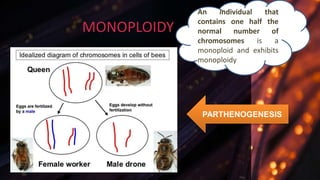
Ploidy refers to the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell or organism. There are several types of ploidy:
Aneuploidy involves an abnormal number of chromosomes and can cause conditions like Down syndrome. Hypoploidy and hyperploidy refer to having fewer or more chromosomes than normal. Specific types include monosomy, nullisomy, trisomy, and tetrasomy. Euploidy involves having full sets of chromosomes and includes diploidy, which is the normal state for somatic cells. Polyploidy is when cells have more than two sets of chromosomes. Ploidy variations can impact fertility and cause genetic disorders.