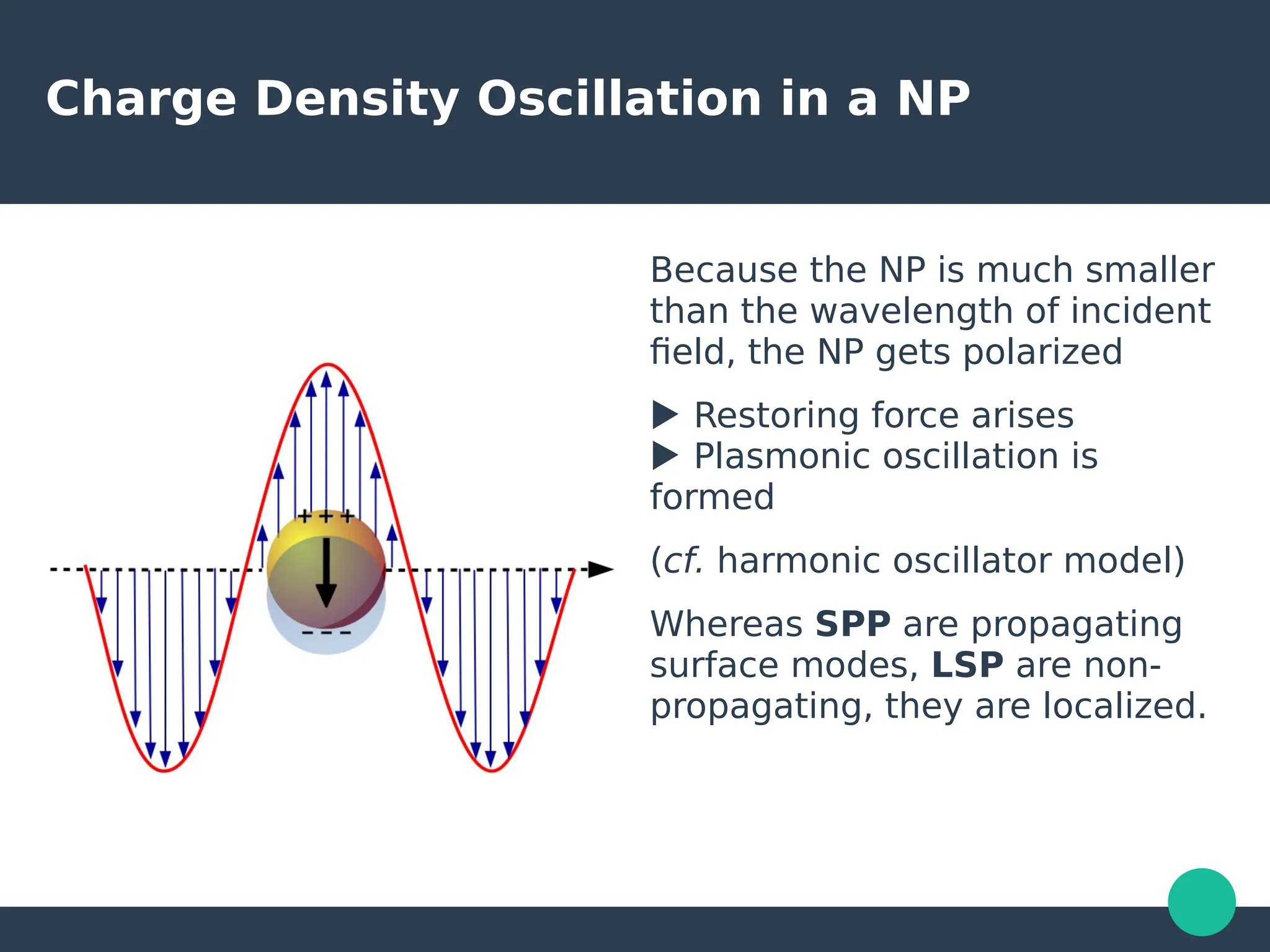
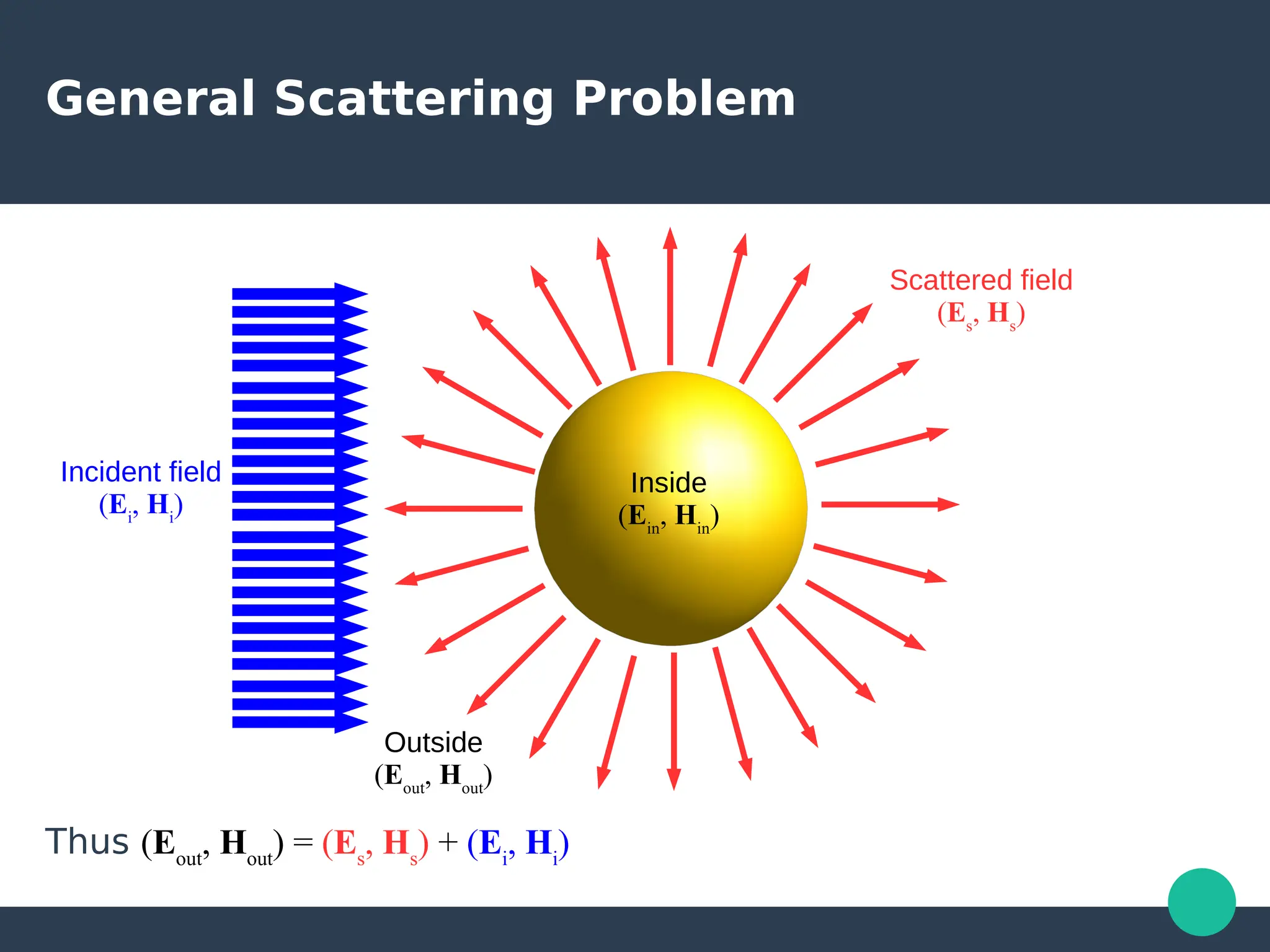
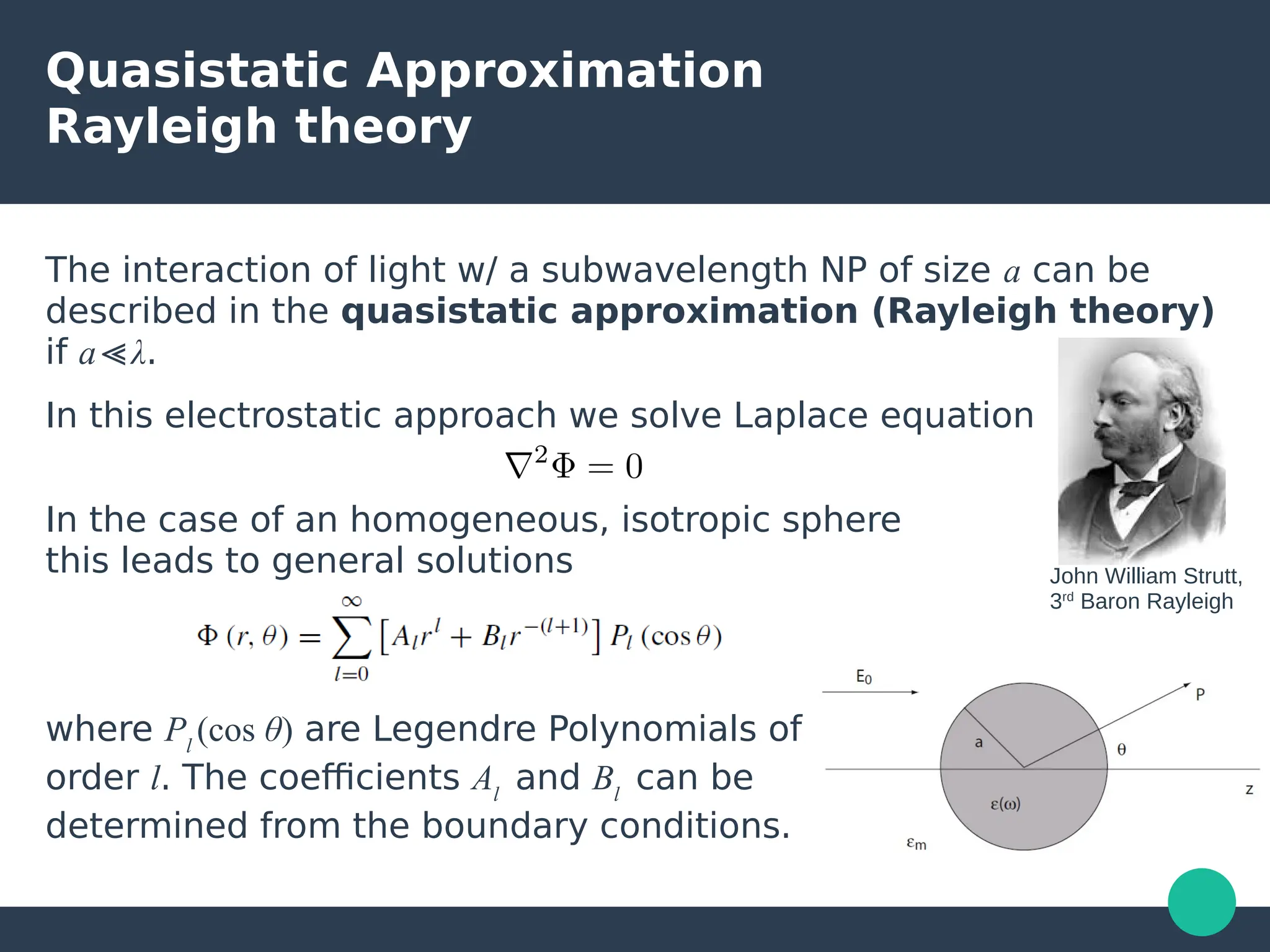
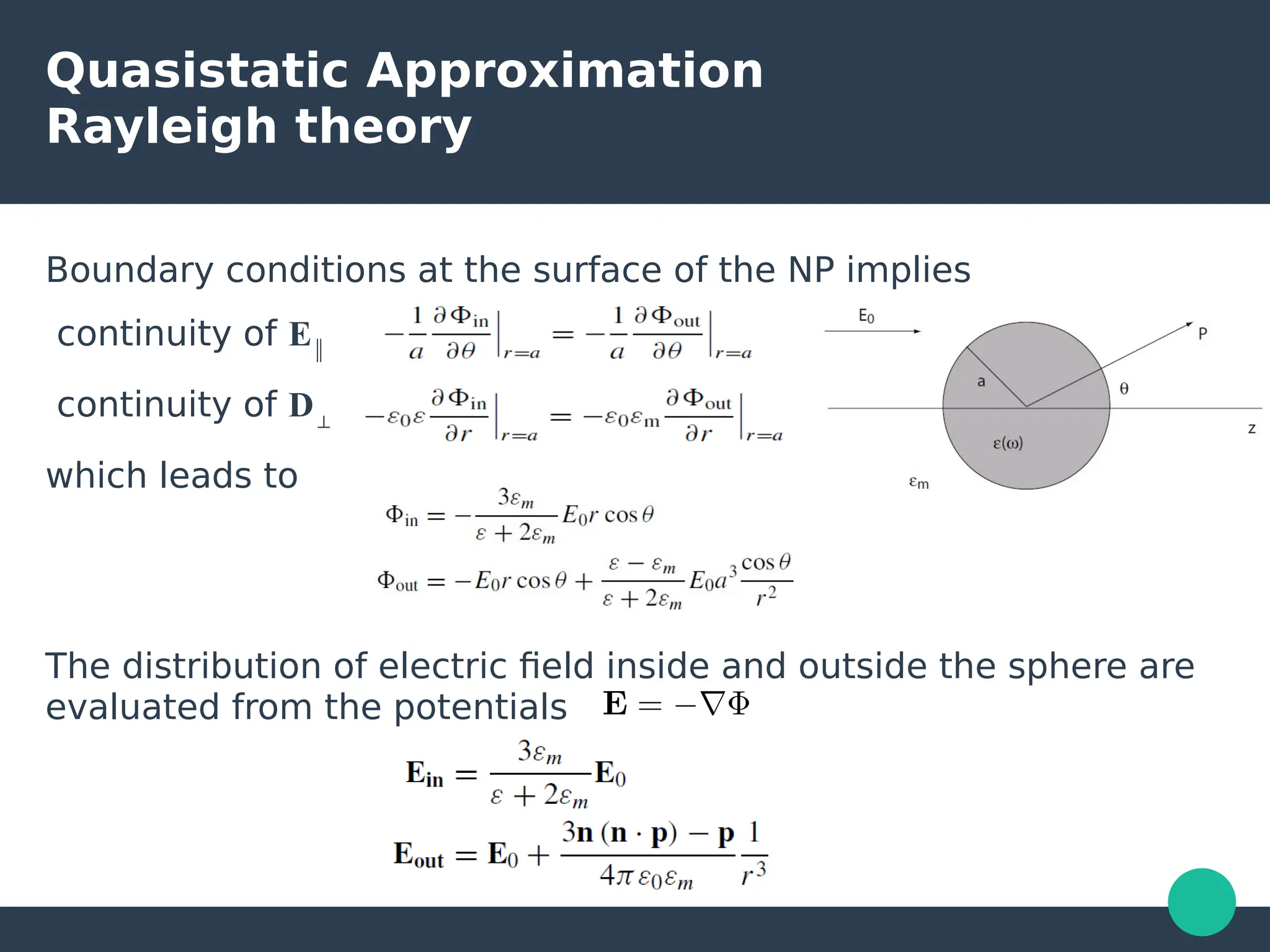
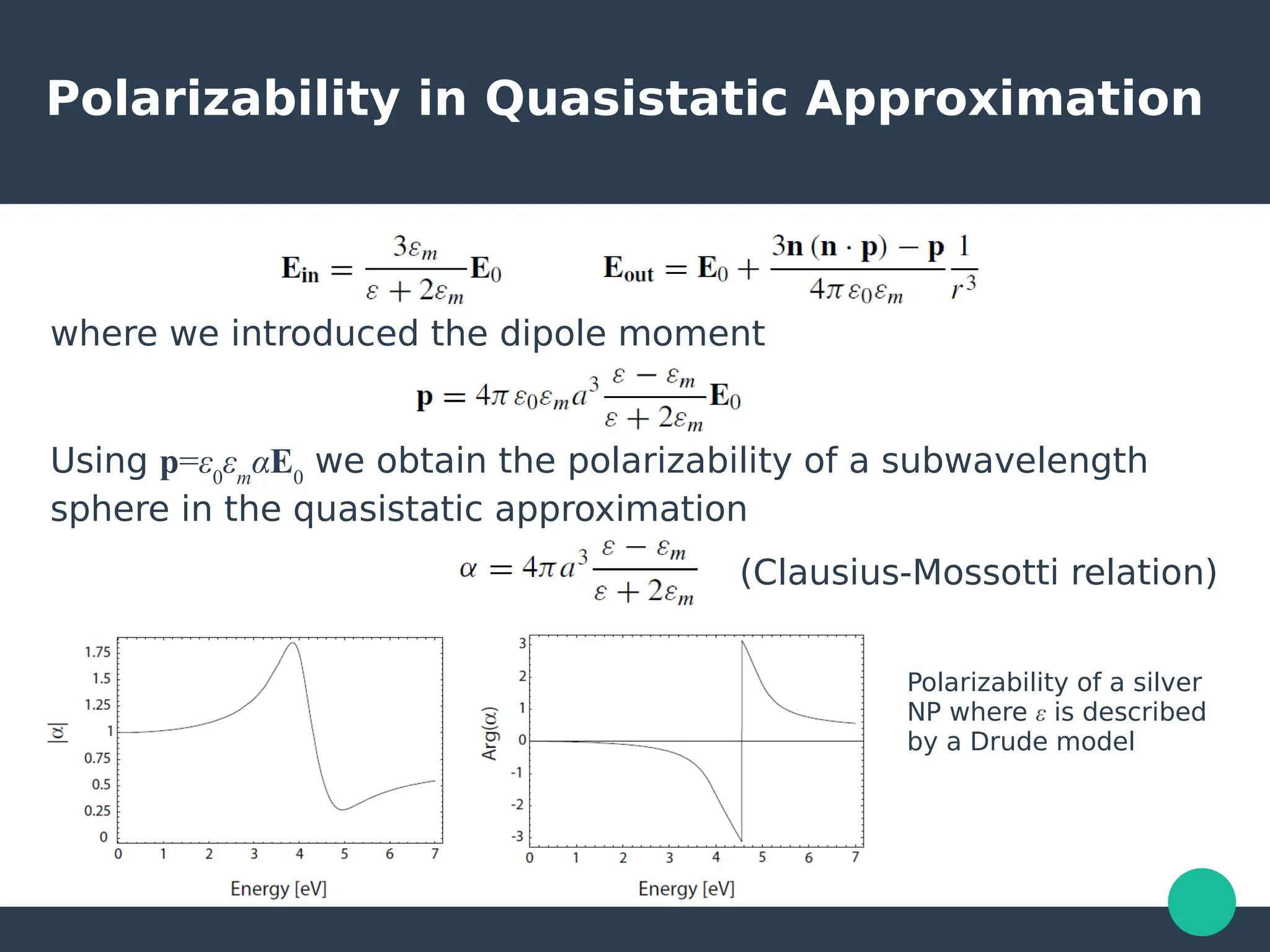
