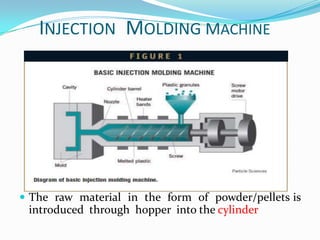
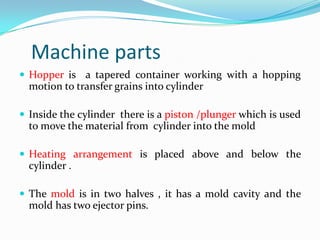
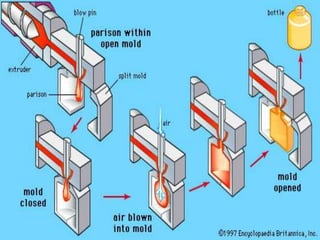
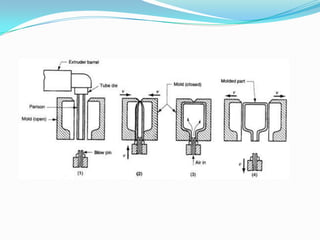
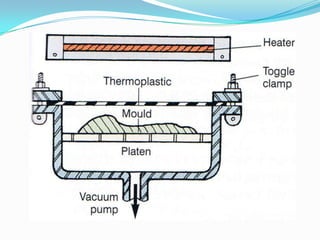
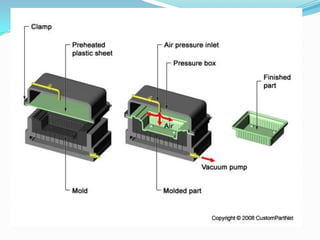
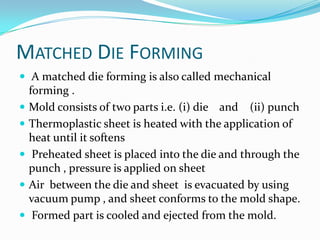
The document discusses different plastic processing methods used by group members Muazz Ali and Irfan Ali. Muazz Ali focuses on injection molding, blow molding, and injection blow molding. Irfan Ali discusses extrusion blow molding, stretch blow molding, and thermoforming. Both members provide details on the basic principles, processes, parameters, advantages, disadvantages and applications of each plastic processing technique.