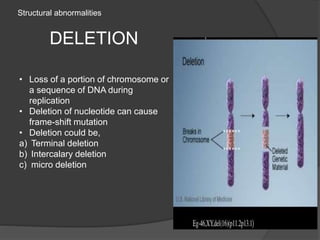
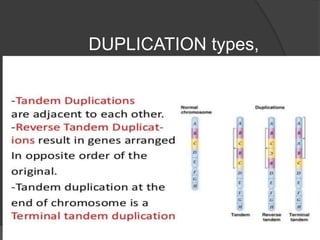
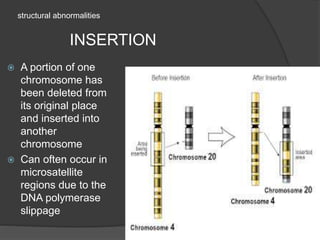
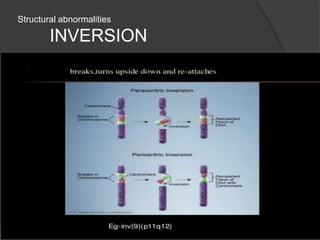
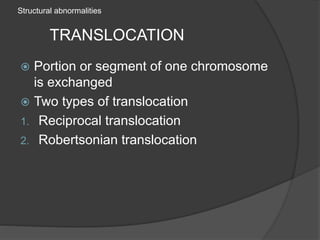
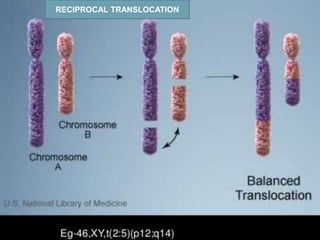
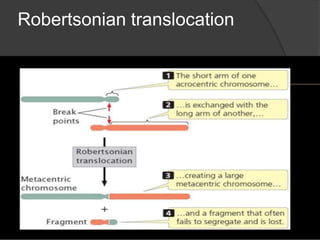
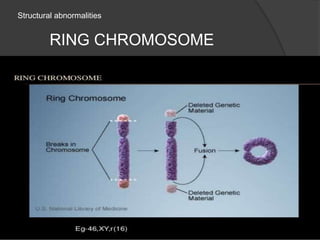
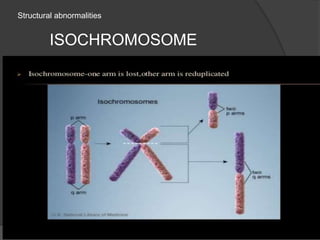
Chromosomal abnormalities can be either numerical, involving atypical chromosome counts like trisomies and monosomies, or structural involving changes in chromosome structure. Some examples of numerical abnormalities include Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. Structural abnormalities involve changes such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations that can alter the genetic material on chromosomes.




![How do chromosomal abnormalities happens
???
Usually due to error in cell division i.e.
mitosis and meiosis
Different types of chromosomal abnormalities
can be organized into two basic groups,
1] Numerical abnormalities
2] Structural abnormalities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chrabb-180331095944/85/chromosomal-abnormalities-6-320.jpg)

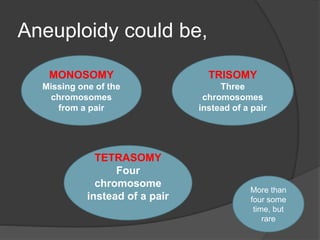
![MONOSOMY
Form of aneuploidy with the presence of
only one chromosome from a pair.
Human condition due to monosomy;
1] Turner’s syndrome
2] Cri du chat syndrome
3] 1p36 deletion syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chrabb-180331095944/85/chromosomal-abnormalities-9-320.jpg)



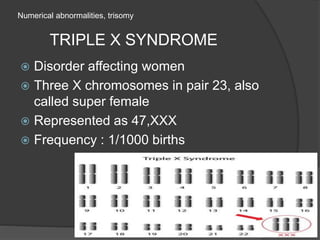
![TRISOMY
Form of aneuploidy with the presence of three
chromosome instead of normal single pair
chromosome
Human condition due to trisomy
1] Down syndrome
2] Klinefelter’s syndrome
3] Edward syndrome
4] Patau’s syndrome etc.
5] Triple X syndrome
Down
syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chrabb-180331095944/85/chromosomal-abnormalities-13-320.jpg)




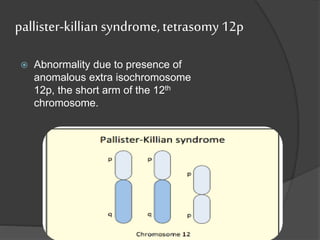
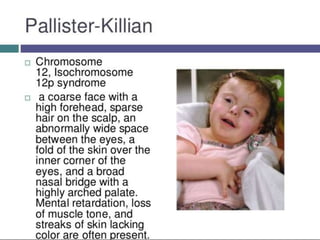
![TETRASOMY
Form of aneuploidy with the presence of
four chromosome instead of normal single
pair chromosome
Human condition due to trisomy
1] cat eye syndrome, tetrasomy 22
2] pallister-killian syndrome, tetrasomy 12p
3] 48,XXXX syndrome/tetrasomy X etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chrabb-180331095944/85/chromosomal-abnormalities-19-320.jpg)