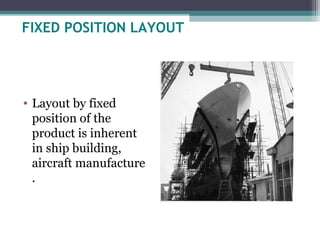
The document discusses different types of plant layouts and their key characteristics. It describes product layouts as arranging machines according to the sequence of operations for a product. Process layouts group similar machines together functionally. Fixed position layouts dedicate space and workers to a single project. Combination layouts blend aspects of product and process layouts. The document compares advantages and disadvantages of each type in factors like production flexibility, material handling costs, and equipment utilization.