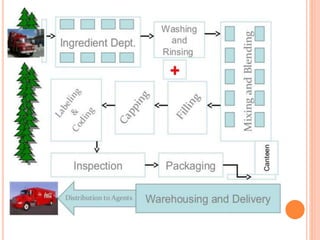
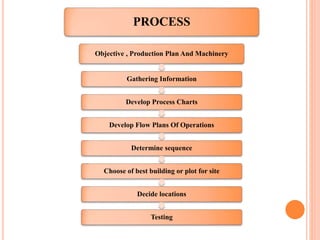
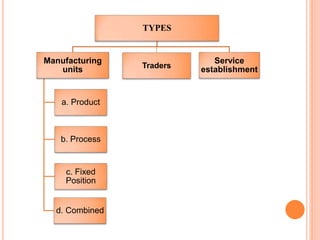
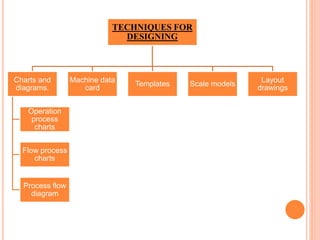
This document defines plant layout and describes its objectives and types. According to the definition, plant layout involves allocating space and arranging equipment to minimize operating costs. The objectives of plant layout include optimizing the flow of materials, utilization of resources, and productivity. There are four main types of manufacturing unit layouts: product layout where materials move sequentially between workstations; process layout where similar machines are grouped; fixed position layout where facilities are arranged around work centers; and combination layouts for facilities producing multiple products. Techniques for designing plant layouts include using charts, diagrams, templates and scale models.