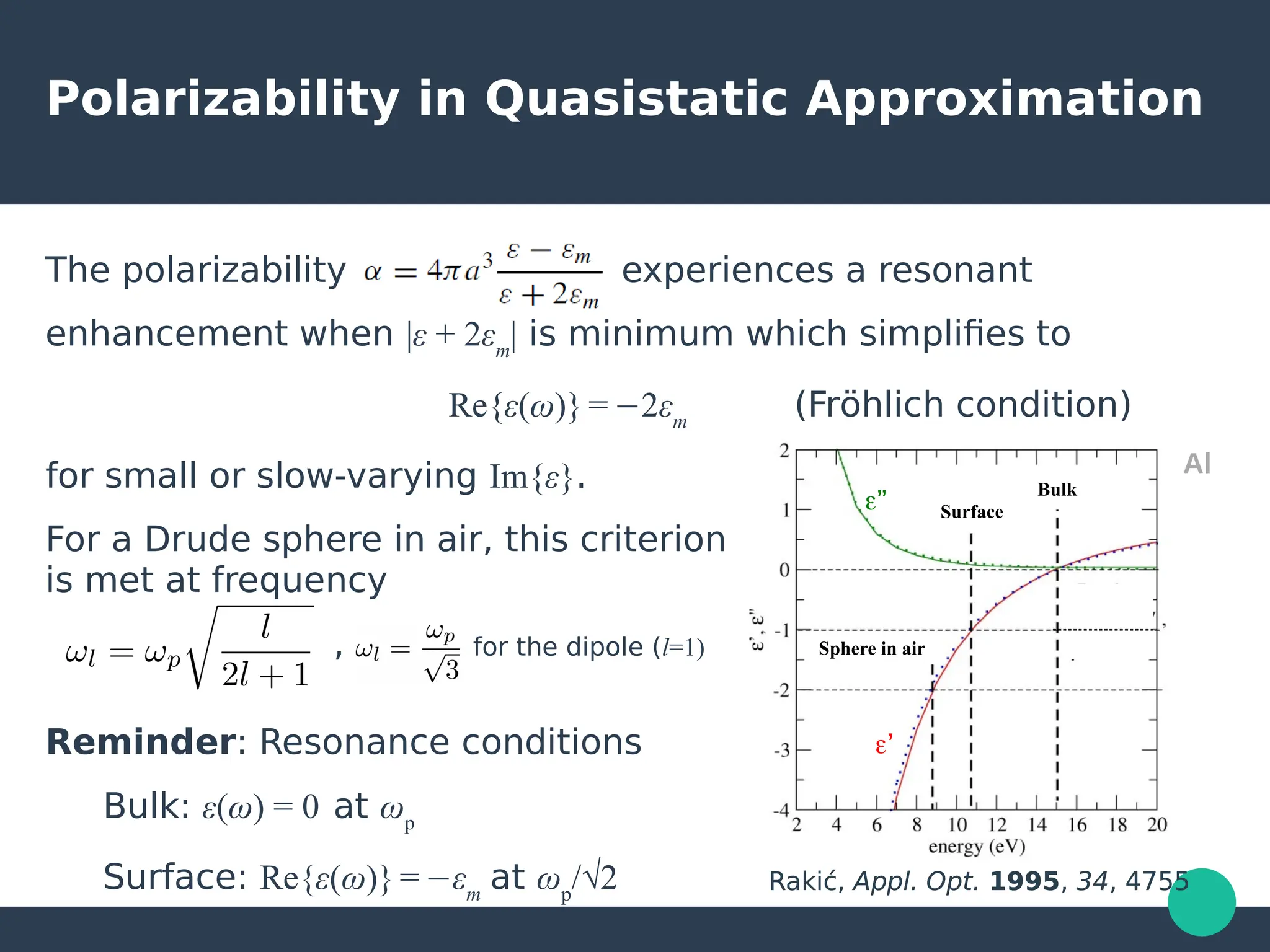
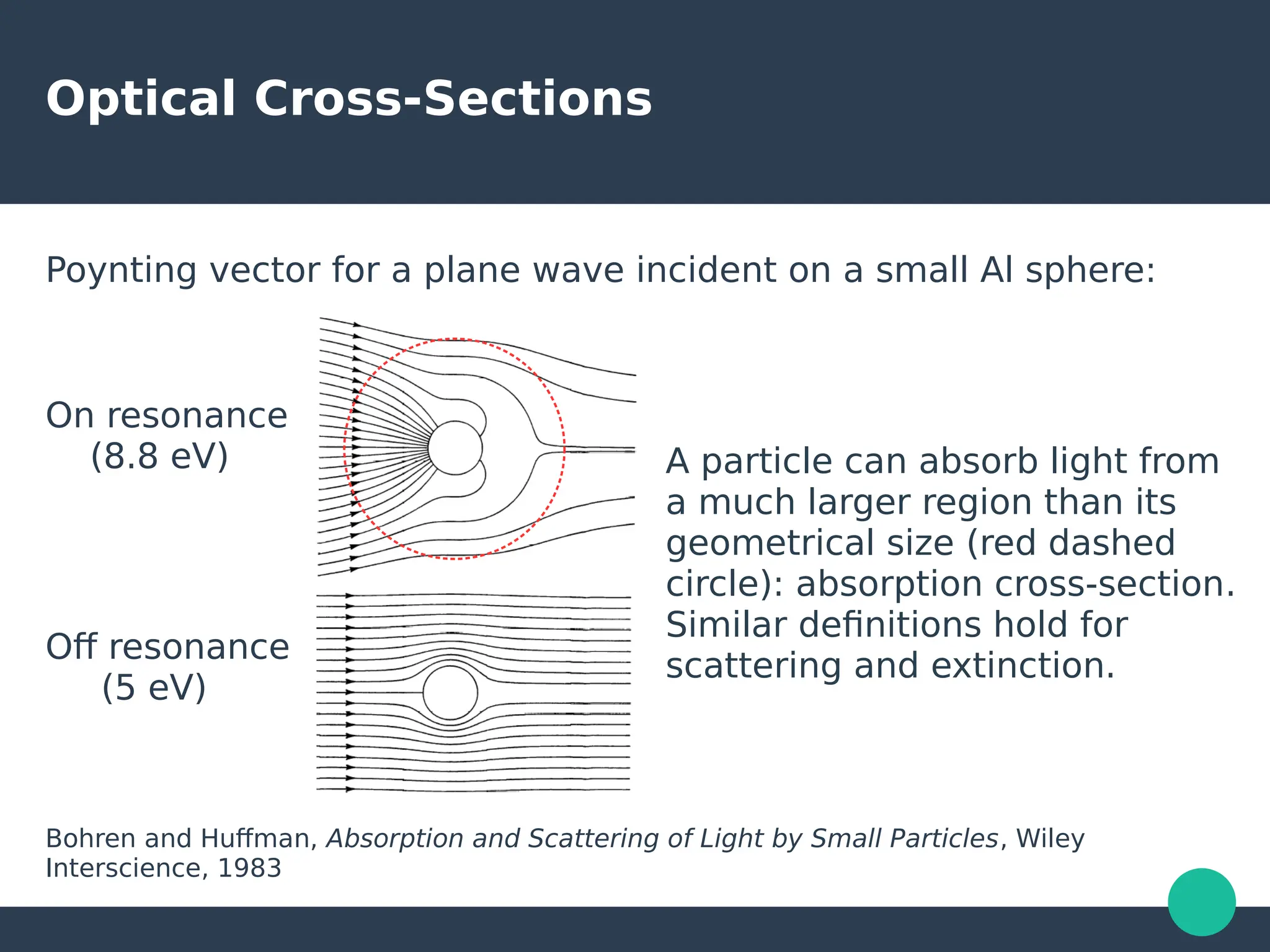
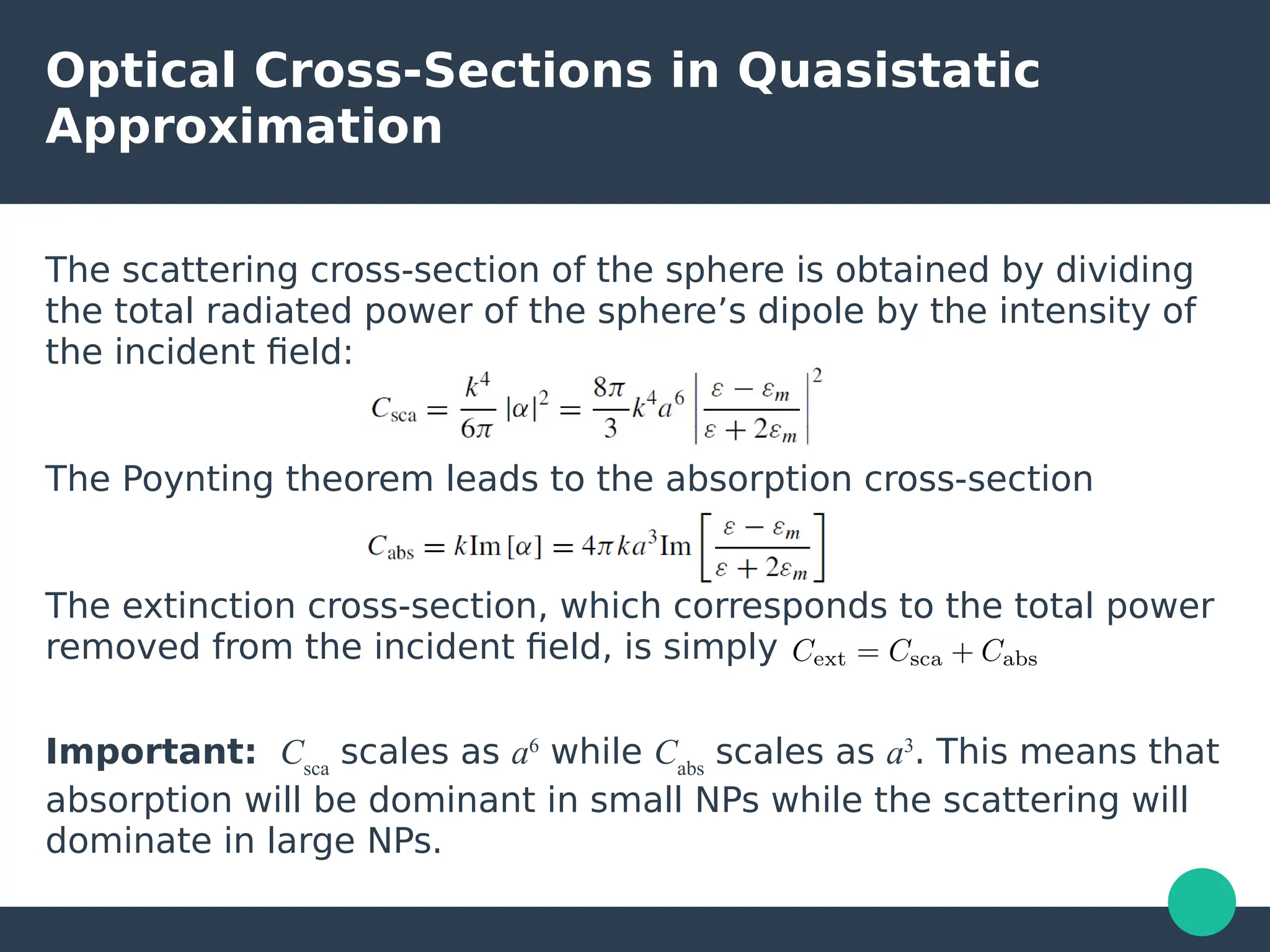
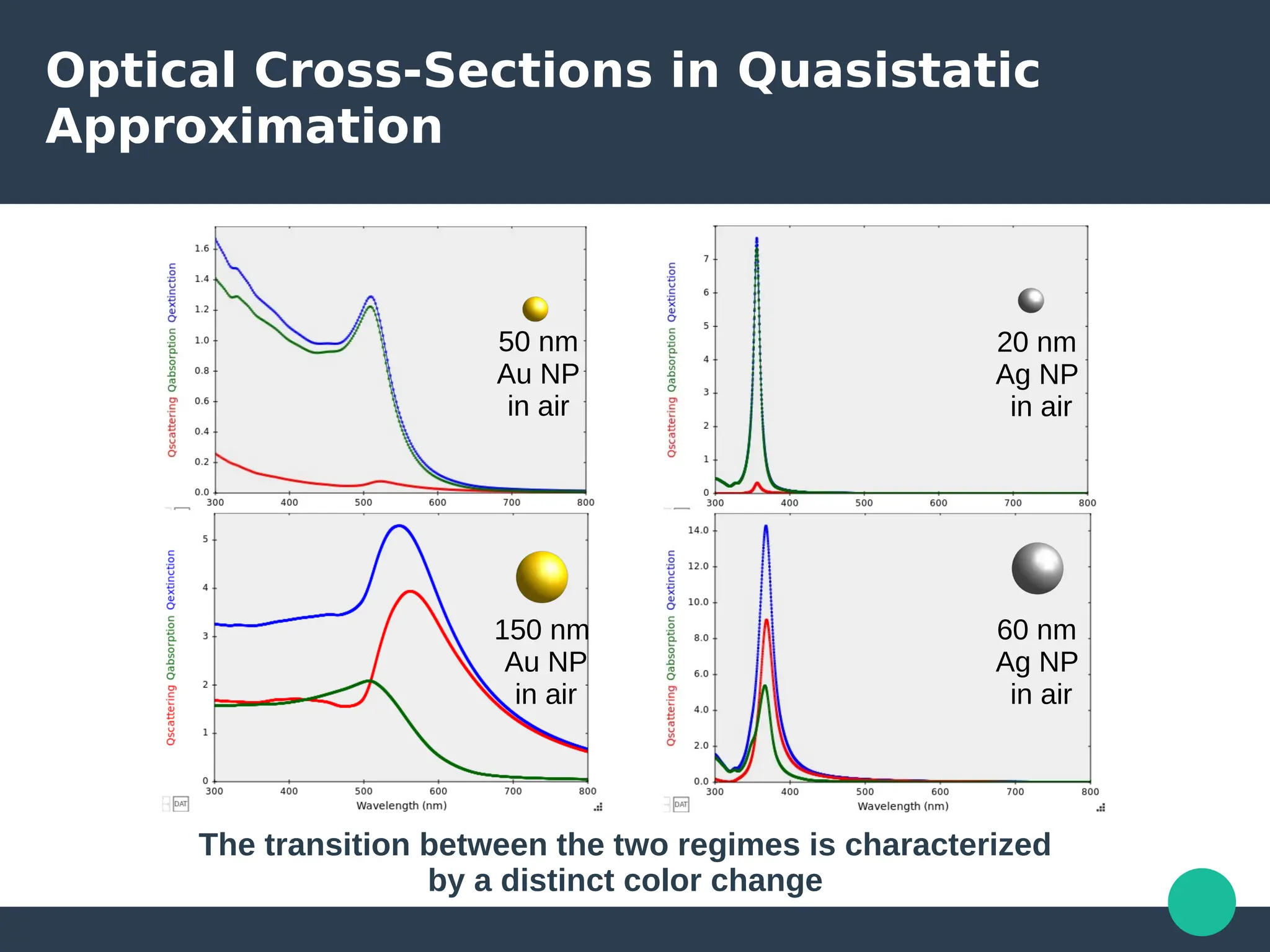
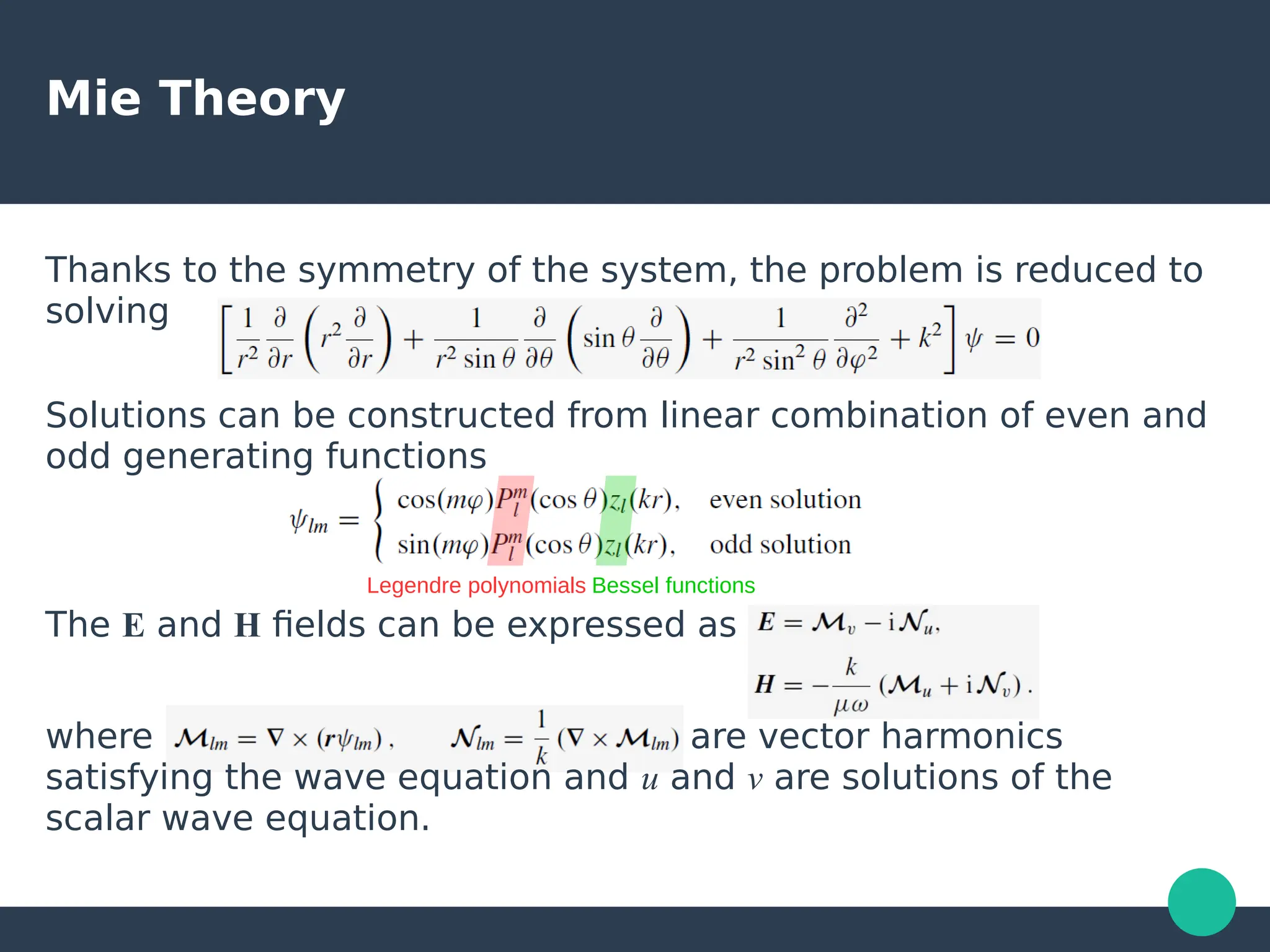
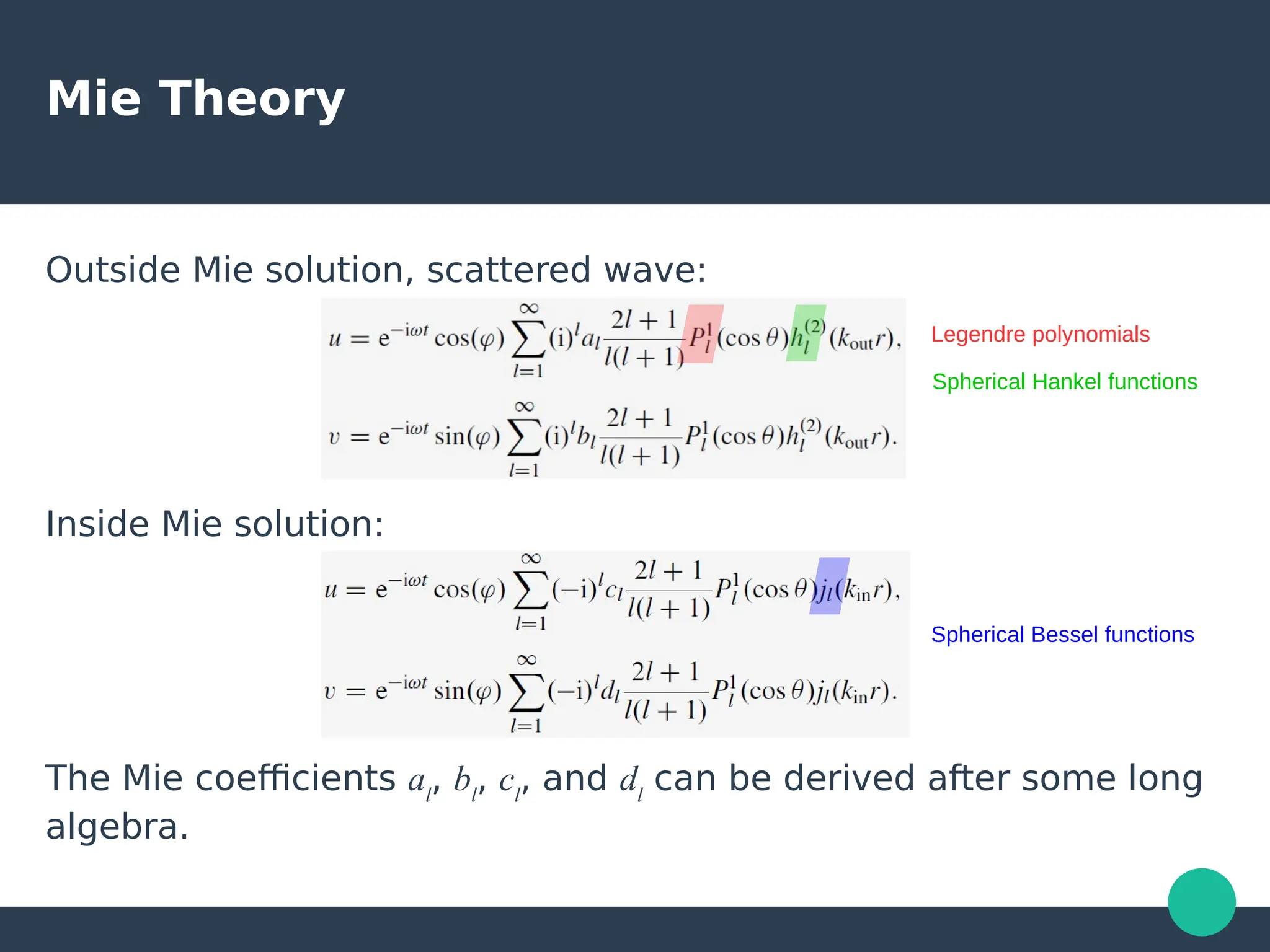
