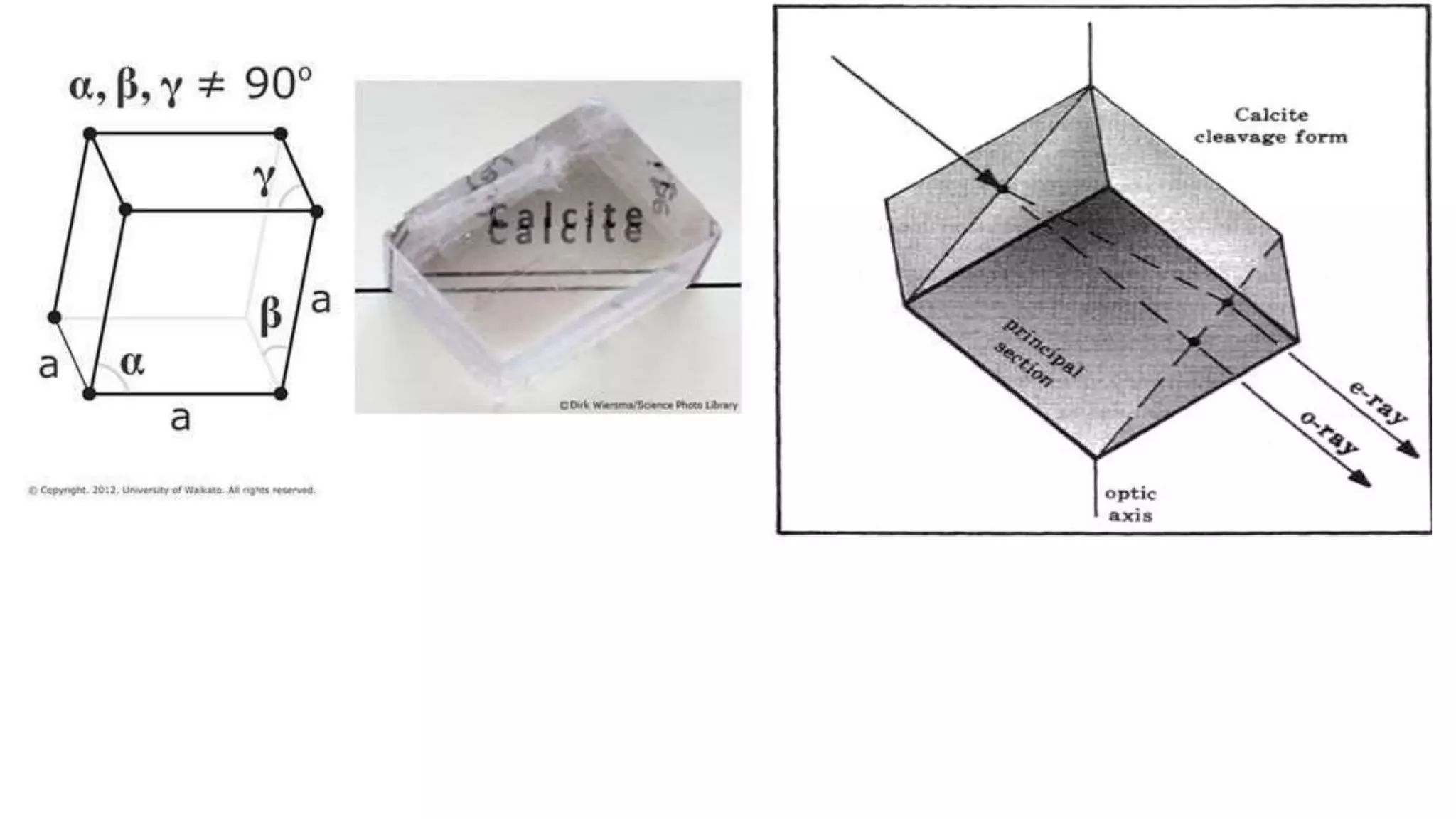
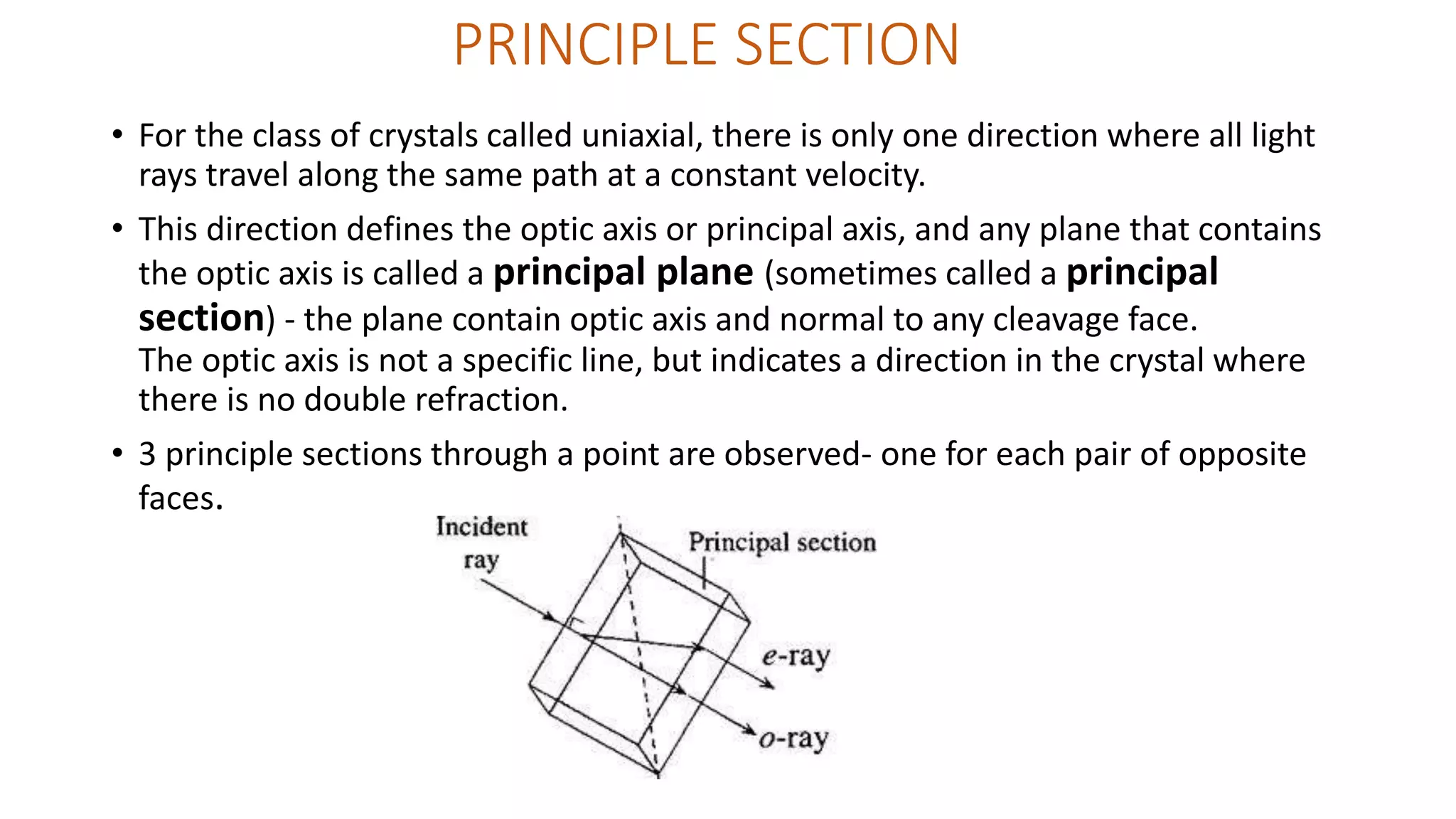
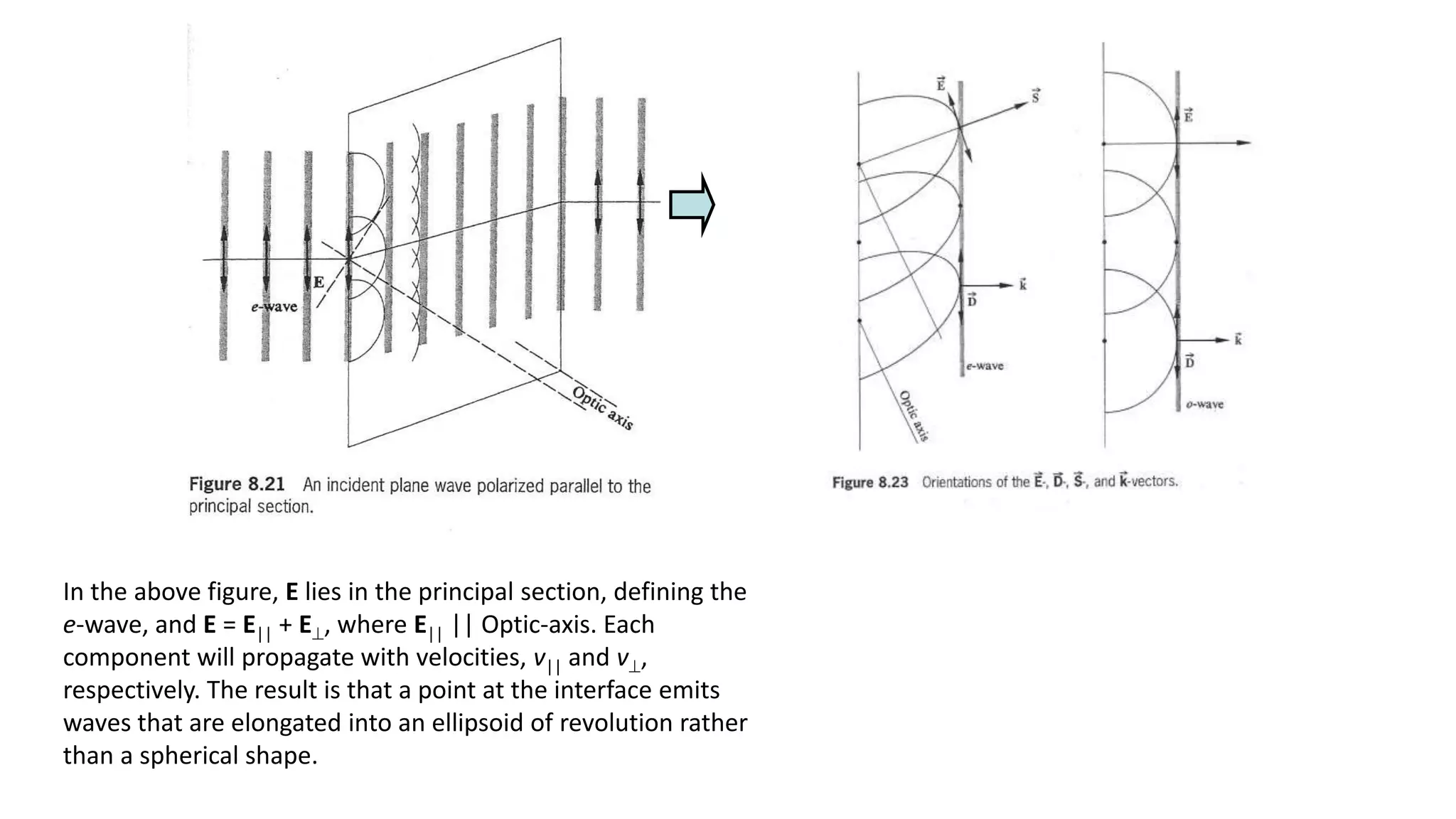
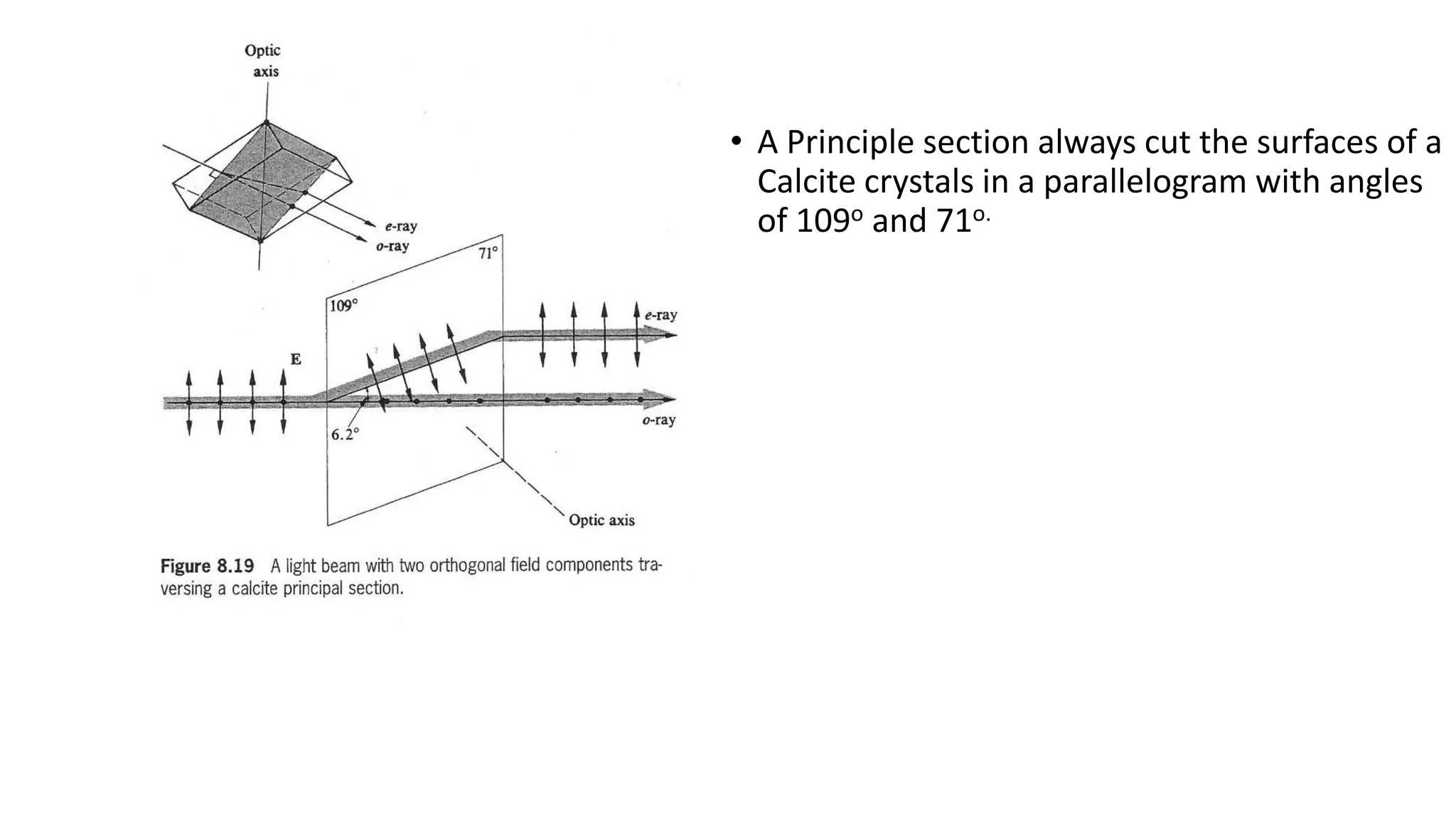
