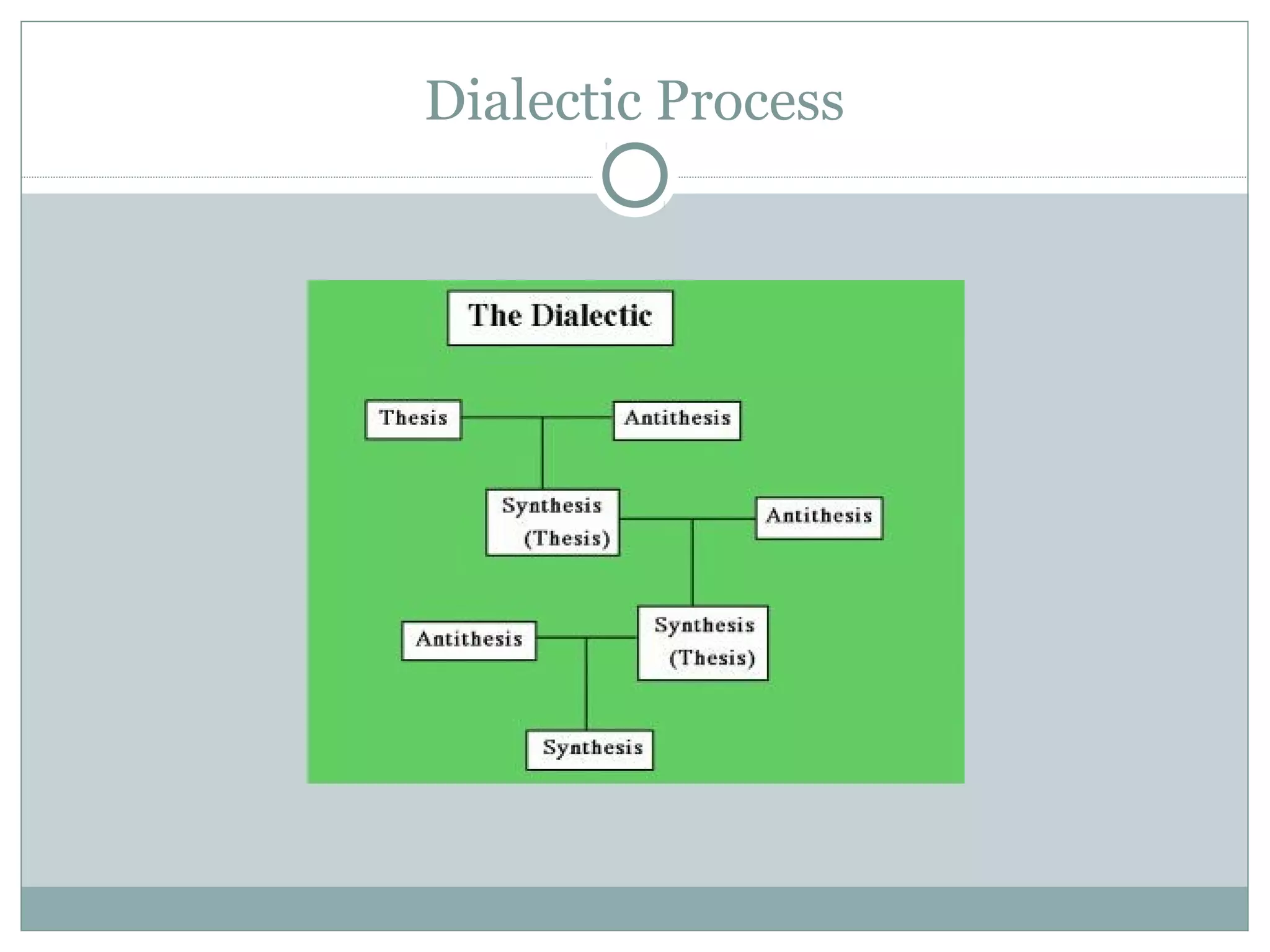
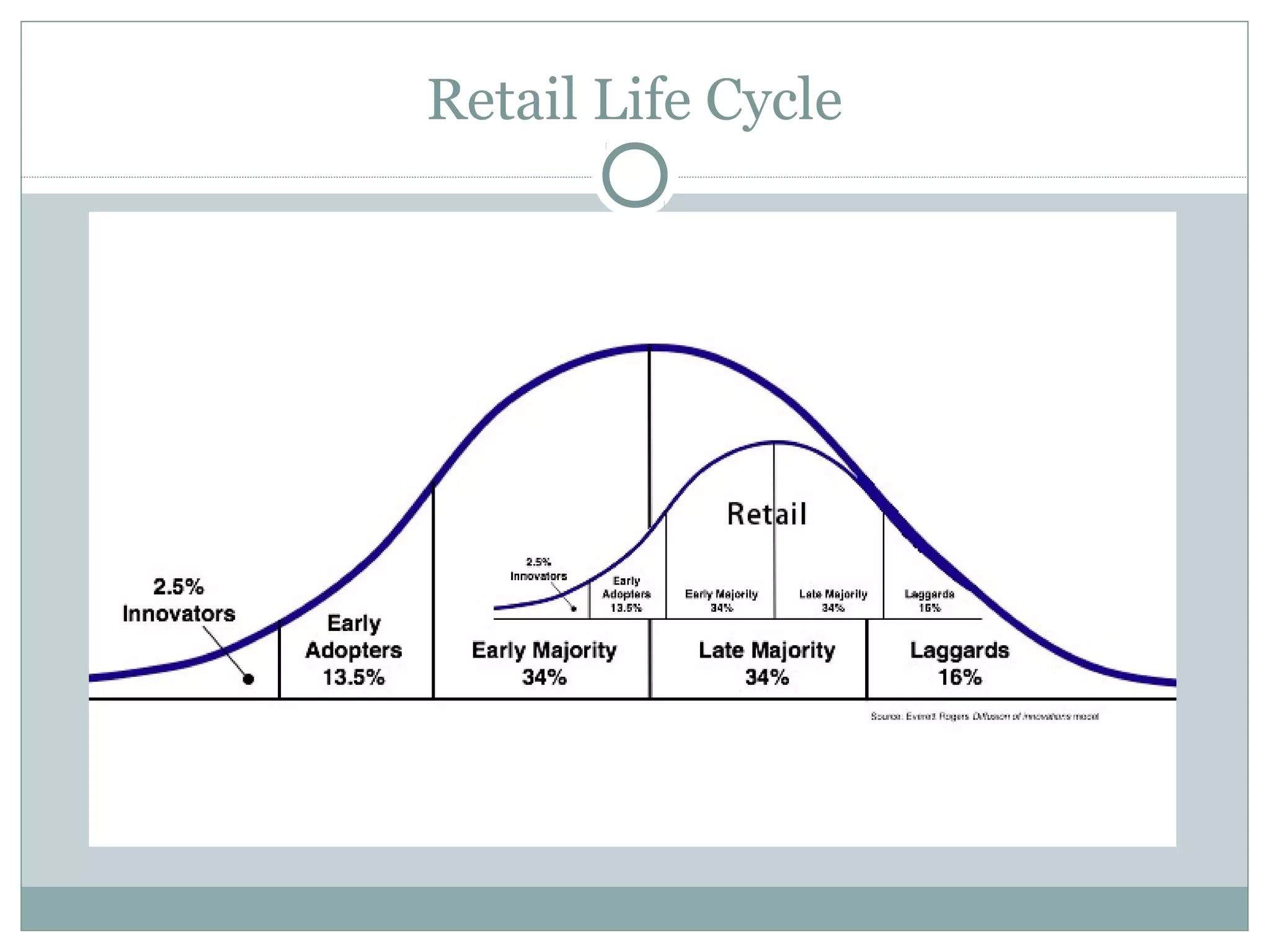
There are two main theories of retailing described in the document: cyclical theories and evolutionary theories. Cyclical theories include the wheel of retailing theory and accordion theory, which propose that retail formats cycle between different stages. Evolutionary theories include the dialectic process theory and natural selection theory, which propose that retail formats evolve and adapt through competition and environmental changes, with the formats best able to adapt being most likely to survive. The document also describes the retail life cycle theory, in which retail organizations pass through stages of innovation, growth, maturity, and decline.