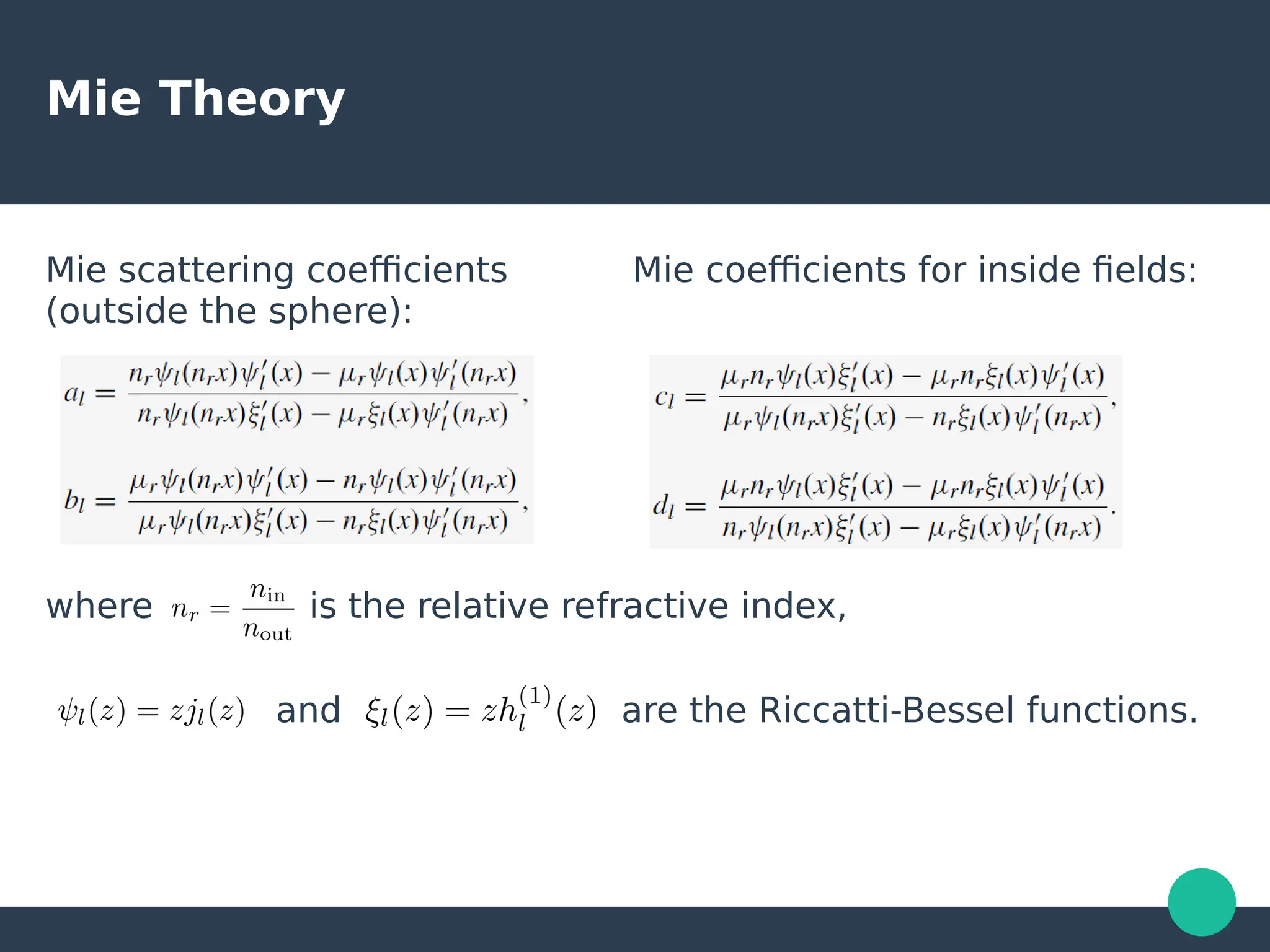
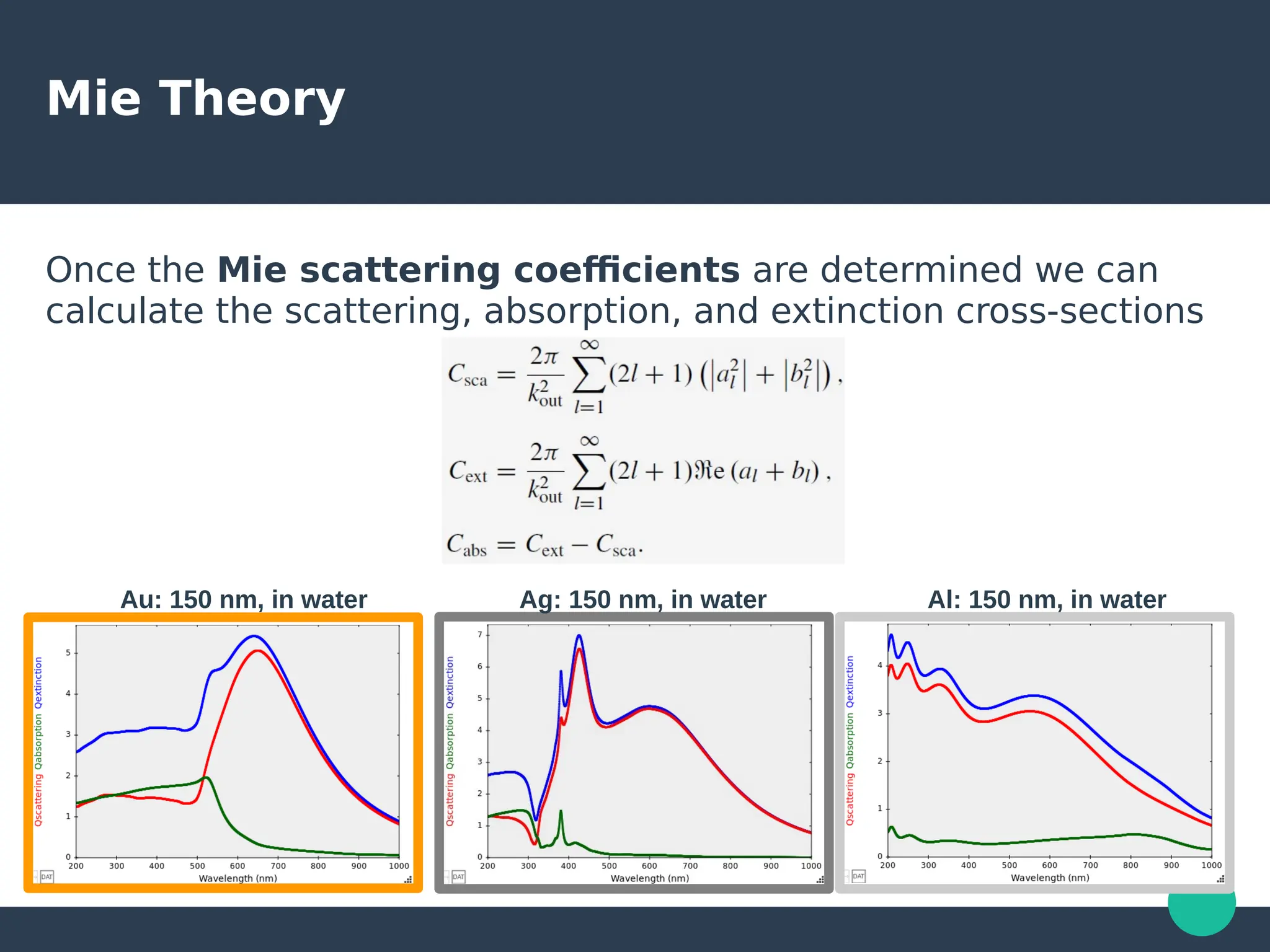
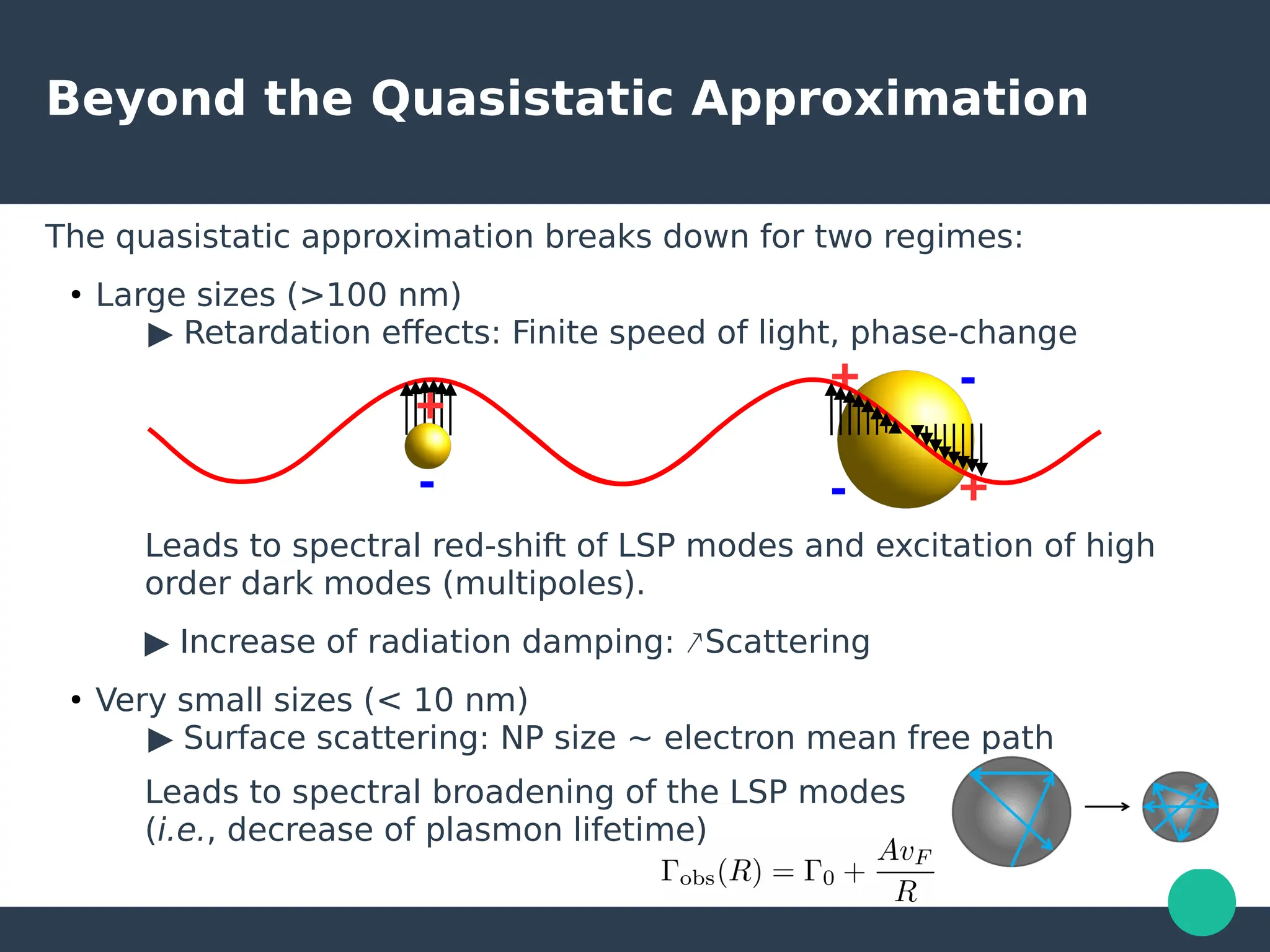
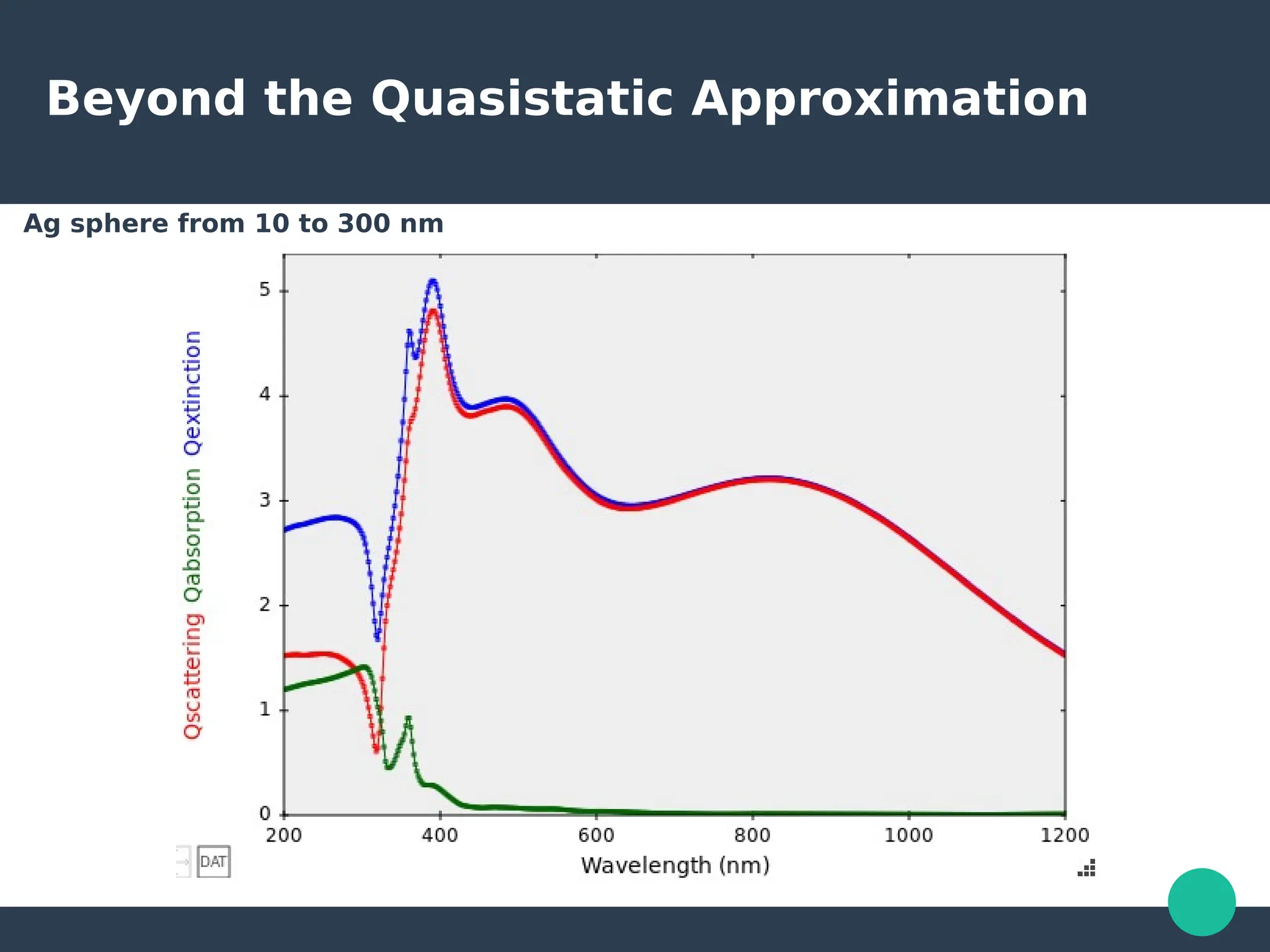
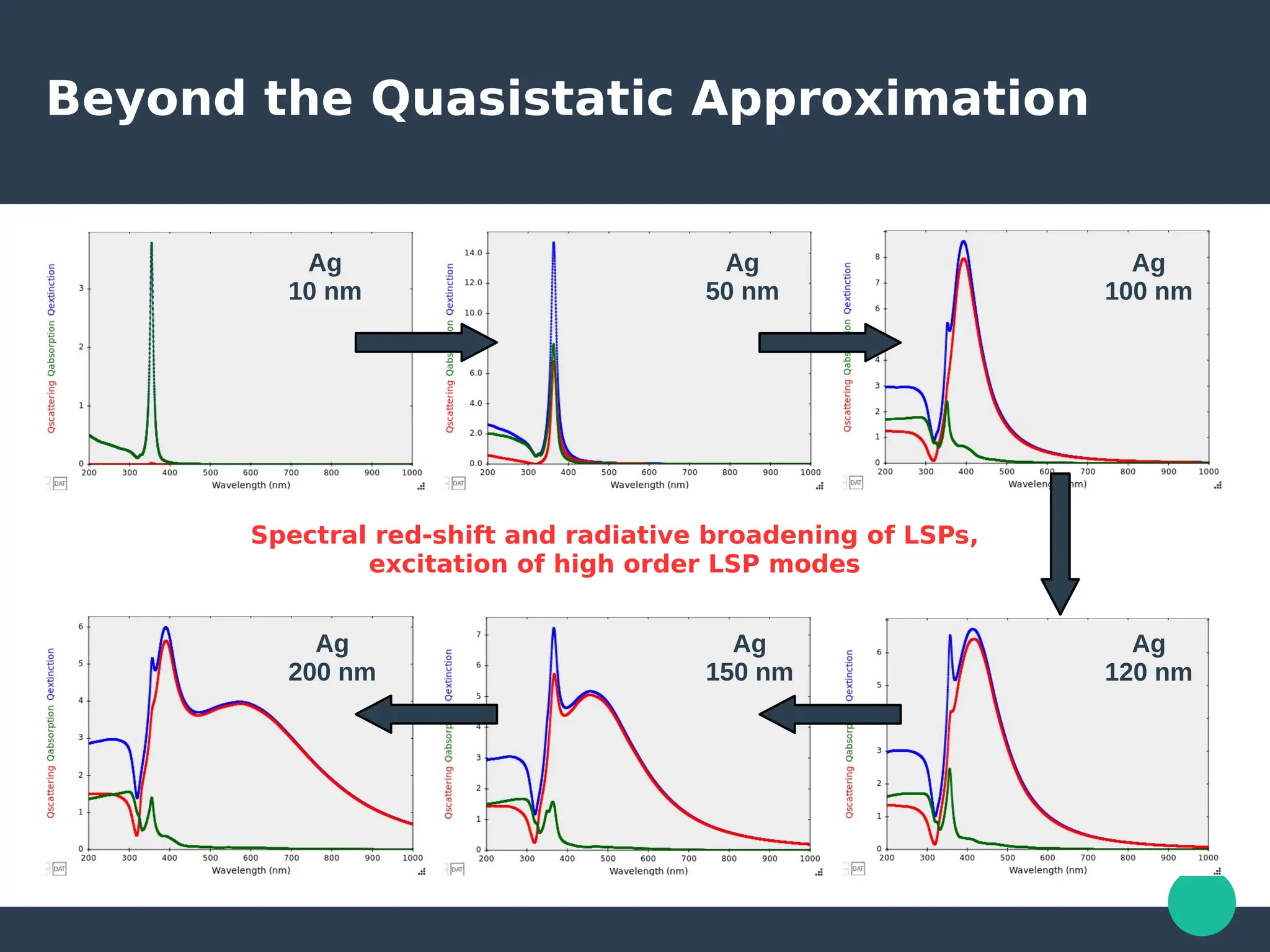