Huygen's theory of double refraction explains the phenomenon of birefringence in crystals like calcite. According to the theory:
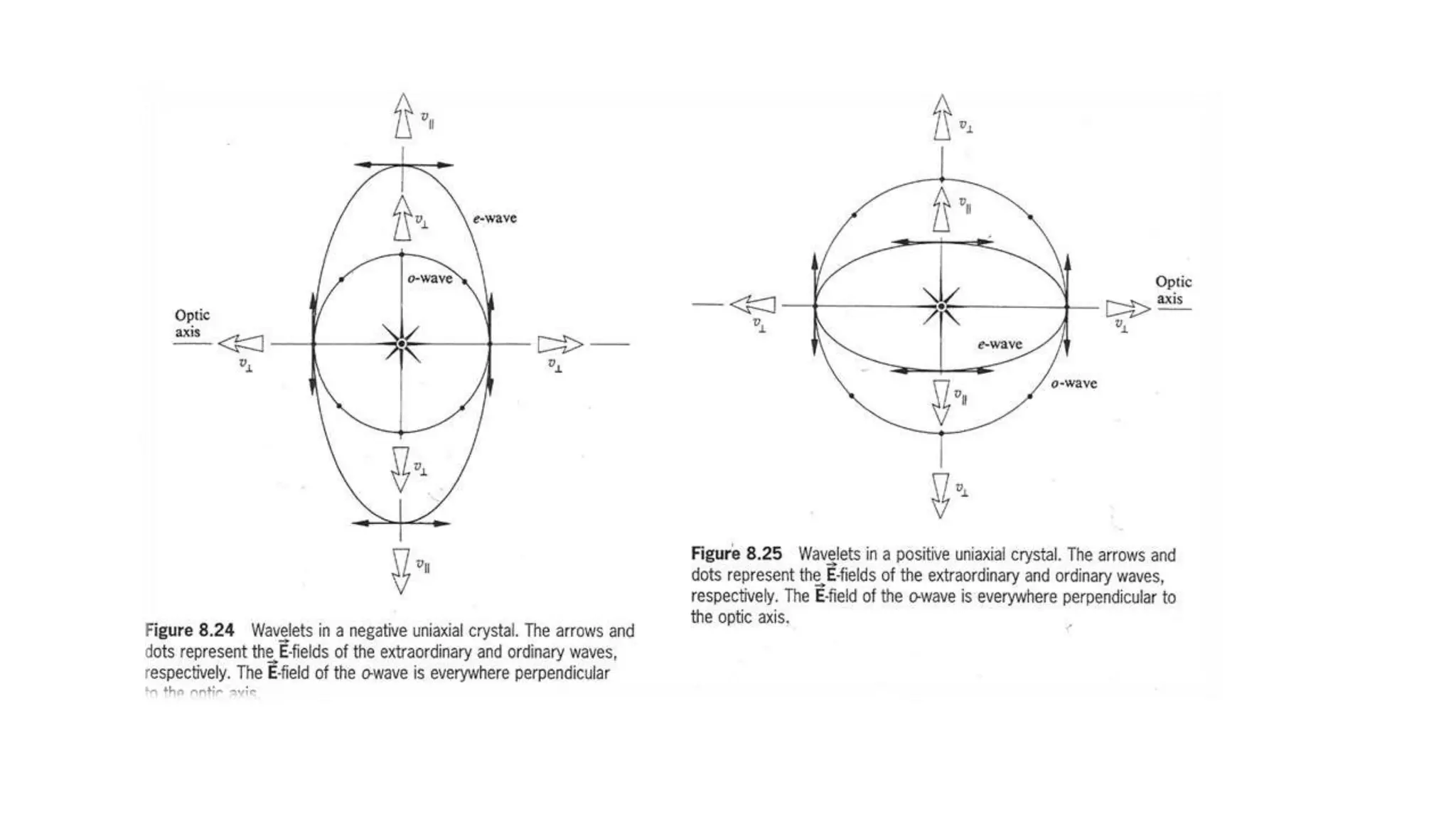
- Each point in a birefringent crystal produces two types of wavefronts - a spherical wavefront for the ordinary ray and an ellipsoidal wavefront for the extraordinary ray.
- The shape of the wavefronts depends on whether the crystal is negative or positive. In negative crystals like calcite, the extraordinary wavefront is outside the ordinary wavefront, while in positive crystals it is inside.
