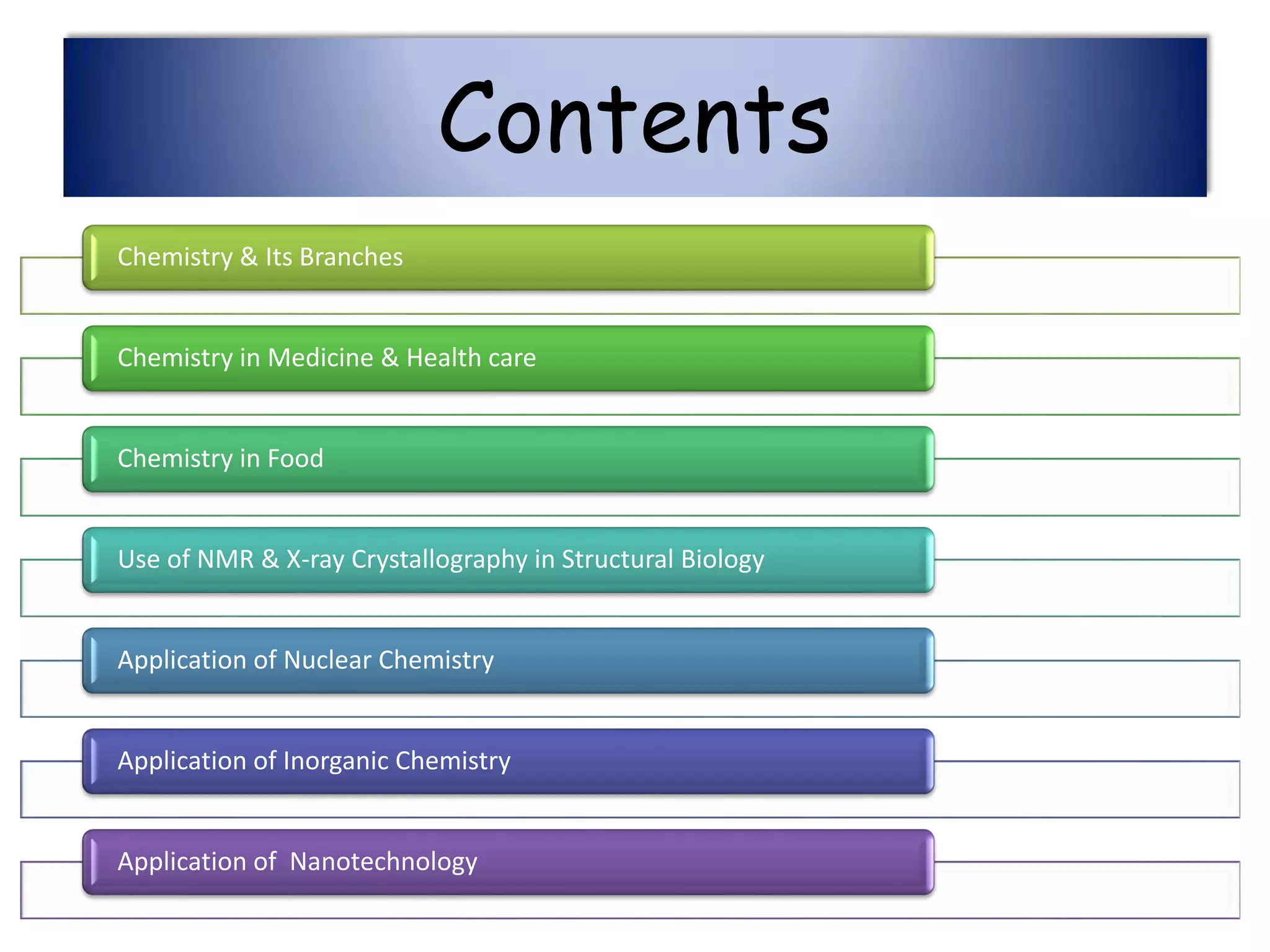
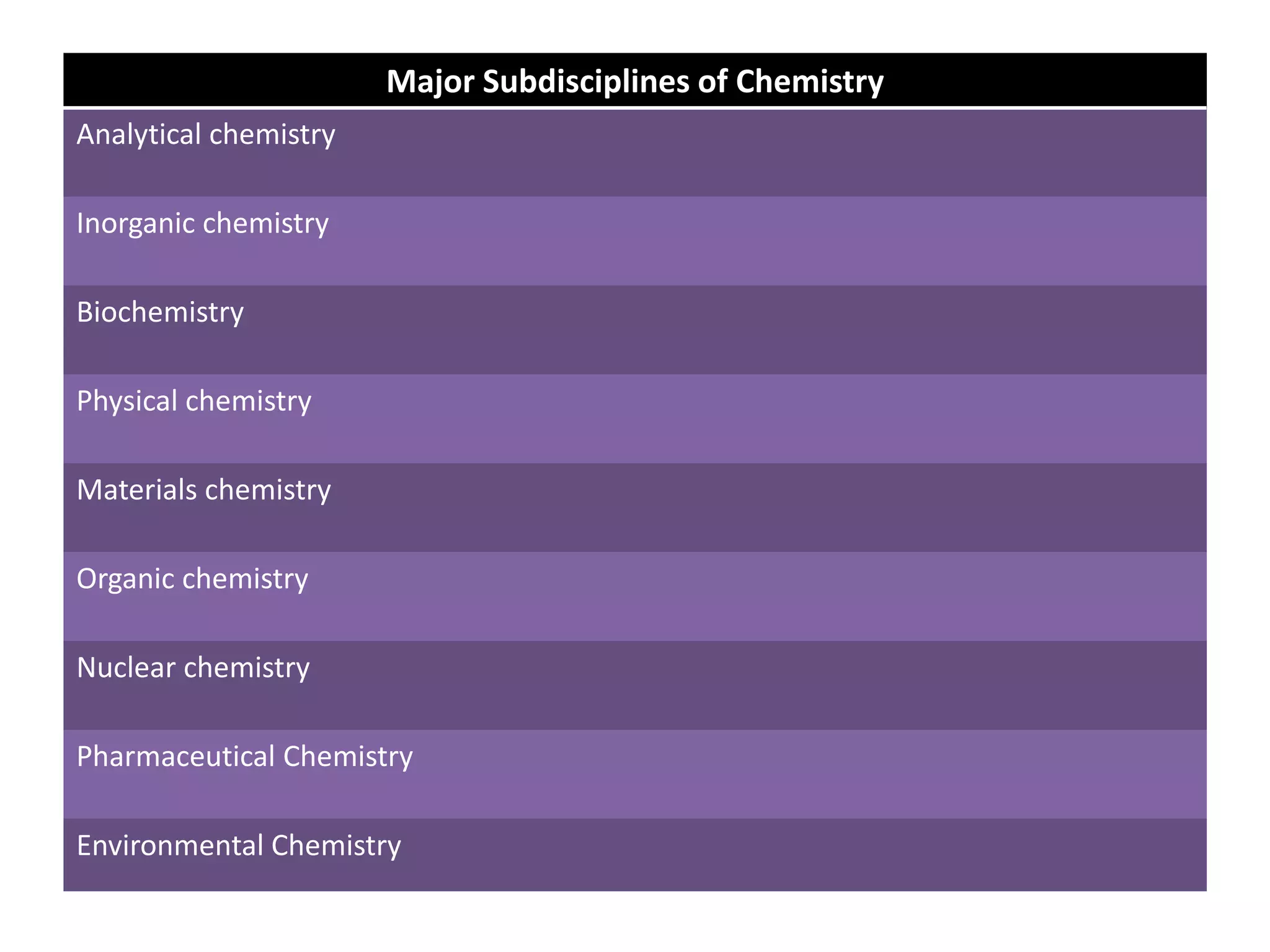
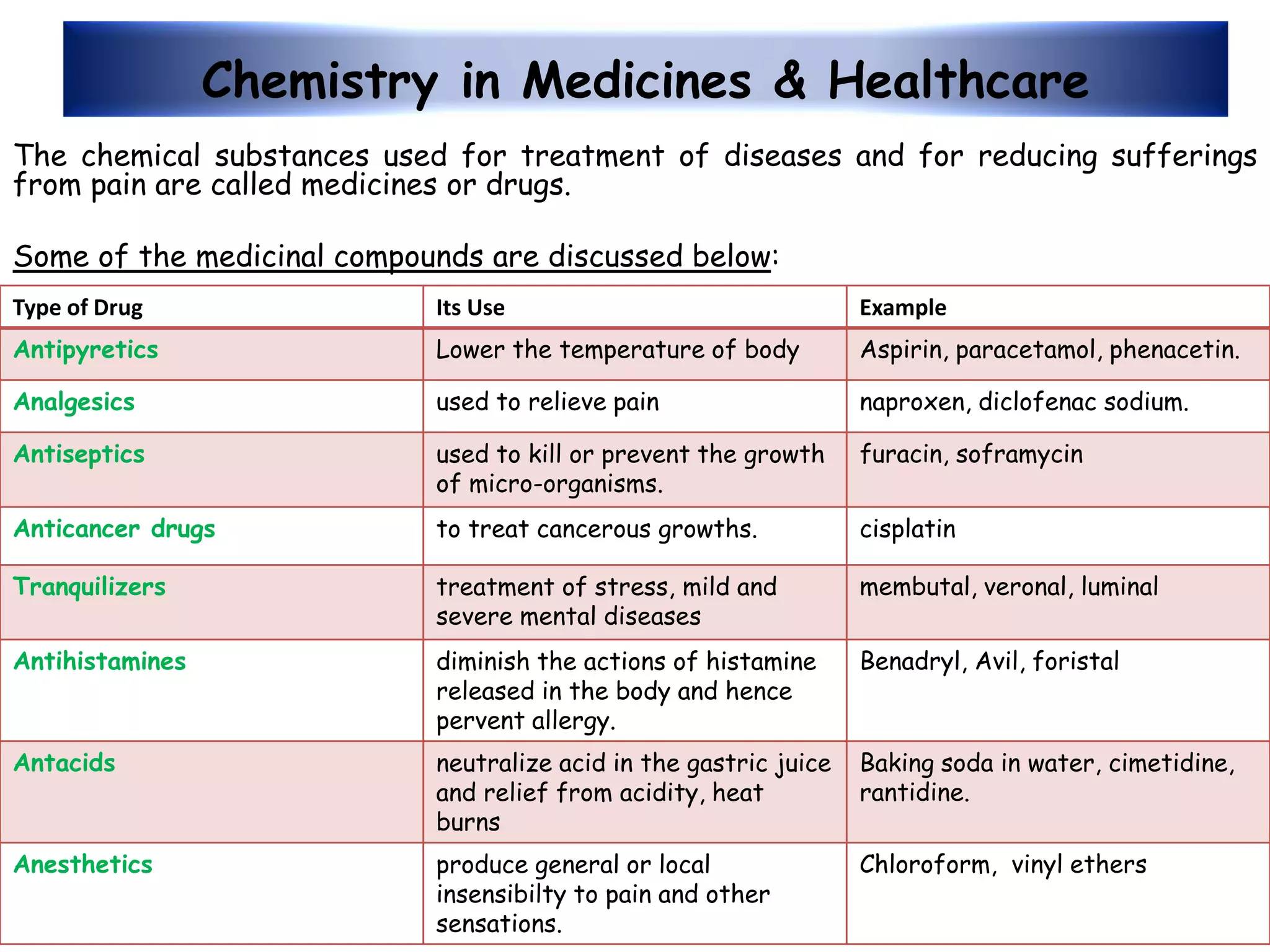