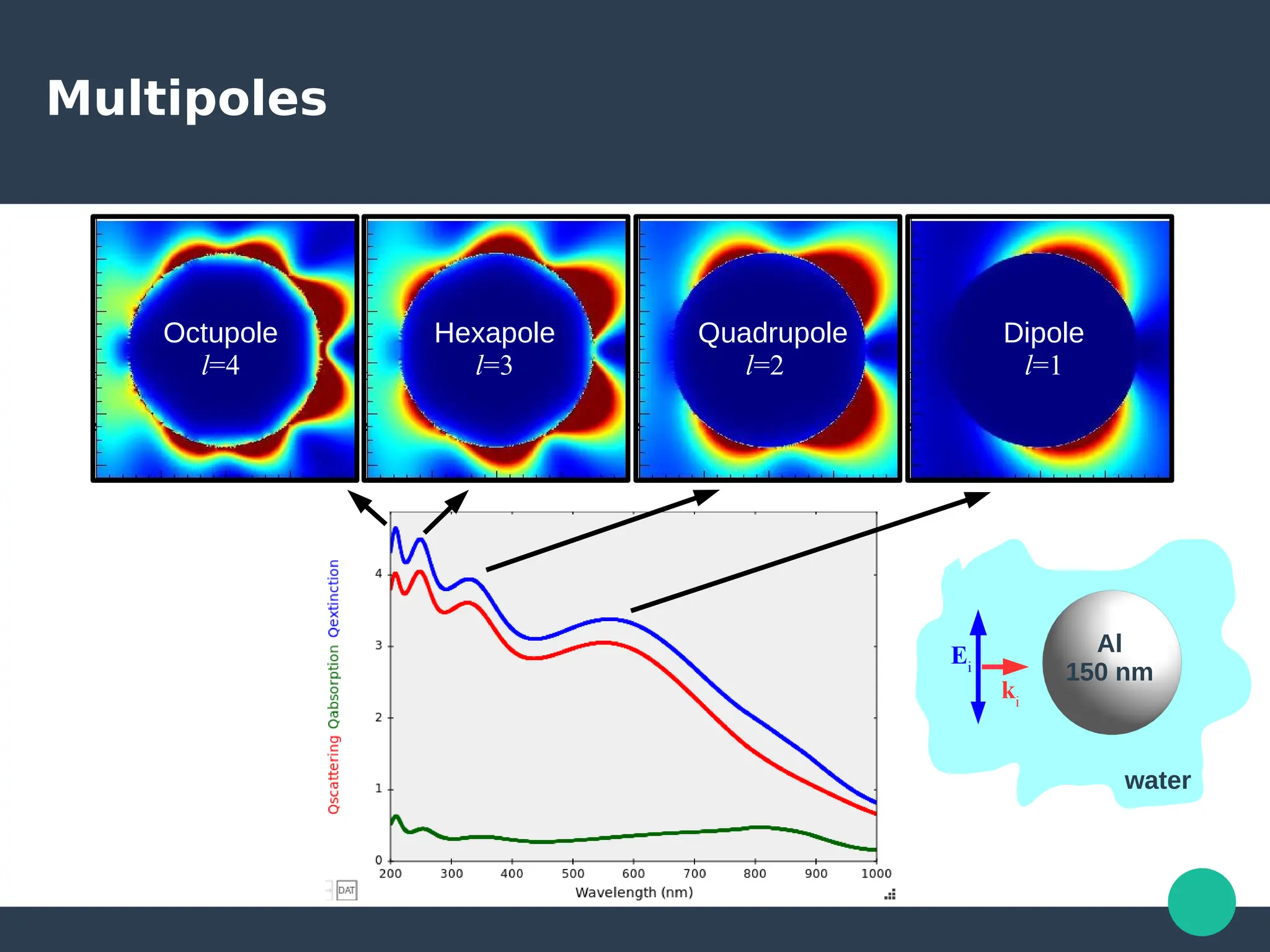
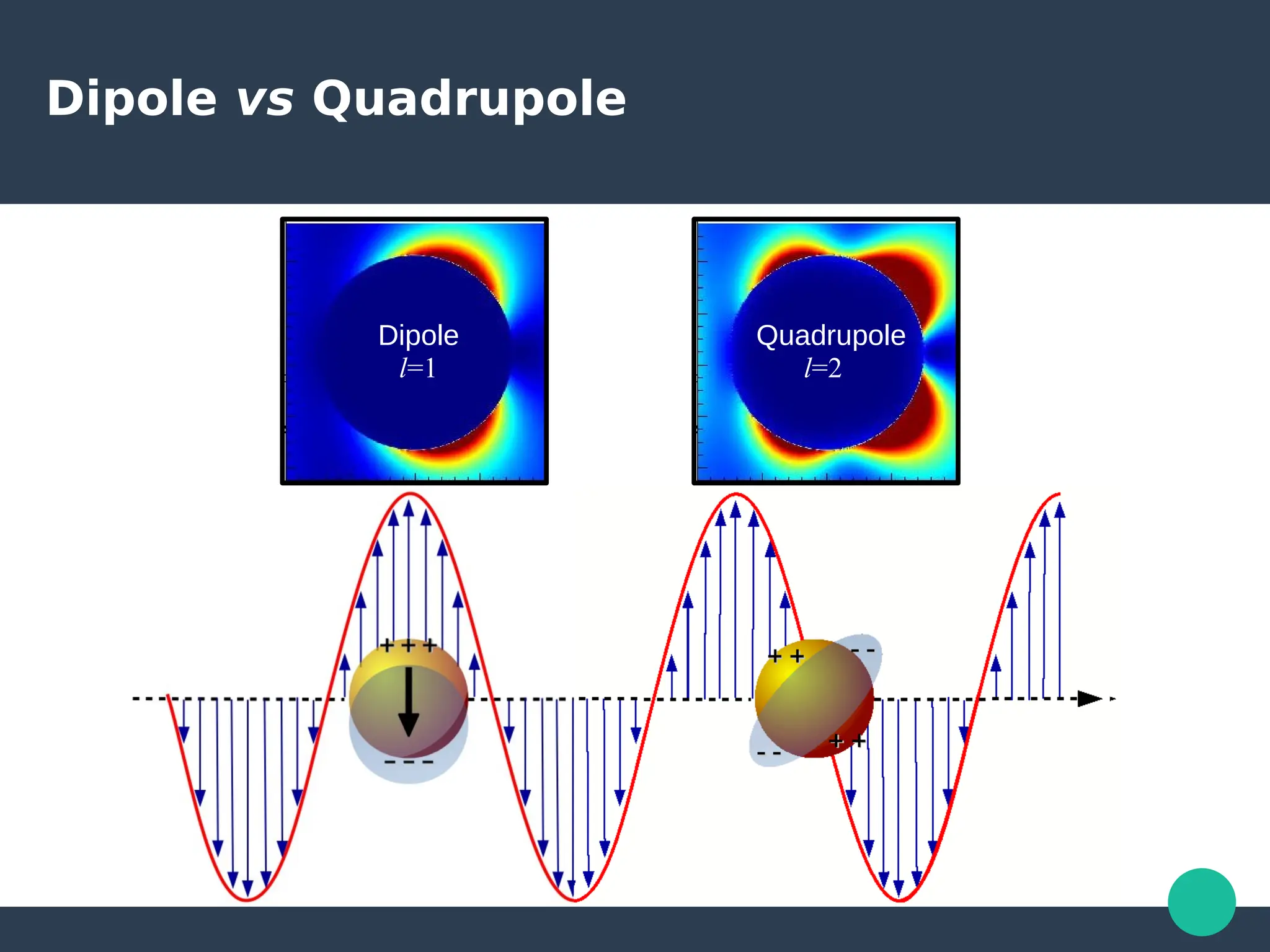
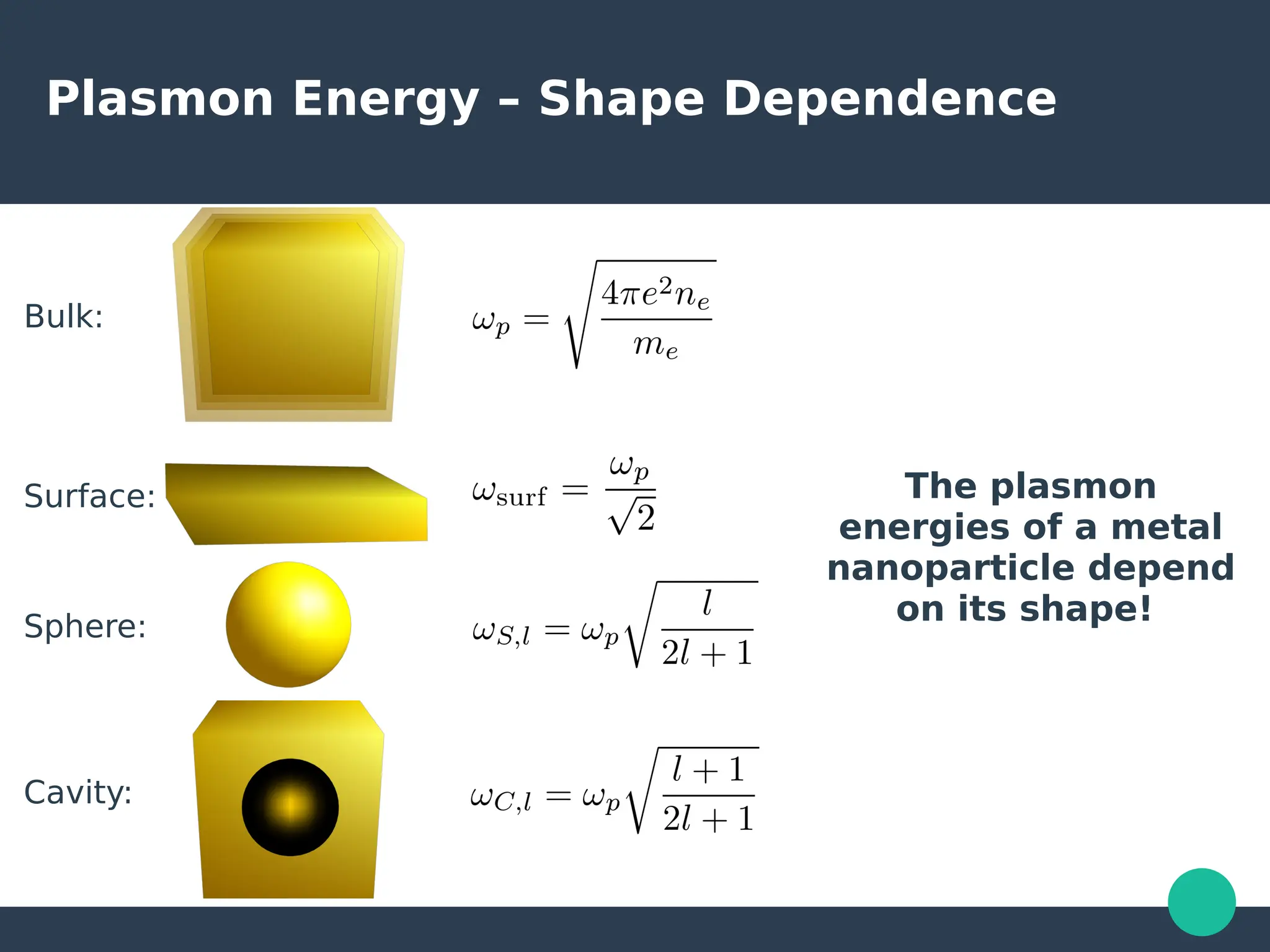
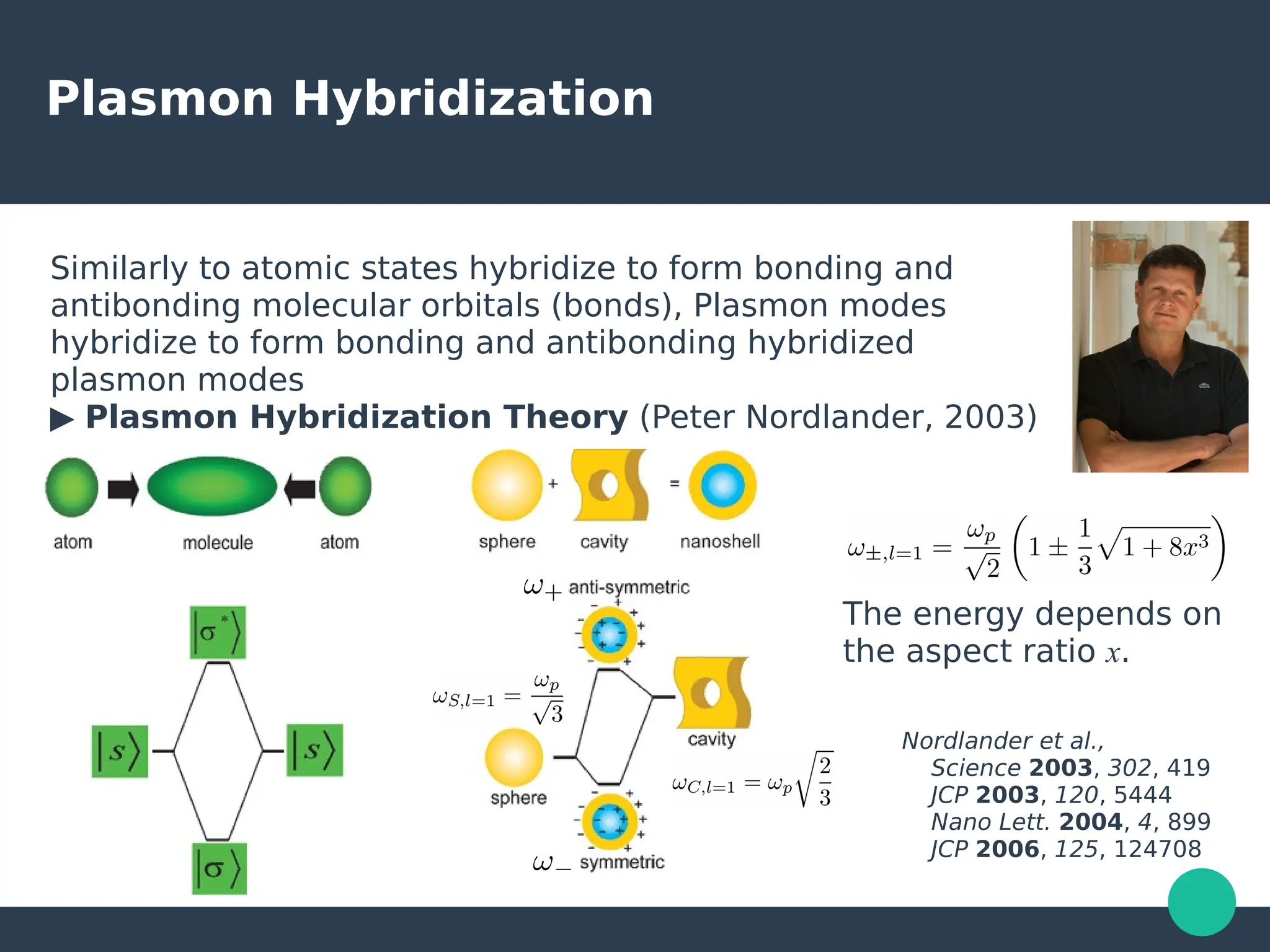
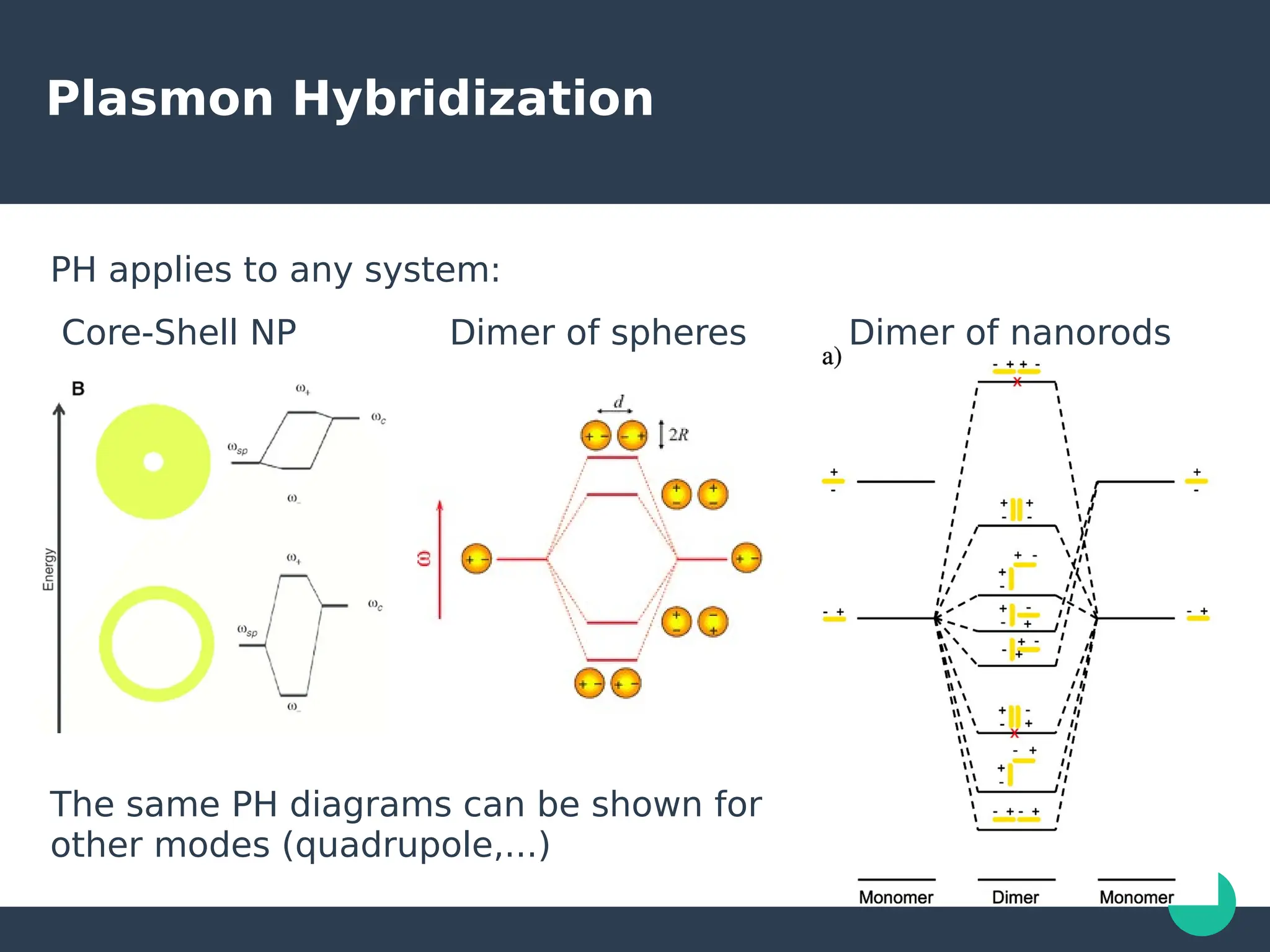
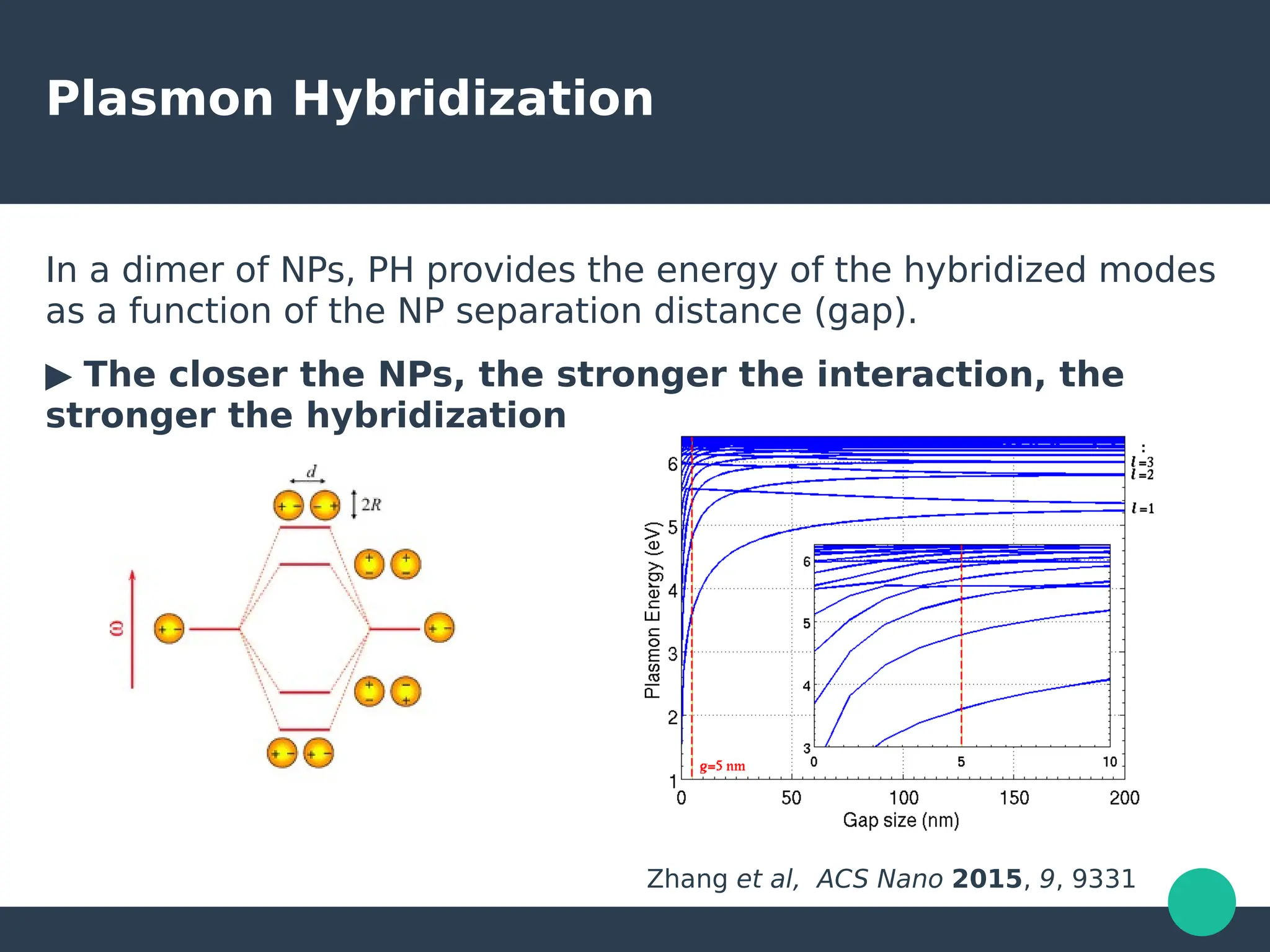
