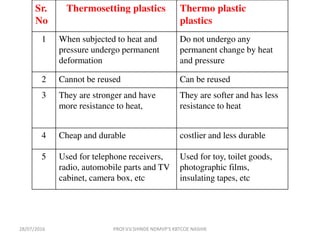
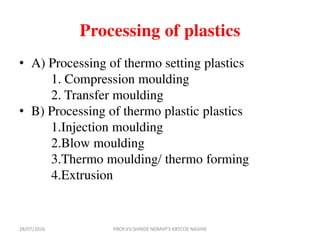
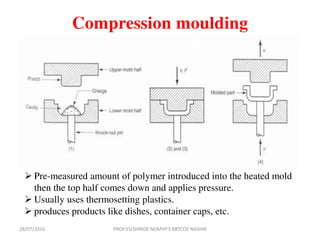
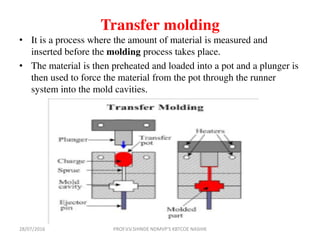
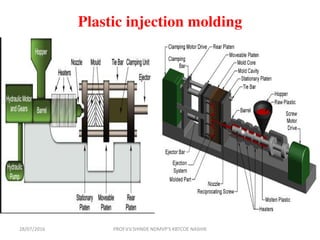
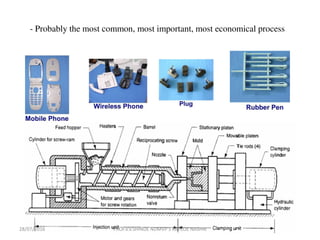
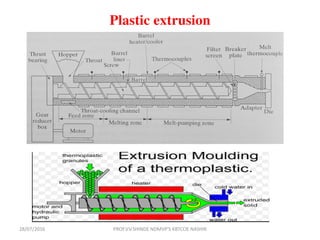
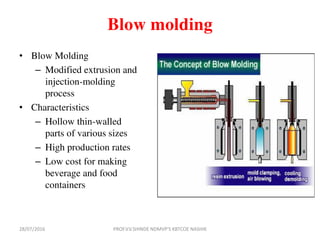
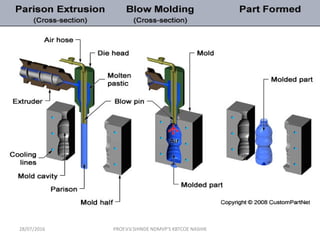
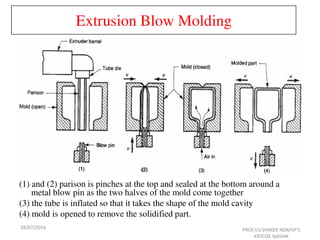
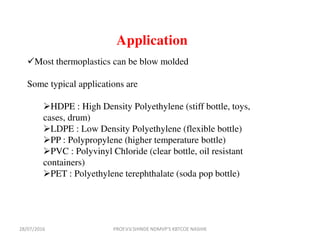
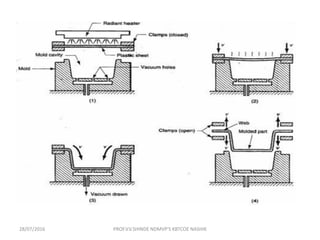
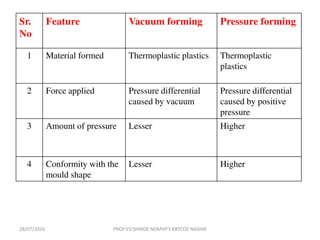
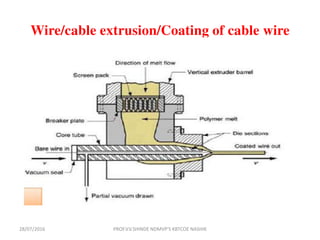
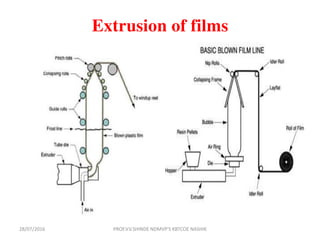
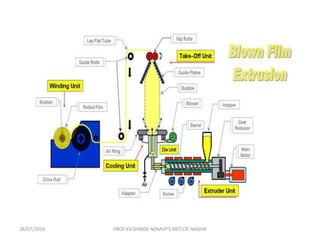
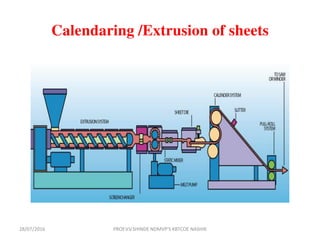
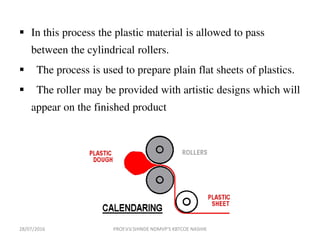
This document discusses various plastic processing techniques. It begins by defining polymers and plastics, noting that polymers are composed of repeating monomer units and occur naturally or can be synthetic. Plastics are typically organic polymers that can be molded. The document then discusses two main types of plastics - thermoplastics, which can be remelted and reshaped, and thermosetting plastics, which permanently set their shape after heating. It proceeds to describe several plastic processing methods like injection molding, compression molding, and extrusion.