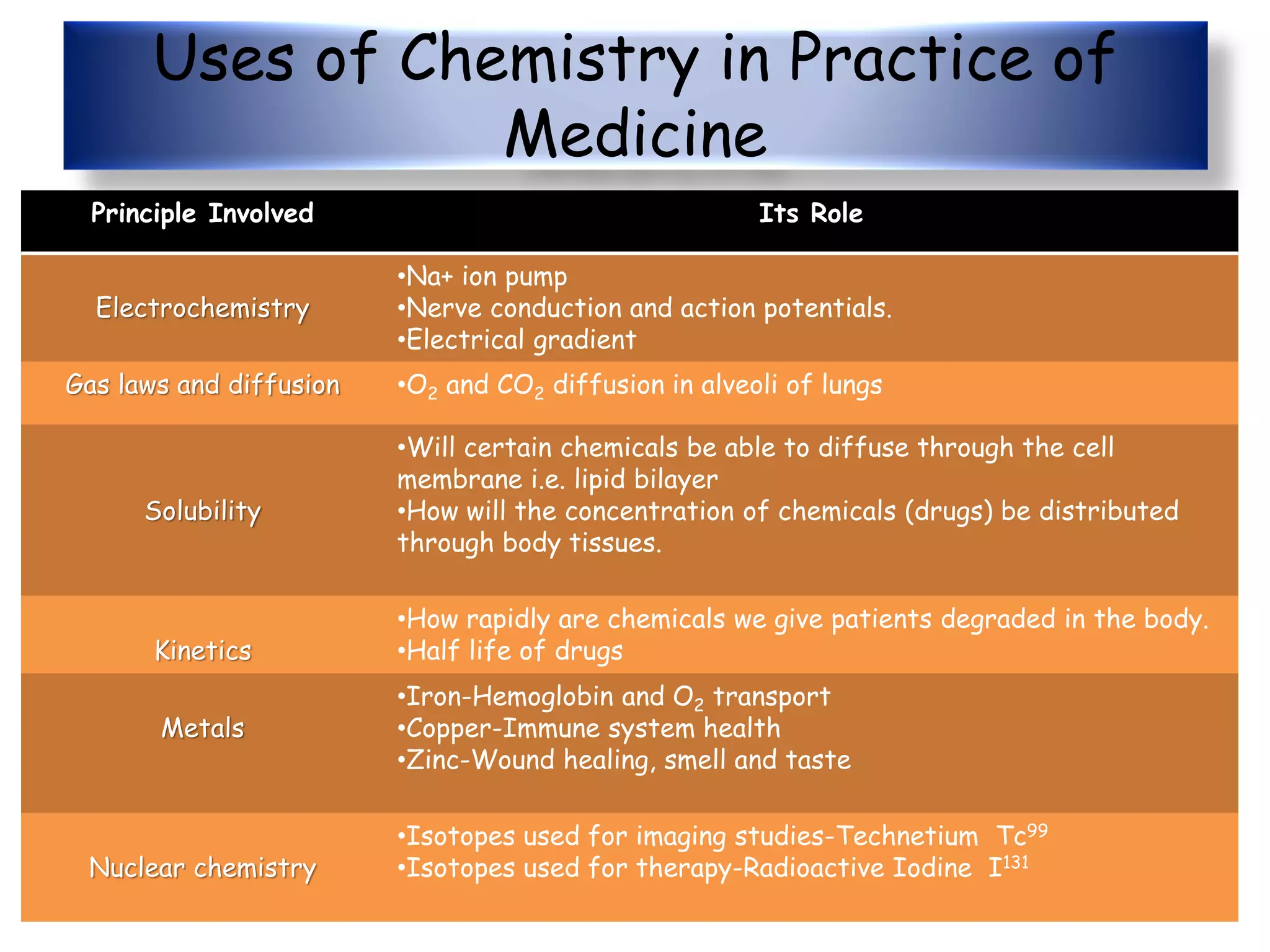
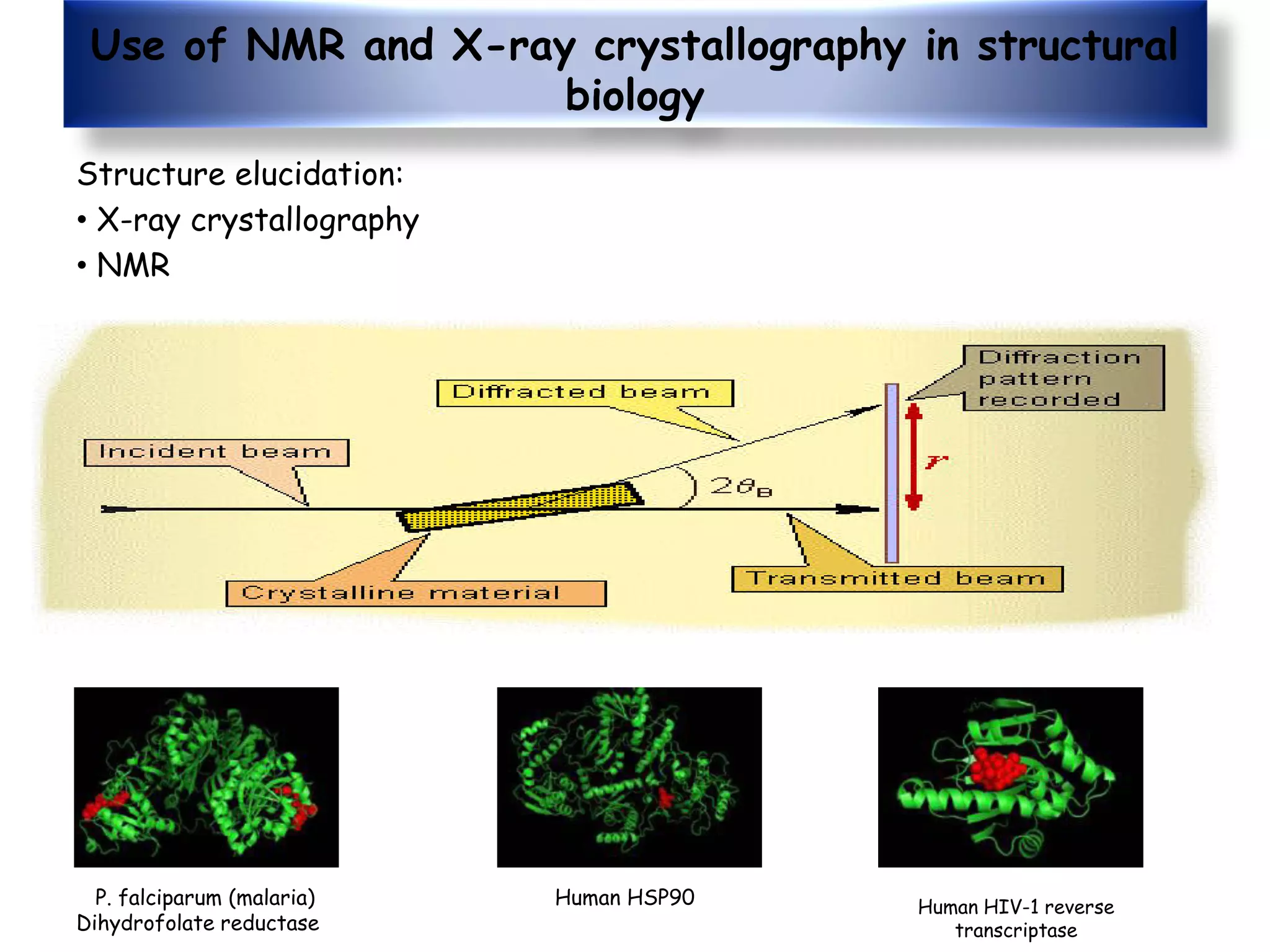
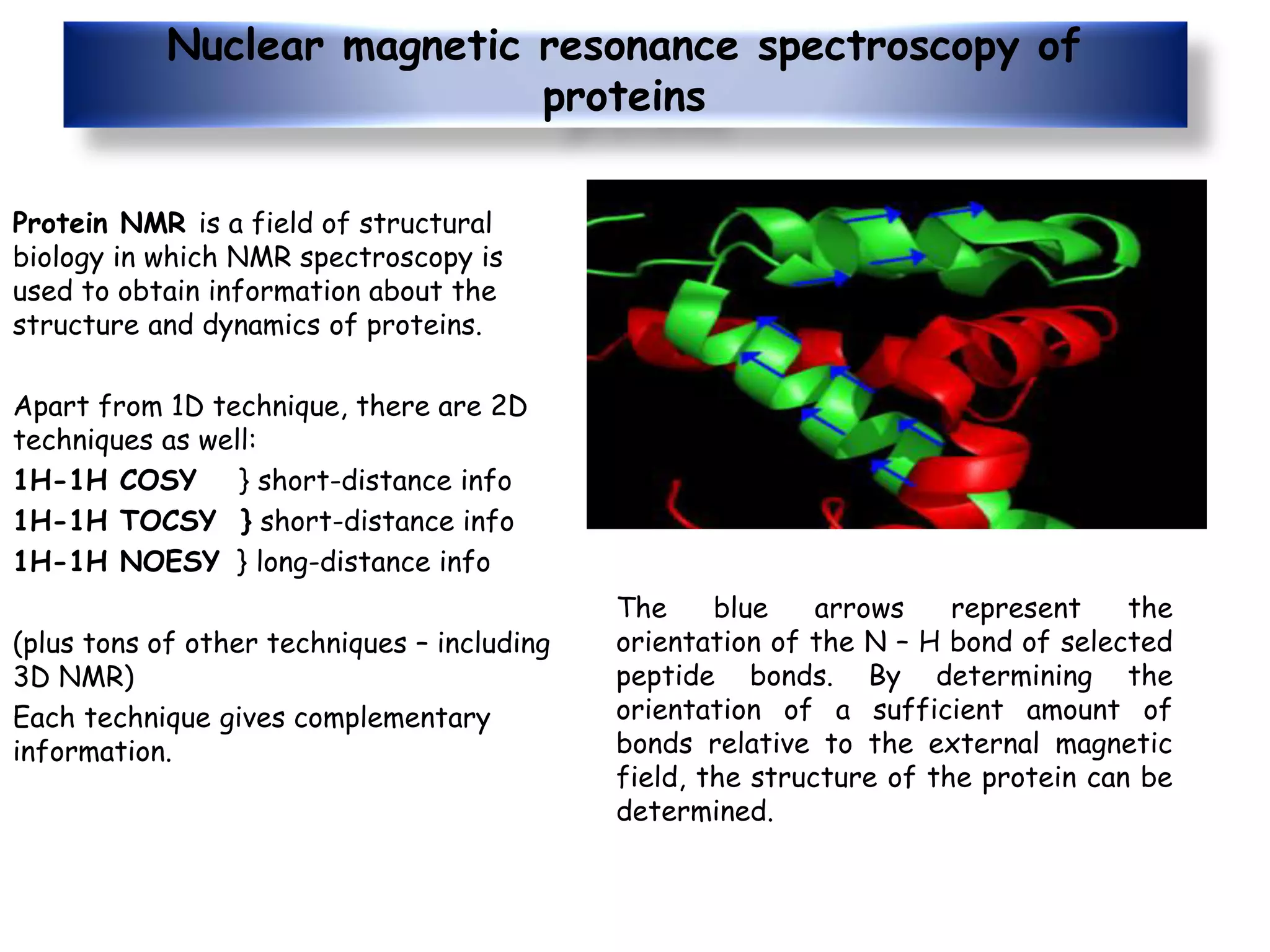
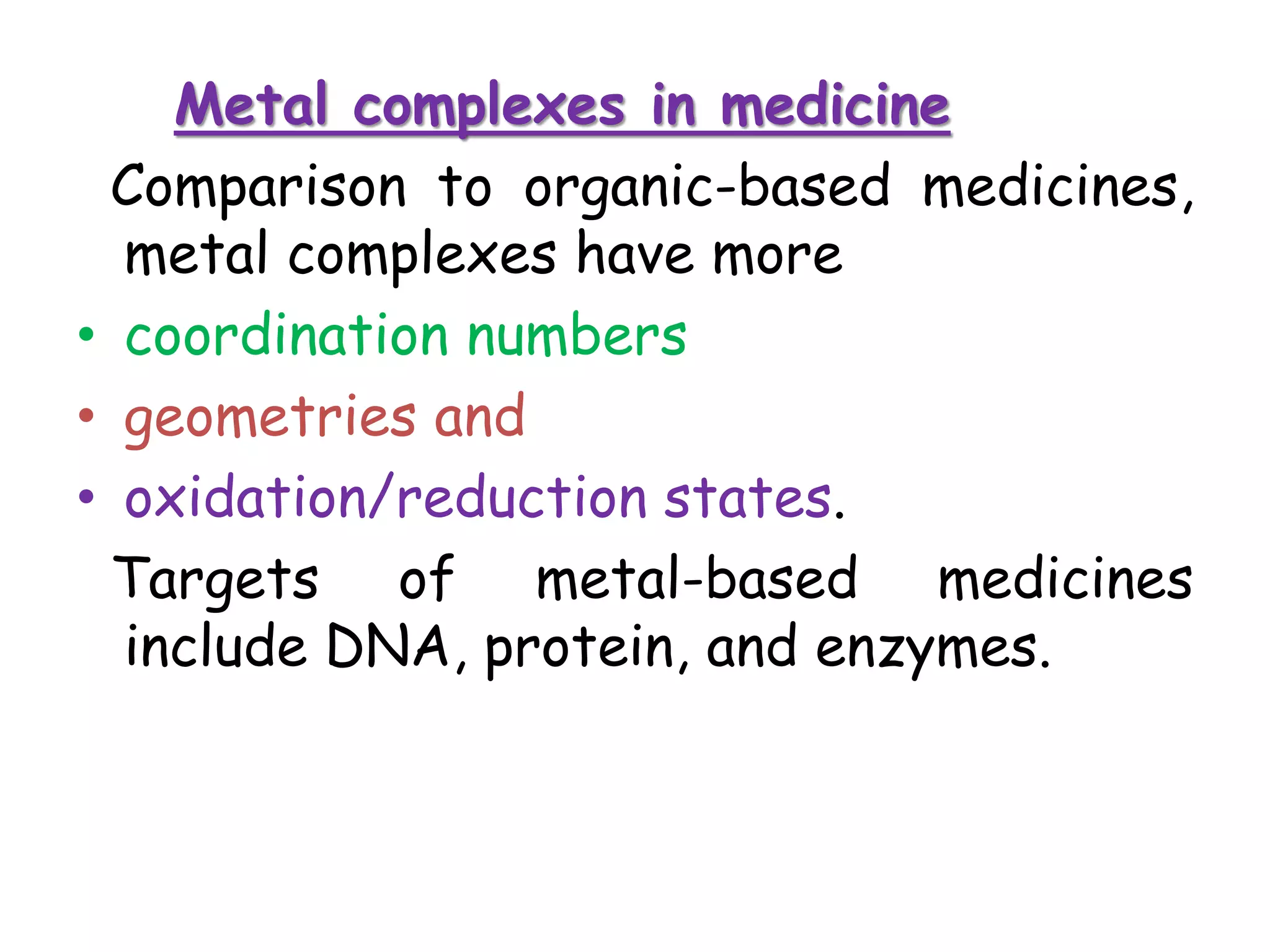
