Pneumonia
- 1. PNEUMONIA
- 3. Pneumonia contents introduction Classification of pneumonia According to causes According to area involved pathophysiology Etiology and risk factors Clinical manifestations Diagnostic tests Medical management Nursing intervention Preventive measures Prognosis Complications
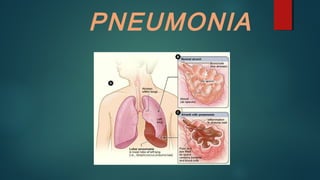
- 4. Pneumonia introduction Is an inflammatory process of the lung parenchyma that is commonly caused by infectious agents. Pneumonia are mainly affected the microscopic air sac known as ALVEOLI . It is cause by streptococcus pneumoniae. In this condition accumulation of fluid in alveoli.
- 6. classification of pneumonia Pneumonia are classified into four types… 1Community – acquired pneumonia 2 hospital acquired pneumonia 3 pneumonia in the immunocompromised host 4 aspiration pneumonia
- 7. Community acquired pneumonia Most people get CAP by breathing in germ that live in the mouth nose and throat Streptococcus pneumonia are the most common cause of the CAP. It is gram positive organism. Viral pathogen include in pneumonia are – Herpes simplex and adenovirus.
- 8. Hospital acquired pneumonia HAP also known as nosocomial pneumonia. This type of pneumonia due to exposed to the potential bacteria from other sources Ex. Respiratory therapy device and equipment transmission of pathogen by the hand of health personnel The common organism responsible for HAP include the pathogen enterobacter species , Escherichia coli , H influenza and staphylococcus.
- 9. Pneumonia in the immunocompromised host Pneumonia in the immunocompromised host occurs with use of- corticosteroid immunosuppressive agents Chemotherapy Nutritional depletion Use of broad spectrum antimicrobial agents AIDS genetic disorder Bacteria are – Pseudomonas , e coli
- 10. Aspiration pneumonia Aspiration pneumonia refers to entry of exogenous or endogenous substance into the lower airway. Gastric contents , exogenous or ingestion may impair in the lungs This lead to bact. growth and resulting pneumonia .
- 12. Classification of pneumonia (cont…) According to areas involved Lobar pneumonia; if one or more lobe is involved Broncho-pneumonia; the pneumonic process has originated in one or more bronchi and extends to the surrounding lung tissue.
- 14. Pneumonia Mode of transmission Ways you can get pneumonia include: Bacteria and viruses living in your nose, sinuses, or mouth may spread to your lungs. You may breathe some of these germs directly into your lungs (droplets infection). You breathe in (inhale) food, liquids, vomit, or fluids from the mouth into your lungs (aspiration pneumonia).
- 15. Pneumonia risk factor Immuno-suppresed patients Cigarette smoking Difficult swallowing (due to stroke, dementia,parkinsons disease, or other neurological conditions) Alcoholism malnutrition
- 16. Pneumonia Chronic lung disease {COPD} Other serious illness such as heart disease, liver cirrhosis, and DM Recent cold, laryngitis or flu
- 18. pathophysiology Streptococcus pneumonia a major cause of bacterial pneumonia , generally resides in the nasopharynx. The streptococci reach the alveoli. They multiply in the alveolus and invade alveolar epithelium. to inflammation and pouring of an exudates into the air space. WBCs migrates to alveoli, become more
- 21. Pneumonia Pathophysiology conti… This will lead to partial occlusion of alveoli and bronchi causing decrease in alveolar oxygen content. Venous blood that goes to affected areas without being oxygenated and return to the heart. This will lead to arterial hypoxemia and even death due to interference with ventilation.
- 23. Pneumonia Clinical manifestations chills Rapidly rising fever ( 39.5 to 40.5 degree) Stabbing chest pain aggravated by respiration and coughing Tachypnea, nasal flaring Patient is very ill and lies on the affected side to decrease pain Deep breathing
- 24. Use of accessory muscles of respiration e.g. abdomen and intercostal muscles Cough with purulent, blood tinged, rusty sputum Shortness of breath low energy, and fatigue Cyanosed lips and nail beds
- 26. Pneumonia Diagnostic tests History taking Physical examination Chest x-ray Blood test Sputum culture
- 28. Pneumonia medical managment antibiotic, depending on sputum and blood culture Oxygen therapy Chest physiotherapy
- 31. Fluid and electrolyte balance Bronchodilator medication Nasotrachial suctioning may be used to maintain airway patency.
- 33. Pneumonia Nursing intervention Maintain a patent airway and adequate oxygenation. Obtain sputum specimens as needed. Use suction if the patient can’t produce a specimen. perform chest physiotherapy.
- 34. Pneumonia Nursing intervention (cont…) Provide a high calorie, high protein diet of soft foods. To prevent aspiration during nasogastric tube feedings, check the position of tube, and administer feedings slowly. To control the spread of infection, dispose secretions properly.
- 36. Pneumonia Nursing intervention (cont…) Provide a quiet, calm environment, with frequent rest periods. Monitor the patient’s ABG levels, especially if he’s hypoxic. Assess the patient’s respiratory status. Auscultate breath sounds at least every 4 hours. Monitor fluid intake and output. Evaluate the effectiveness of administered medications. Explain all procedures to the patient and family.
- 37. Pneumonia Preventive measures Removing secretion is important because retained secretion interfere with gas exchange. Coughing and breathing techniques. Sterilization of respiratory therapy equipment Suctioning of secretion in the unconscious who have poor cough and swallowing reflexes, to prevent aspiration of secretions and its accumulation.
- 38. Pneumonia Prognosis With treatment, most patients will improve within 2 weeks. Elderly or very sick patients may need longer treatment.
- 39. Pneumonia Complications Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Pleural effusion Lung abscess Respiratory failure (which requires mechanical ventilator) Sepsis, which may lead to organ failure
- 41. FOR ANY MISTAKE
- 42. FOR YOUR ATTENTION Any Queries BY -- HARIOM SUMAN [ bittu ]
- 43. WISH YOU ALL THE BEST
