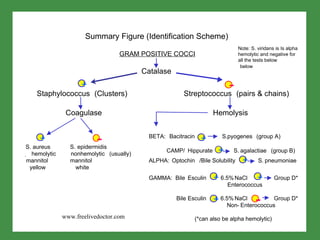
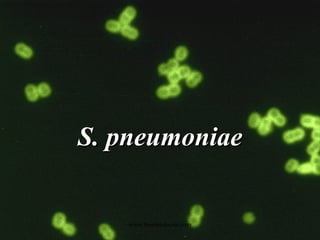
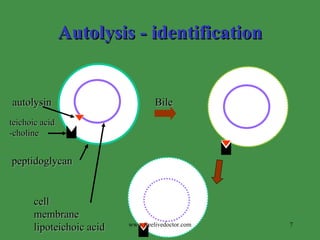
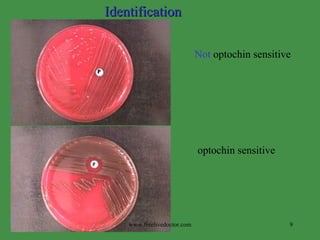
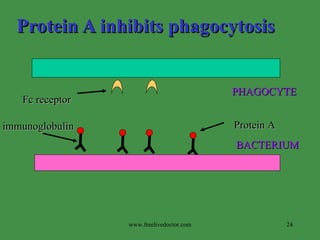
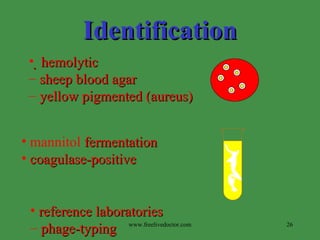
This document summarizes key information about Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus species. S. pneumoniae is a leading cause of pneumonia, particularly in young and old with damaged respiratory tracts. It is identified by being gram positive diplococci that are bile soluble and optochin susceptible. Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most common opportunistic pathogens causing infections like pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and abscesses. It produces exotoxins and enzymes that allow it to spread. Identification involves testing for coagulase, hemolytic activity on blood agar, and pigment production. Other Staphylococcus species like S. epidermidis are opportunistic pathogens
























![Antibiotic therapy Resistance to penicillin penicillinase lactam antibiotics (including methicillin [MRSA]) often ineffective modified penicillin binding proteins Vancomycin current drug of choice resistance has been observed www.freelivedoctor.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumostaph45-100323031052-phpapp02/85/Pneumostaph45-30-320.jpg)