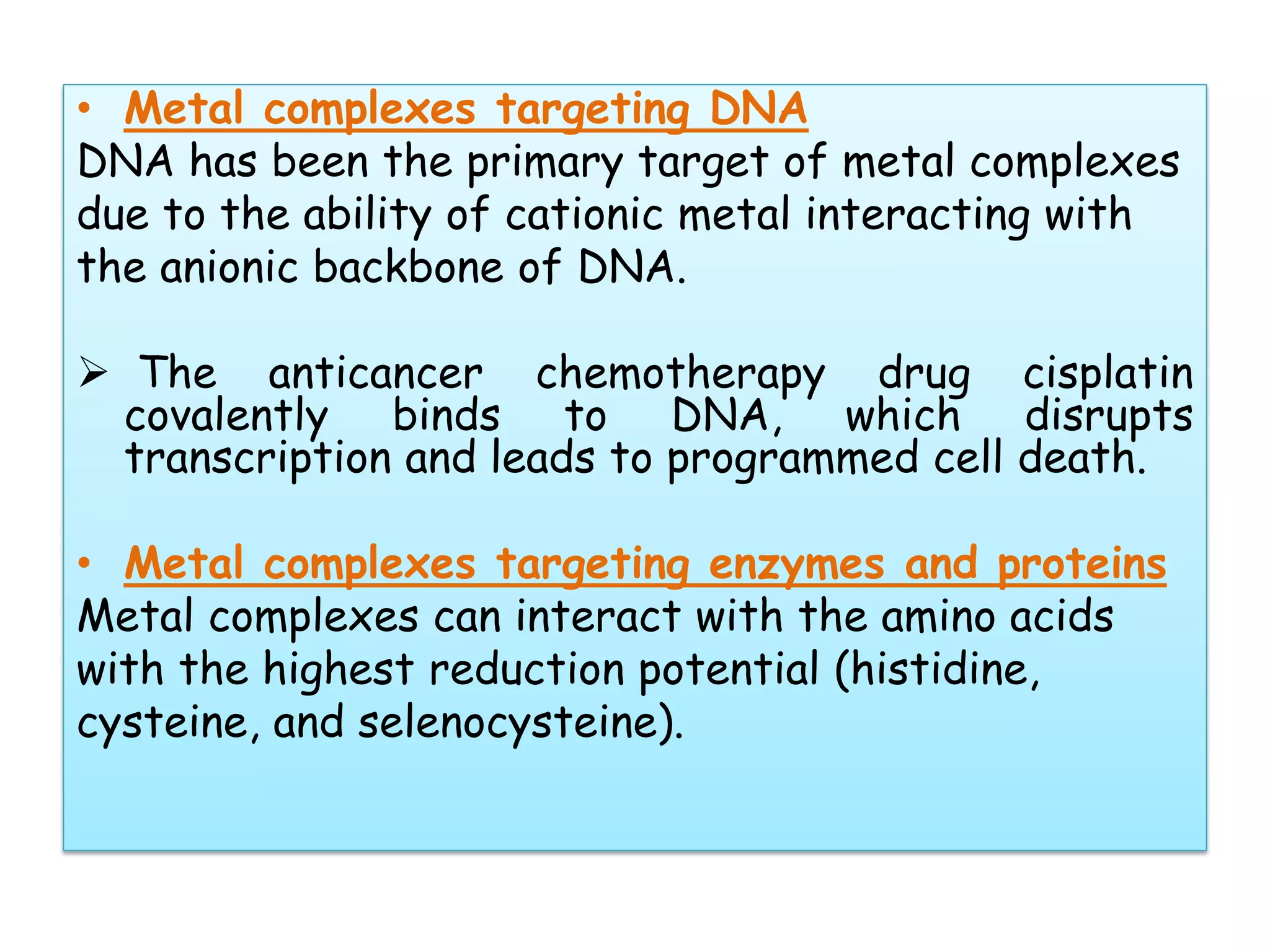
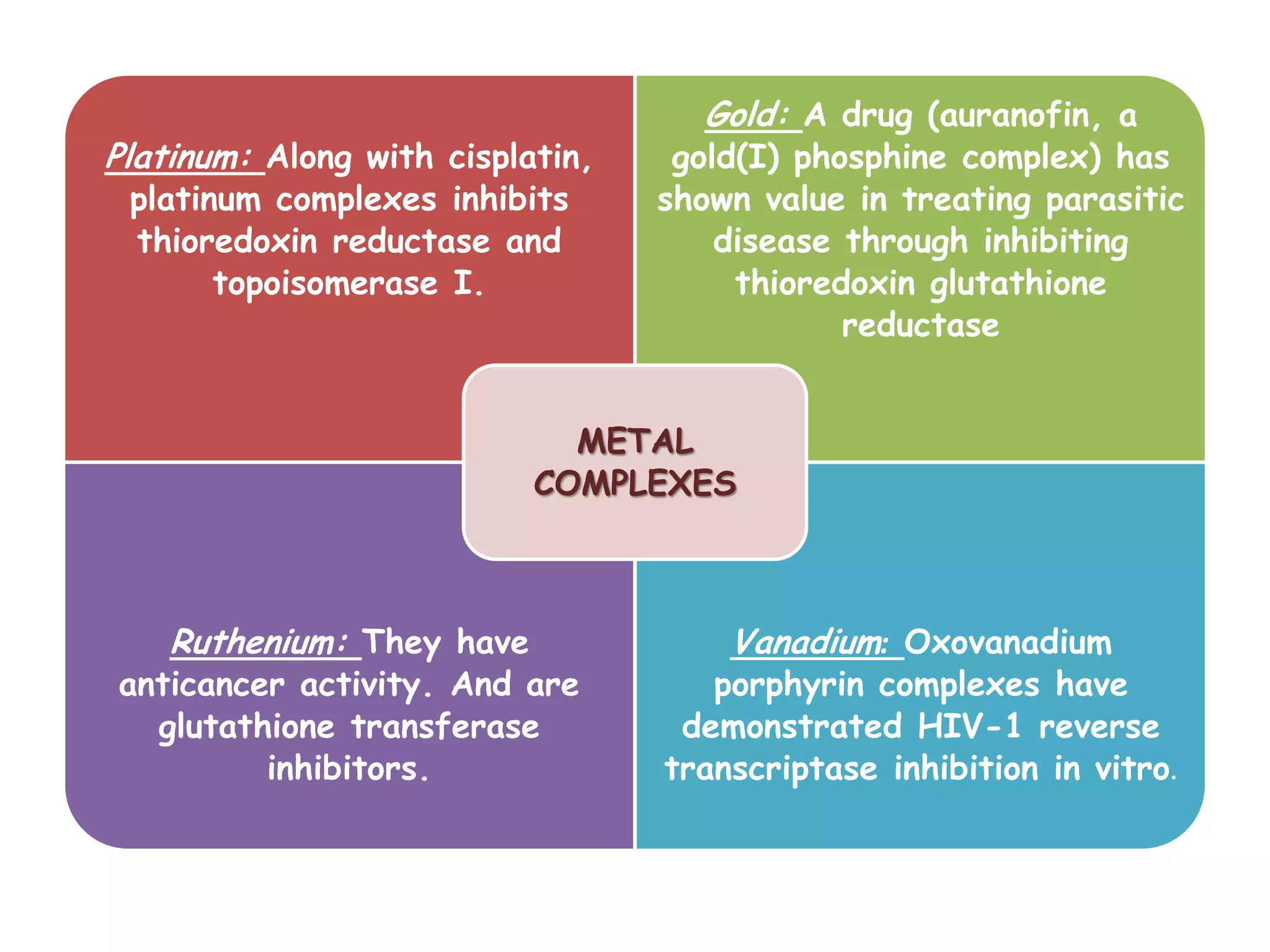
This document provides an overview of the various applications of chemistry in biological and medical sciences. It discusses how chemistry is applied in areas such as medicine and healthcare through drug development, food chemistry through food additives, structural biology through techniques like NMR and X-ray crystallography, nuclear chemistry in medical imaging and diagnosis, inorganic chemistry in metal-based drugs, and nanotechnology for targeted drug delivery and therapy. The document also gives examples of specific applications like anticancer drugs, preservatives, sweeteners, structural analysis of proteins, brain tumor detection using radiolabeling, and nanoparticle-based antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory treatments.