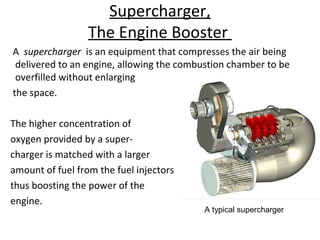
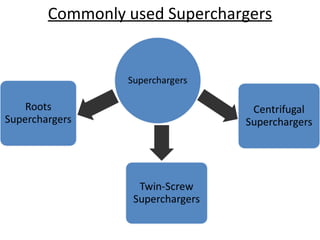
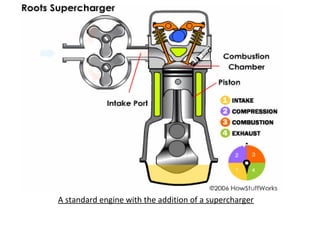
This document discusses different types of superchargers used to boost engine power. It describes how superchargers work by compressing air delivered to the engine, allowing for more fuel and a more powerful combustion. The document categorizes superchargers based on their compression methods and discusses common types like roots, twin-screw, and centrifugal superchargers in detail. It also covers why superchargers are used, how they provide advantages over turbochargers, and concludes that superchargers are still a cost-effective way to significantly increase an engine's horsepower.














![References:
[1]www.superchargerpros.com
[2]auto.howstuffworks.com/supercharger5.htm
[3]wikipedia.org/wiki/Supercharger
[4]www.youtube.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superchargerppt-160814080927/85/Supercharger-ppt-18-320.jpg)
