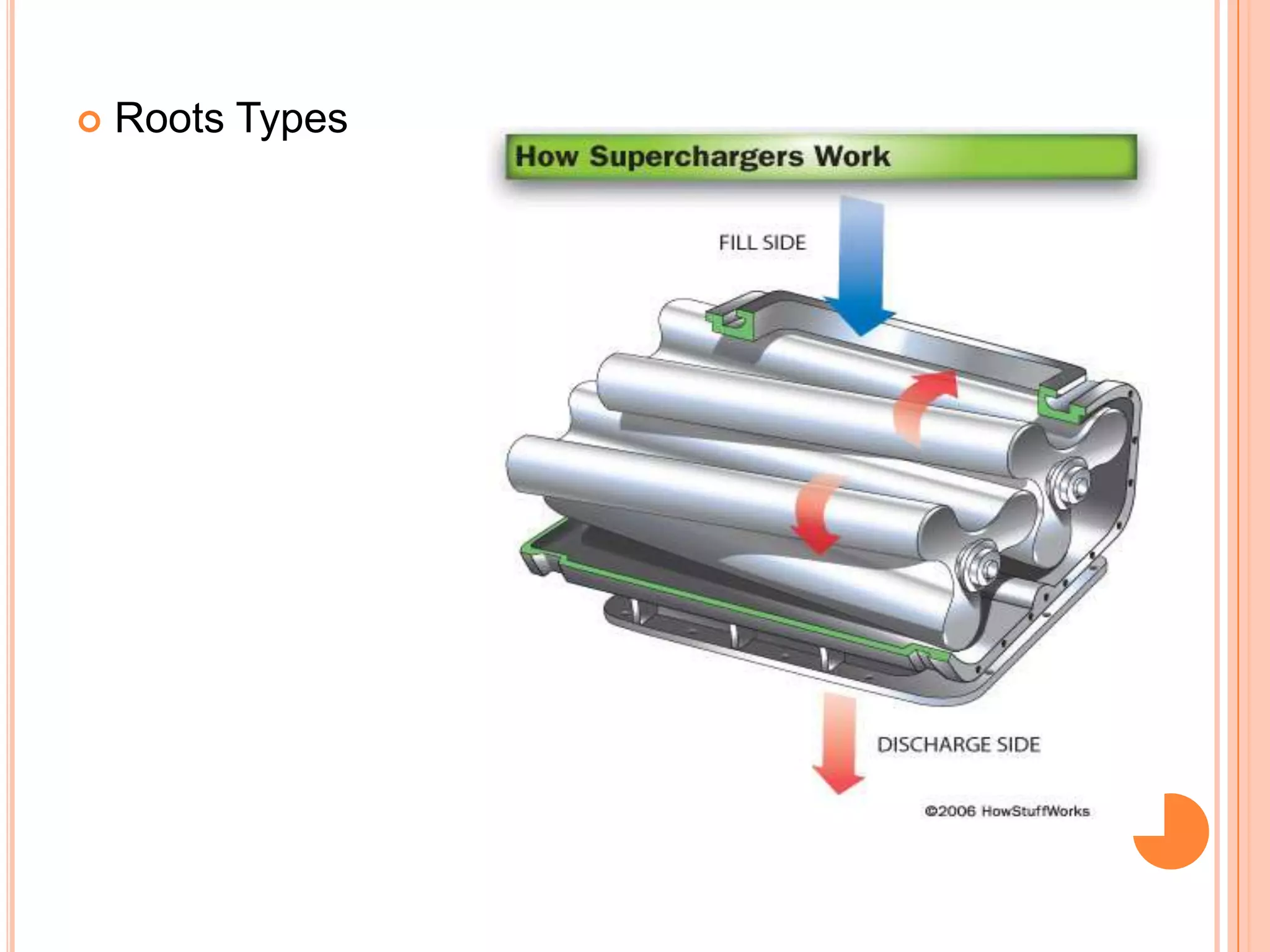
