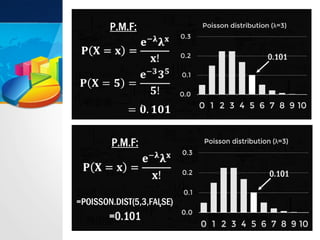
The document discusses the Poisson distribution, a discrete probability distribution useful for modeling rare events. It outlines the conditions, assumptions, and applications of the distribution, such as counting the number of occurrences within a specified time period. Examples include traffic accidents and patient arrivals in emergency rooms, emphasizing the distribution's relevance in fields like queuing theory and genetic research.