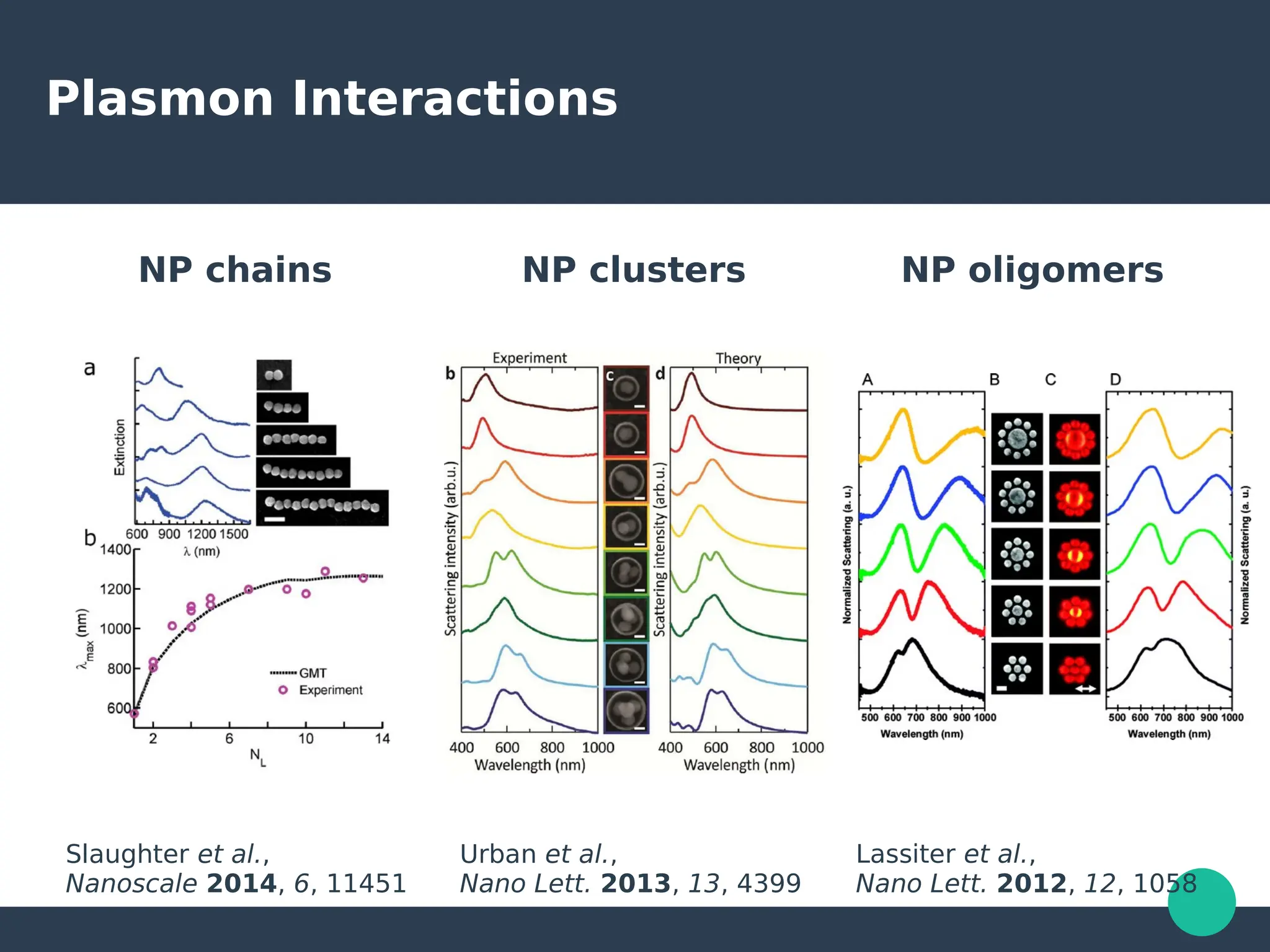
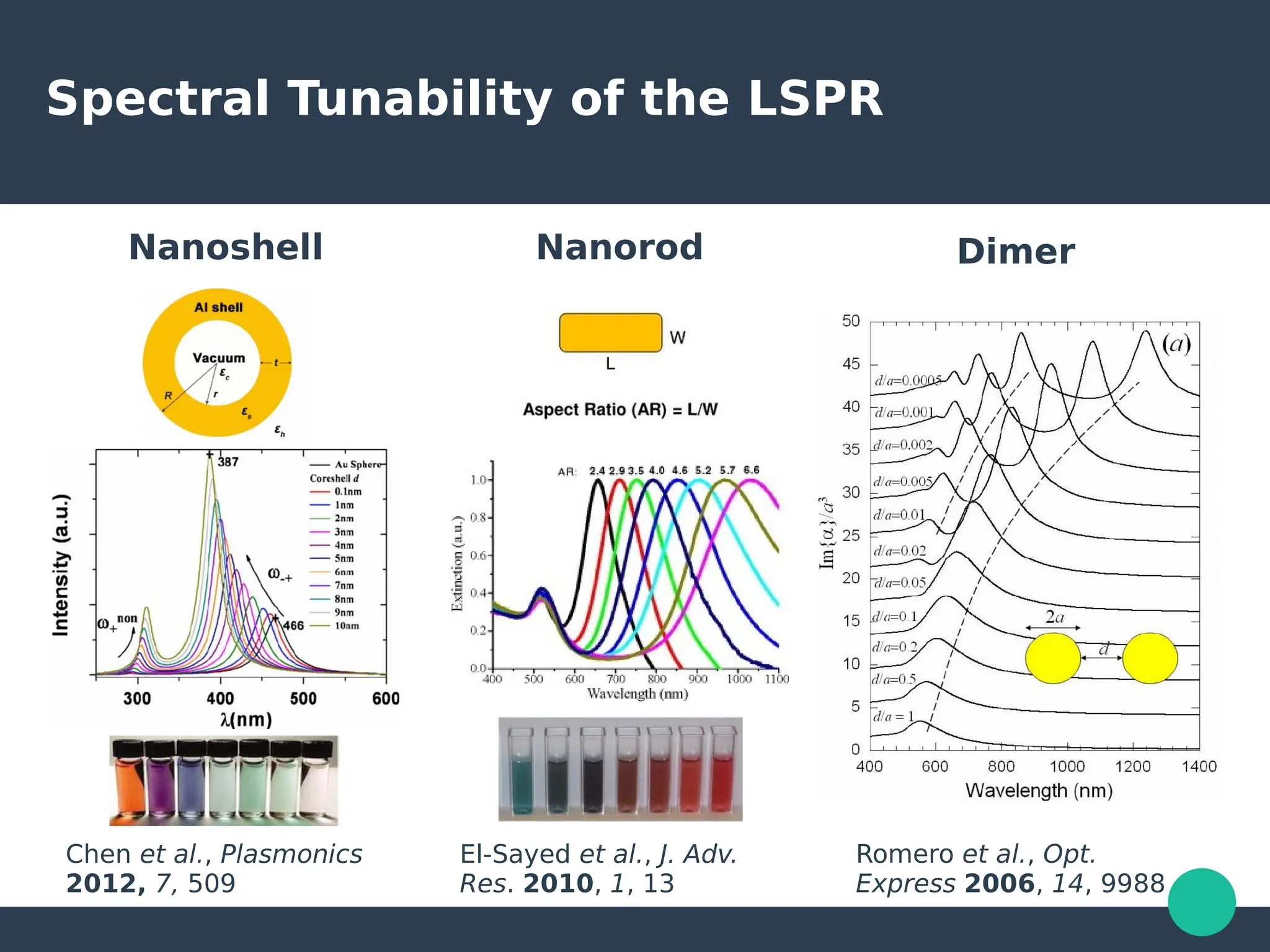
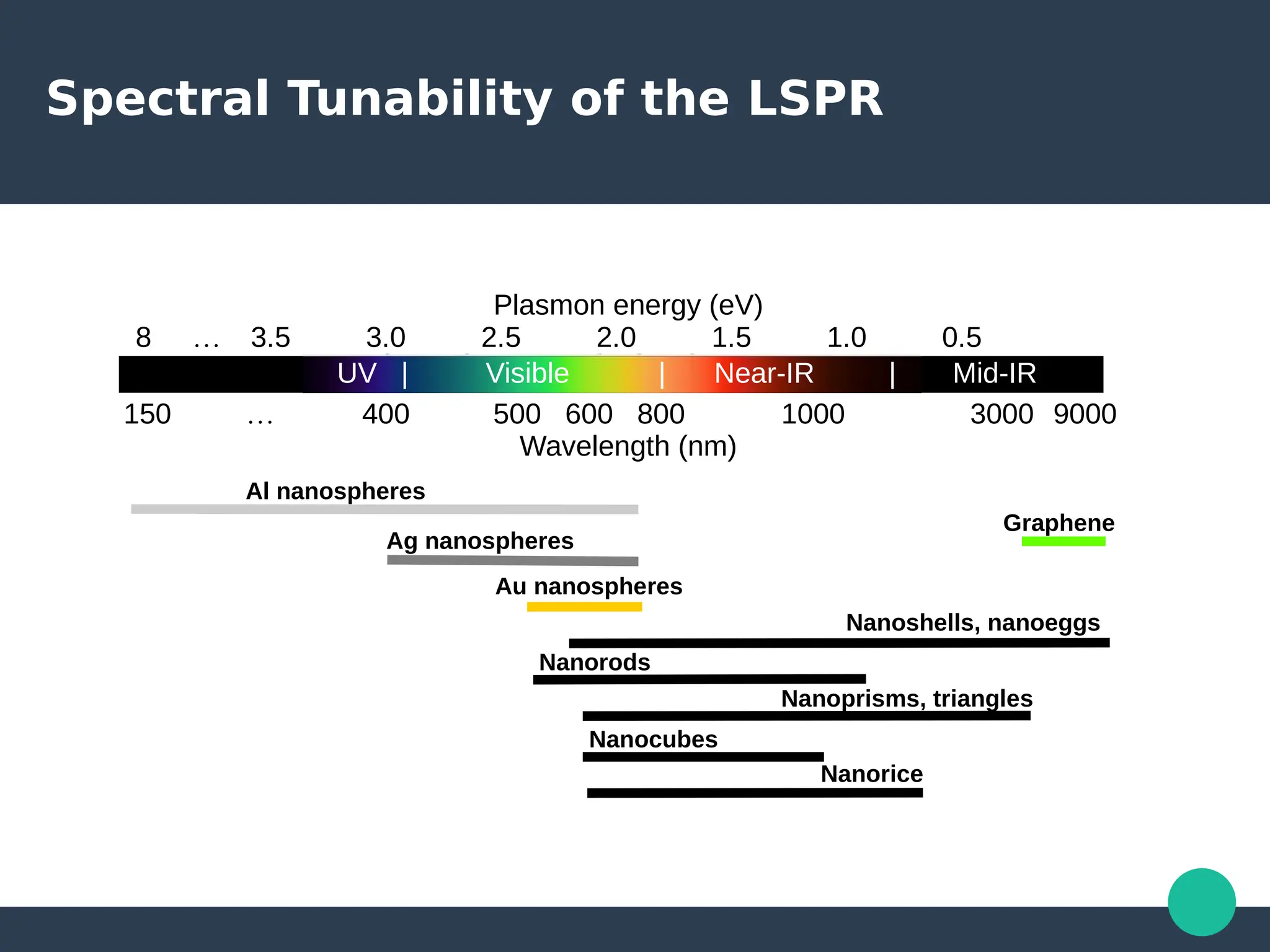
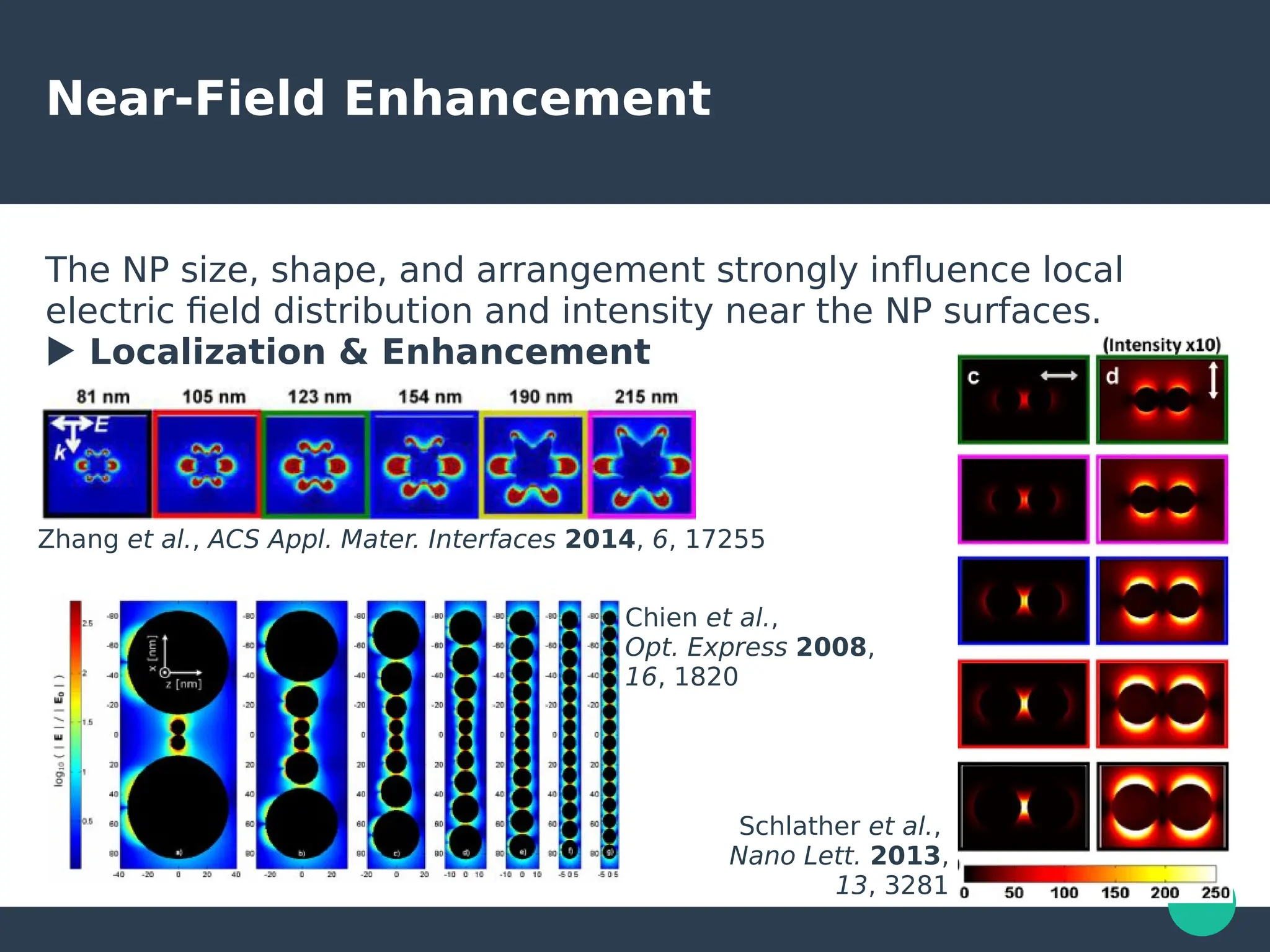
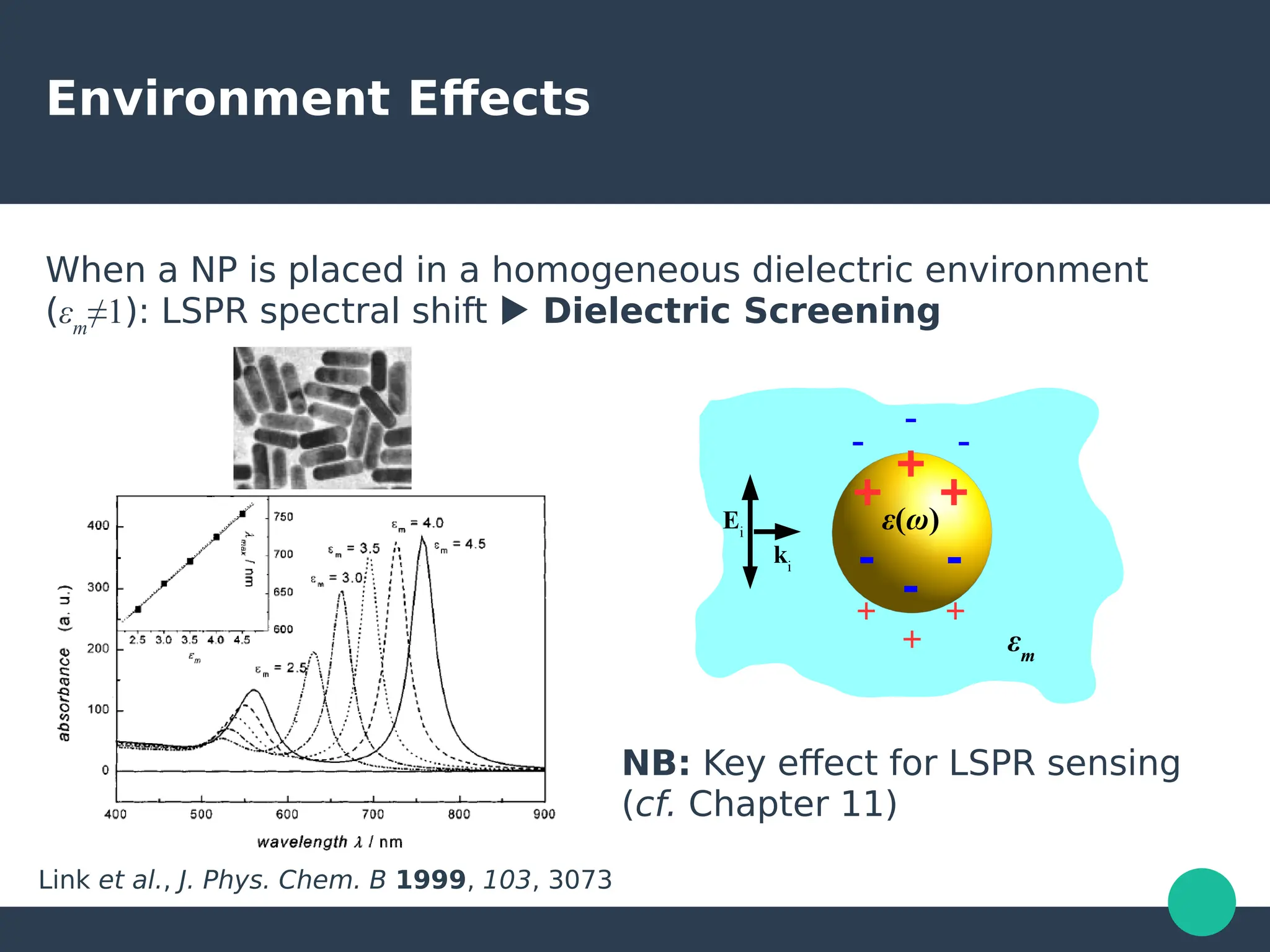
