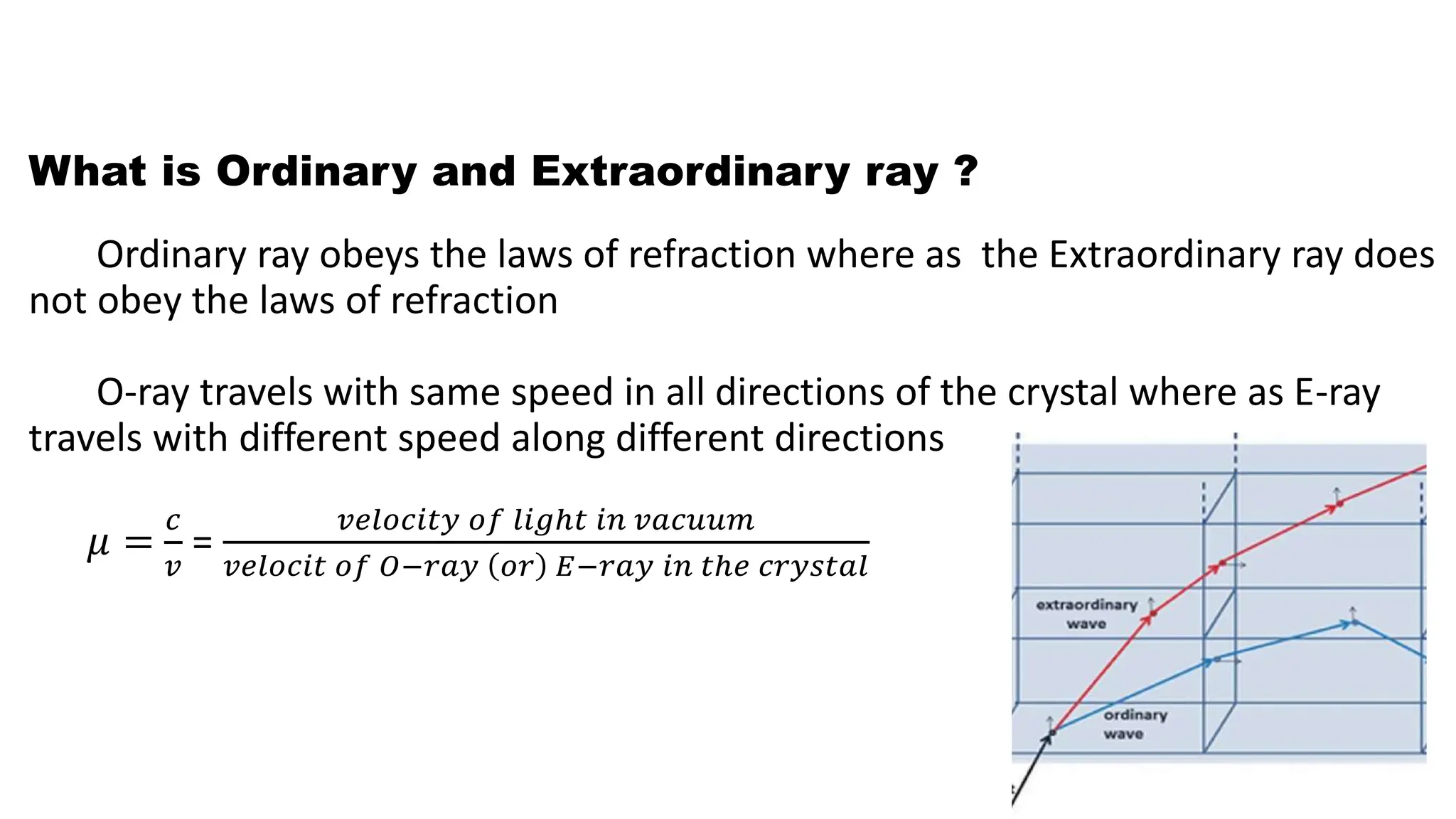
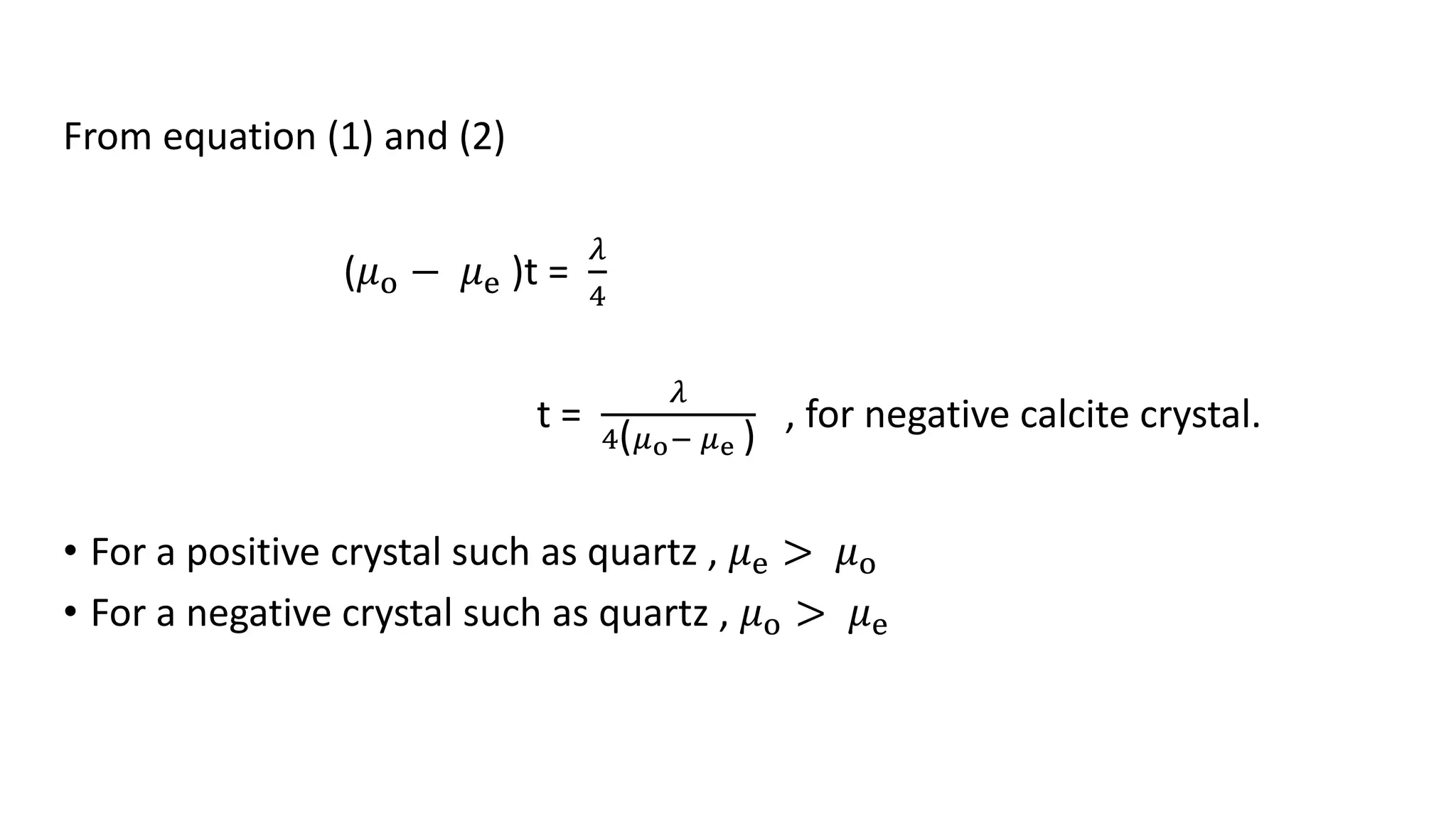
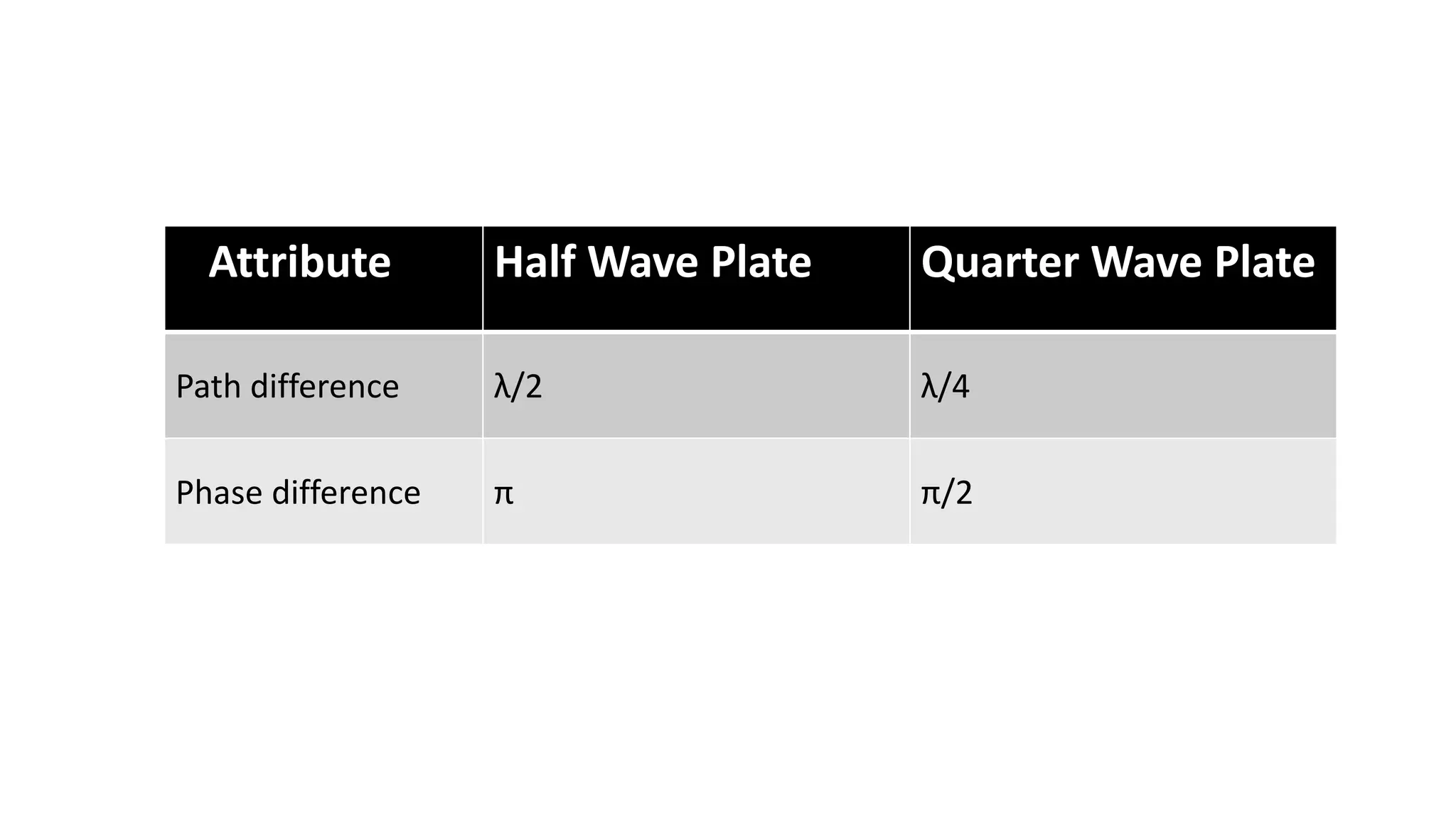
Ordinary rays obey the laws of refraction in crystals, while extraordinary rays do not. O-rays travel at the same speed in all crystal directions, while E-rays have varying speeds. A wave plate alters the polarization of light passing through. A quarter wave plate introduces a λ/4 path difference between O- and E-rays. A half wave plate has a λ/2 path difference. Quarter wave plates convert linear polarization to circular and vice versa, while half wave plates rotate the polarization around the fast axis.