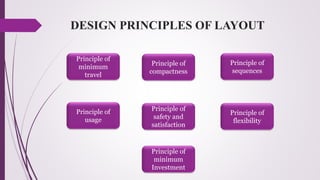
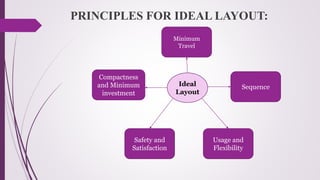
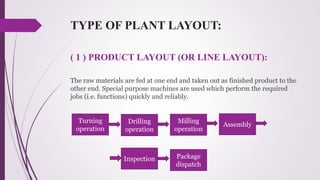
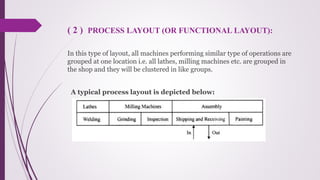
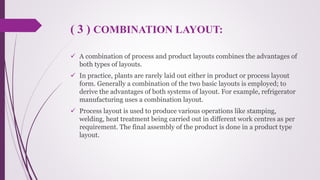
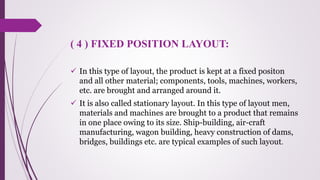
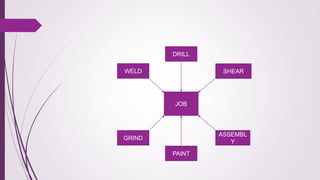
The document discusses plant layout in production management, defining it as the arrangement of machinery and facilities for efficient material flow and cost reduction. It outlines the objectives of effective layouts, including increased productivity and safety, and reviews various layout types such as product, process, combination, and fixed position layouts, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers the significance of material handling, transportation devices, and various equipment like conveyors and forklifts in optimizing production processes.