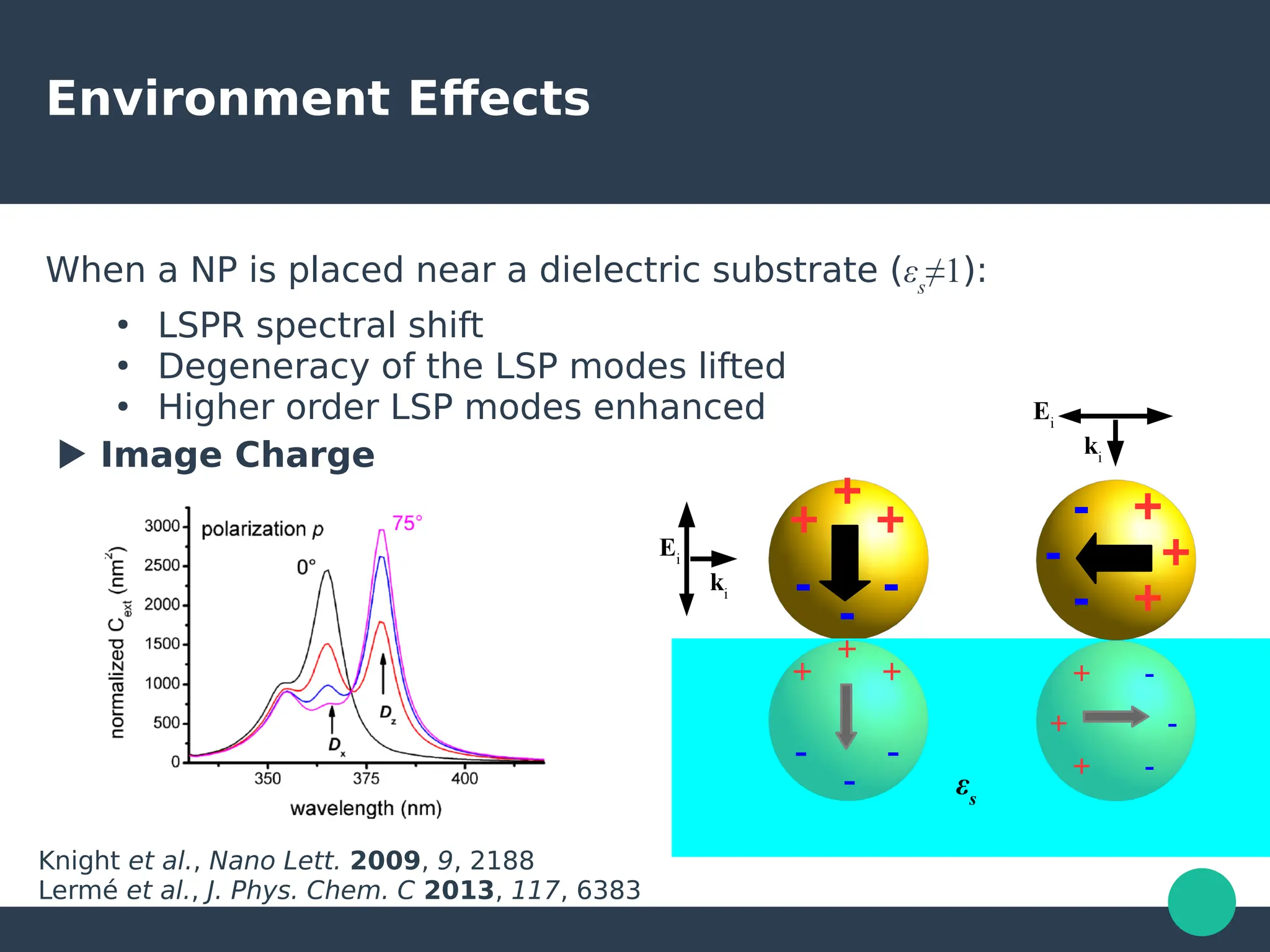
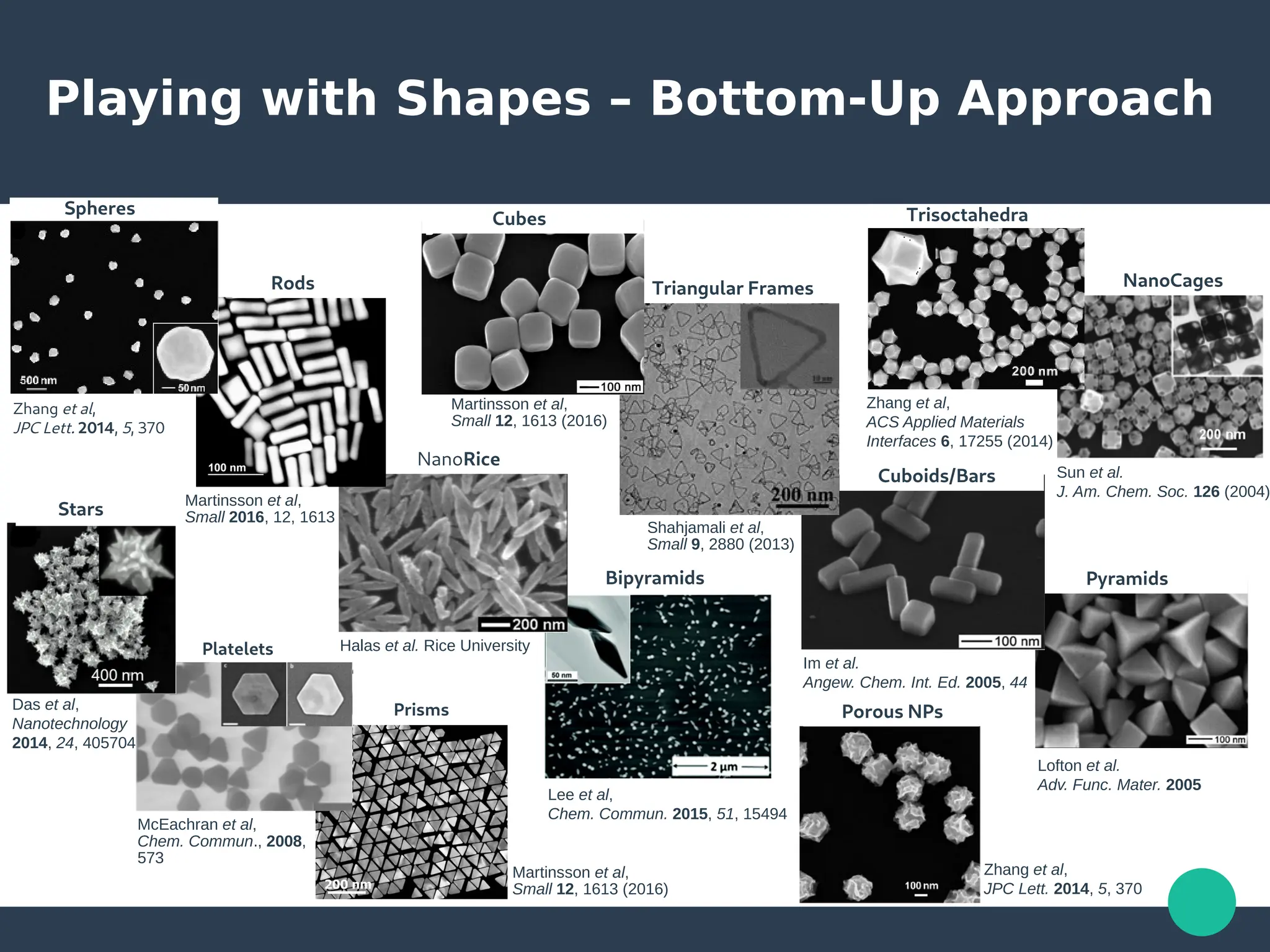
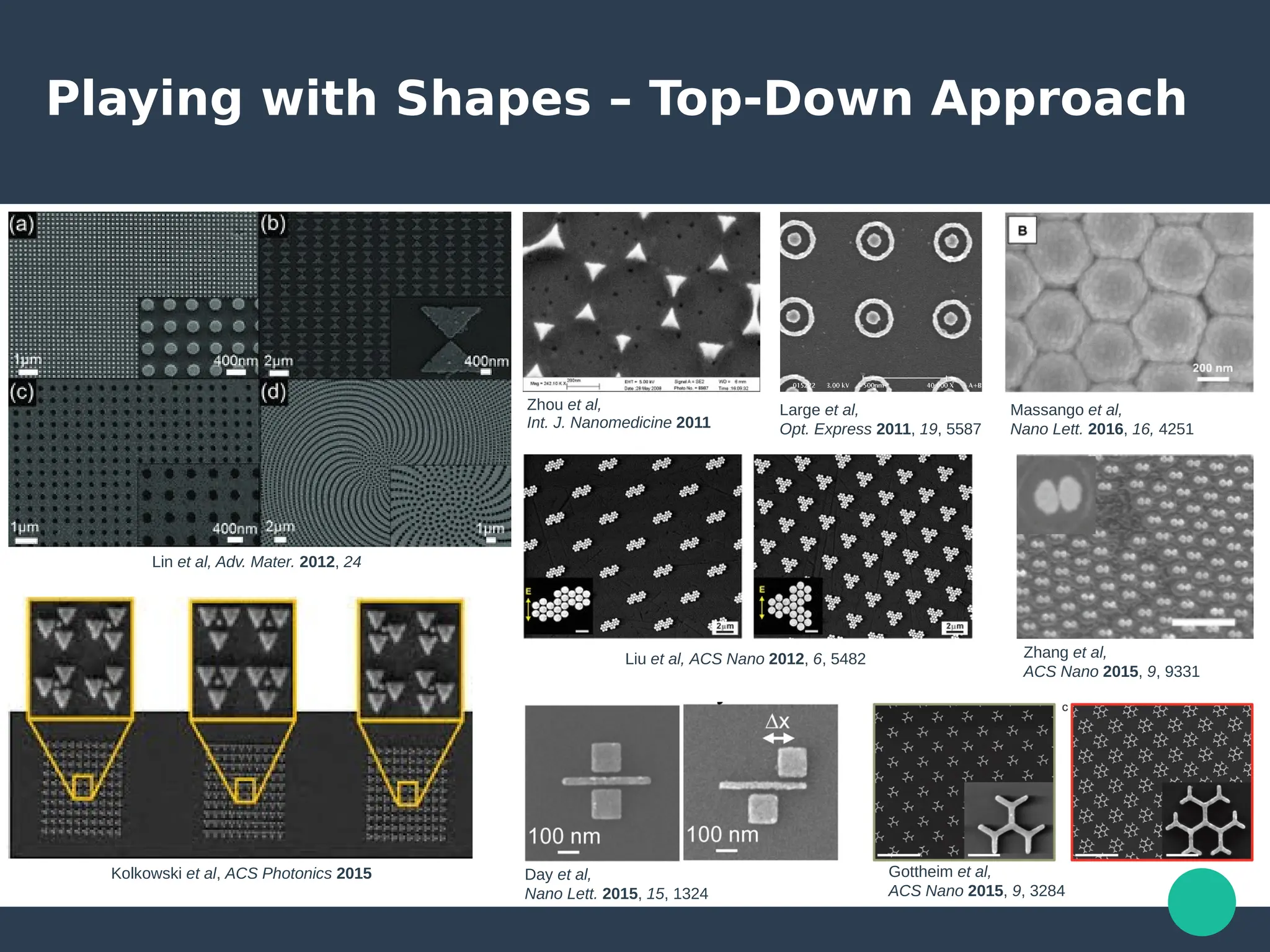
Localized surface plasmons (LSPs) are non-propagating oscillations of free electron gas confined to metallic nanoparticles that are much smaller than the wavelength of light. In the quasistatic approximation, the interaction of light with a nanoparticle can be described by the polarizability and optical cross-sections. For larger nanoparticles, Mie theory provides an analytical solution by describing the scattering fields using vector spherical harmonics. The plasmon resonance depends on the nanoparticle size, shape, composition, and local environment.