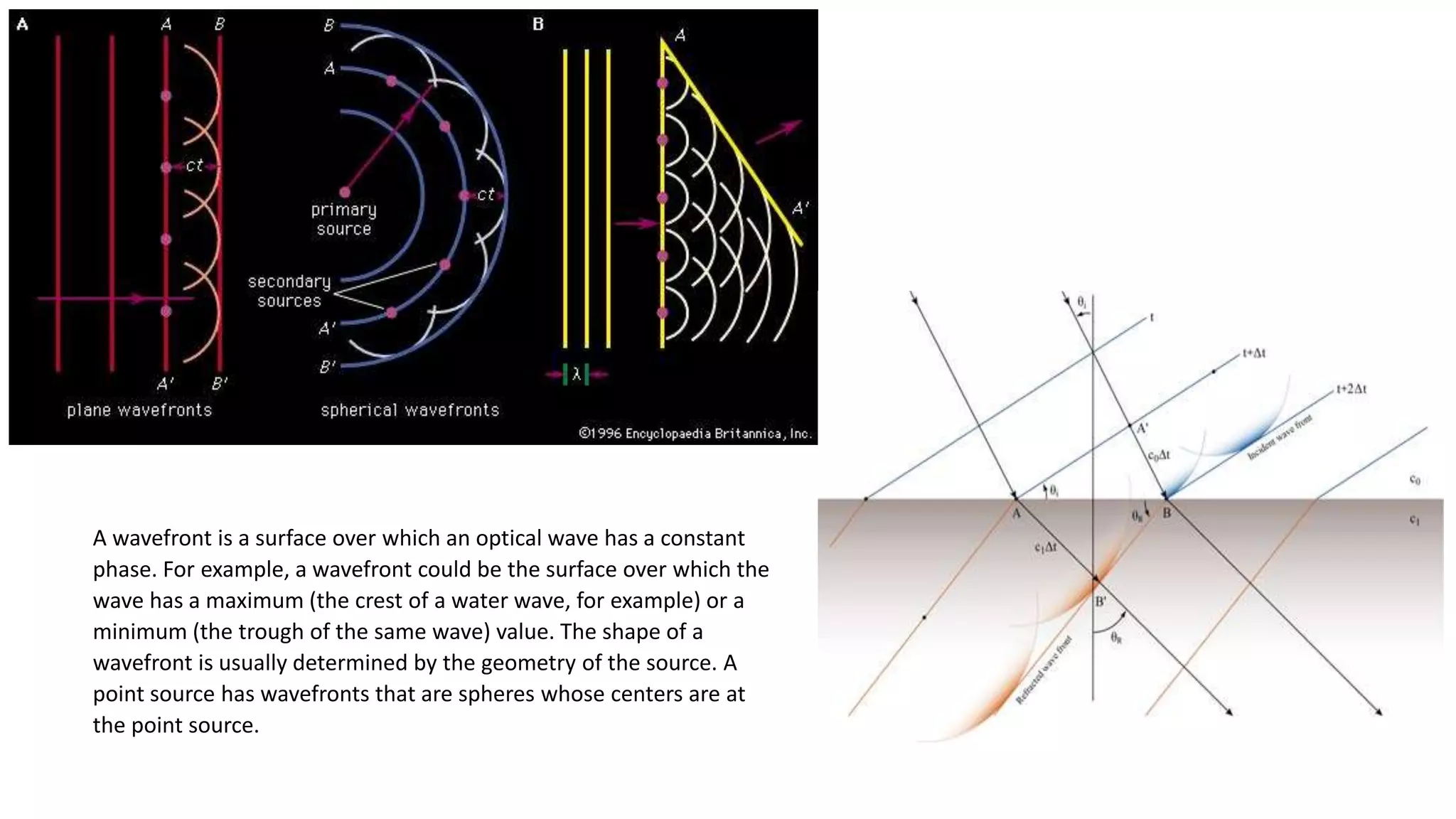
- Huygen's principle treats each point on a wavefront as a secondary source of spherical wavelets, and the envelope of these wavelets makes up the