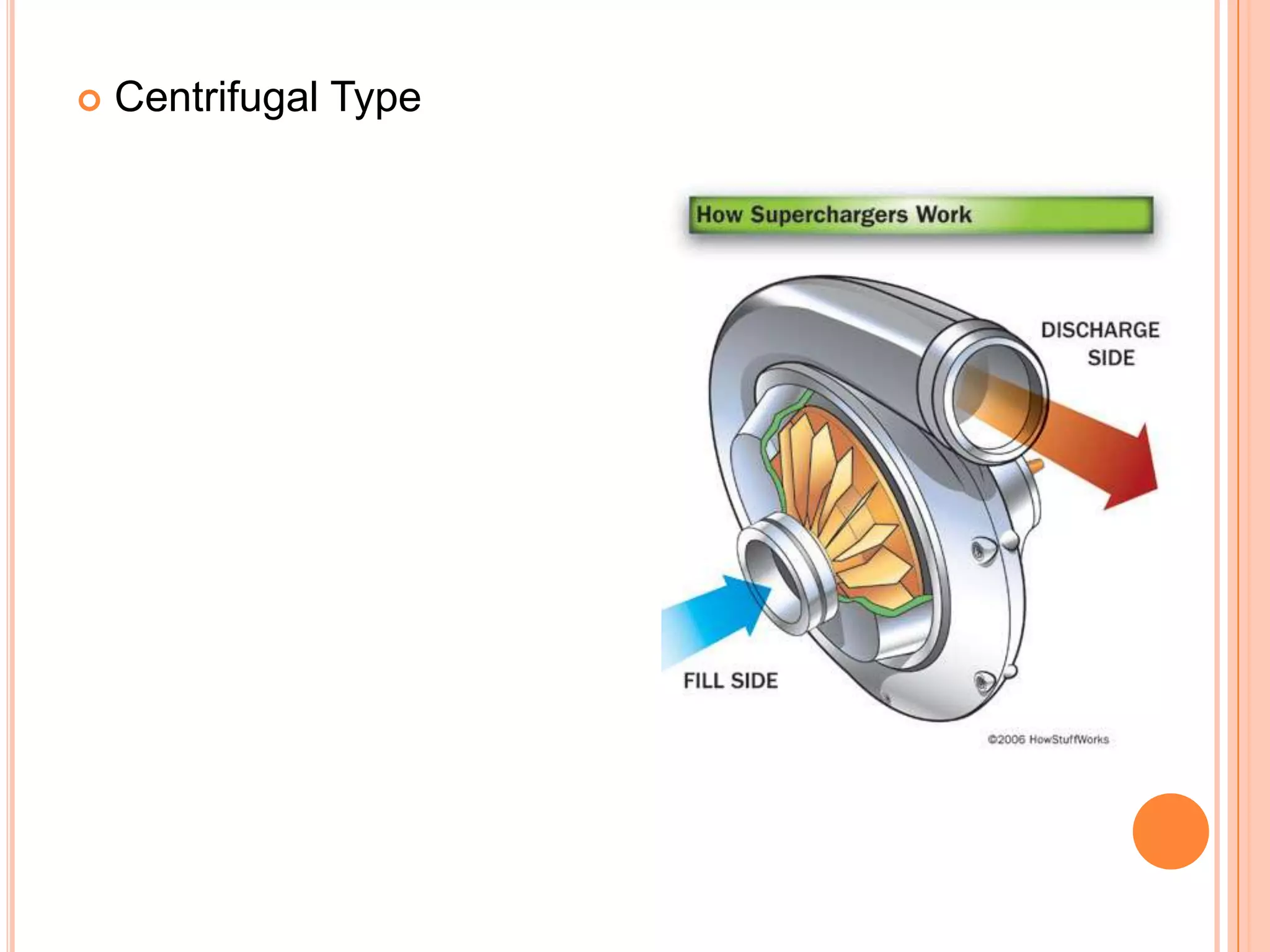
