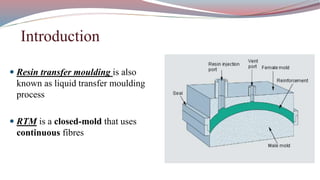
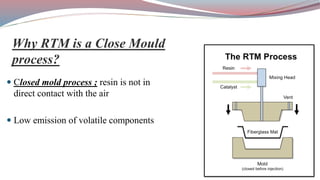
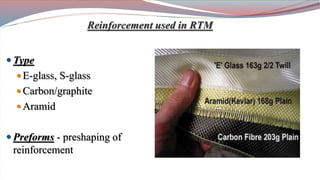
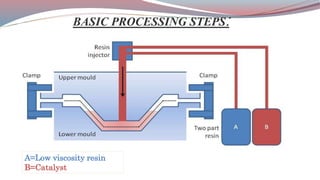
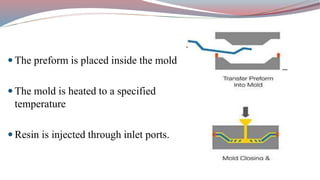
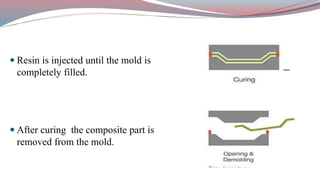
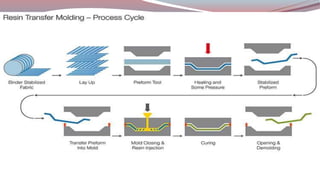
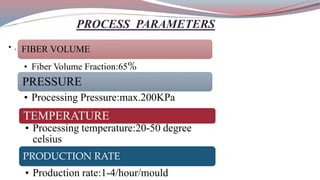
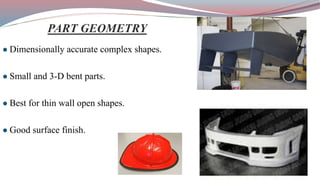
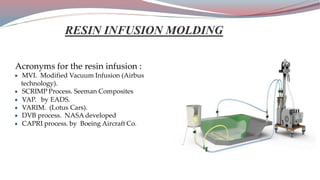
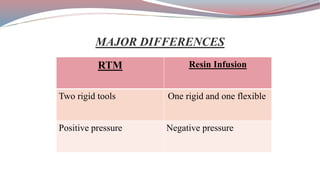
The document discusses resin transfer molding (RTM) and resin infusion molding techniques, detailing the processes, materials, and benefits of each method. RTM is a closed mold process that promotes high fiber volume fractions and low emissions, while resin infusion uses a flexible bag to create negative pressure for molding. Both techniques are cost-effective for producing high-quality composite parts across various applications, including aerospace and automotive sectors.