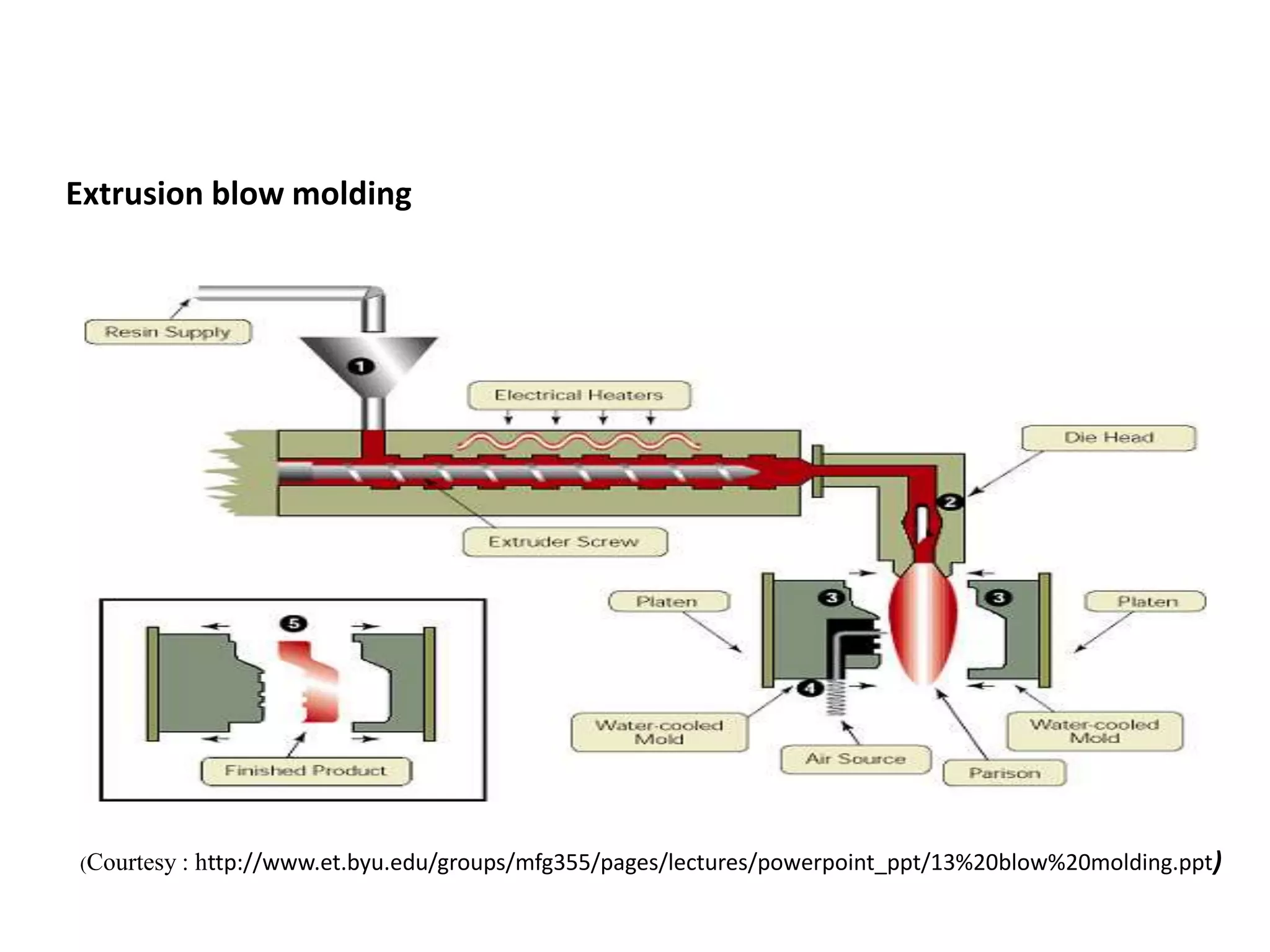
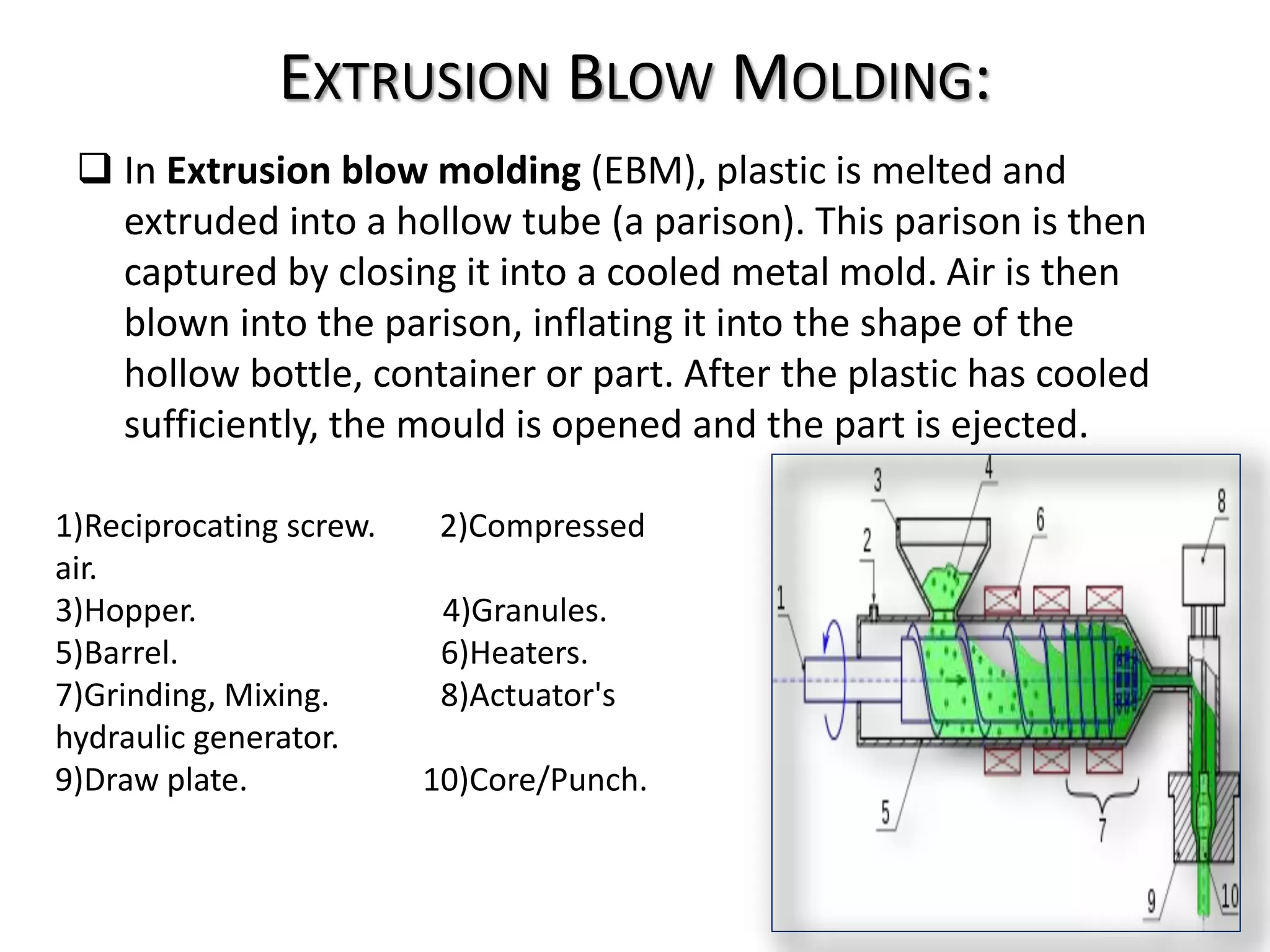
Extrusion blow molding is a manufacturing process used to make hollow plastic parts like bottles. It begins by melting plastic and extruding it into a tube-like parison. The parison is clamped into a mold and compressed air is injected to push the plastic out against the mold walls. As the plastic cools and hardens, the mold opens and the final part is ejected. Common materials for extrusion blow molding include polyethylene, polypropylene, and PET which must have good melt strength. The process offers low costs due to simple molds but is limited to hollow shapes.