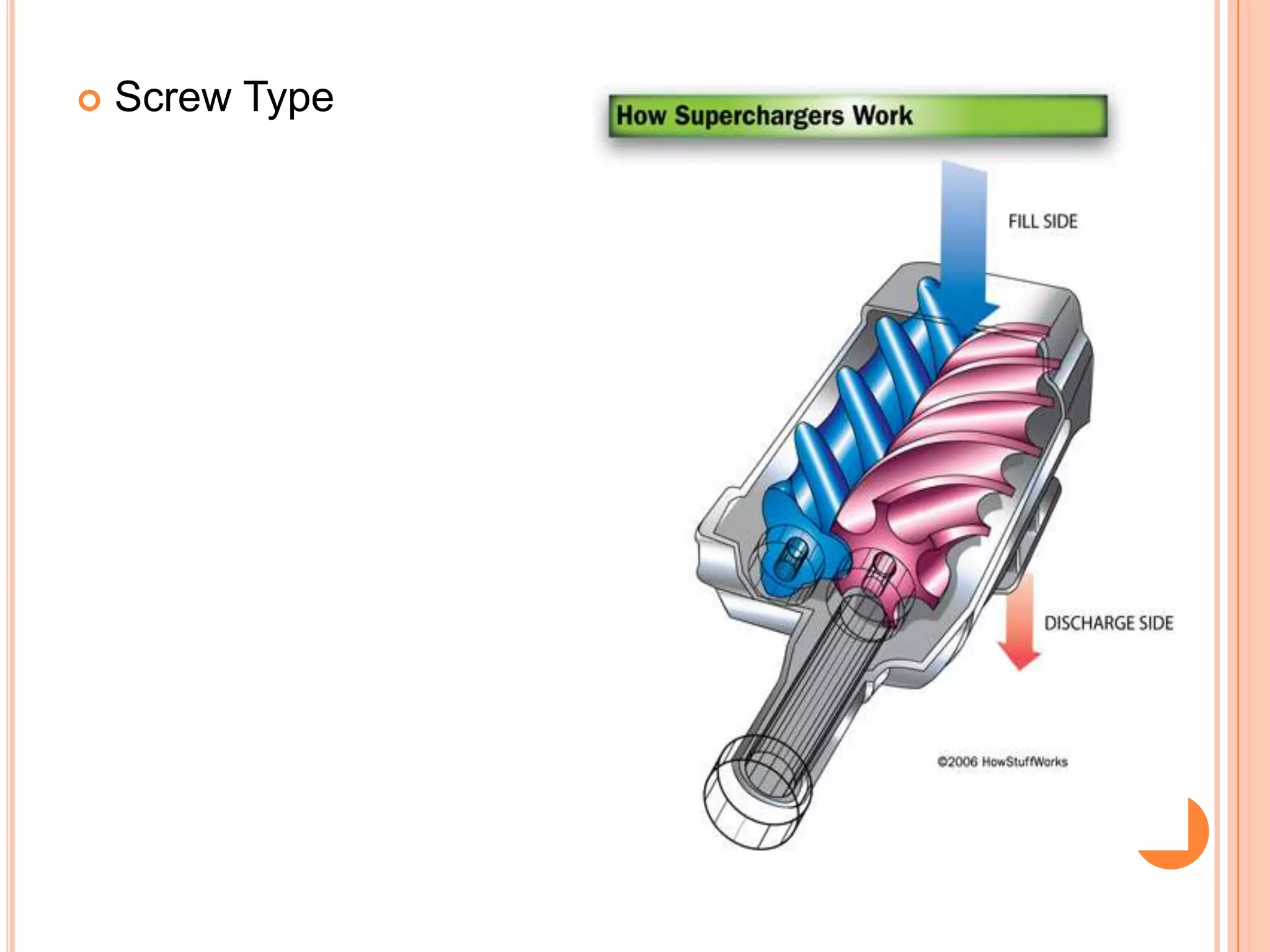
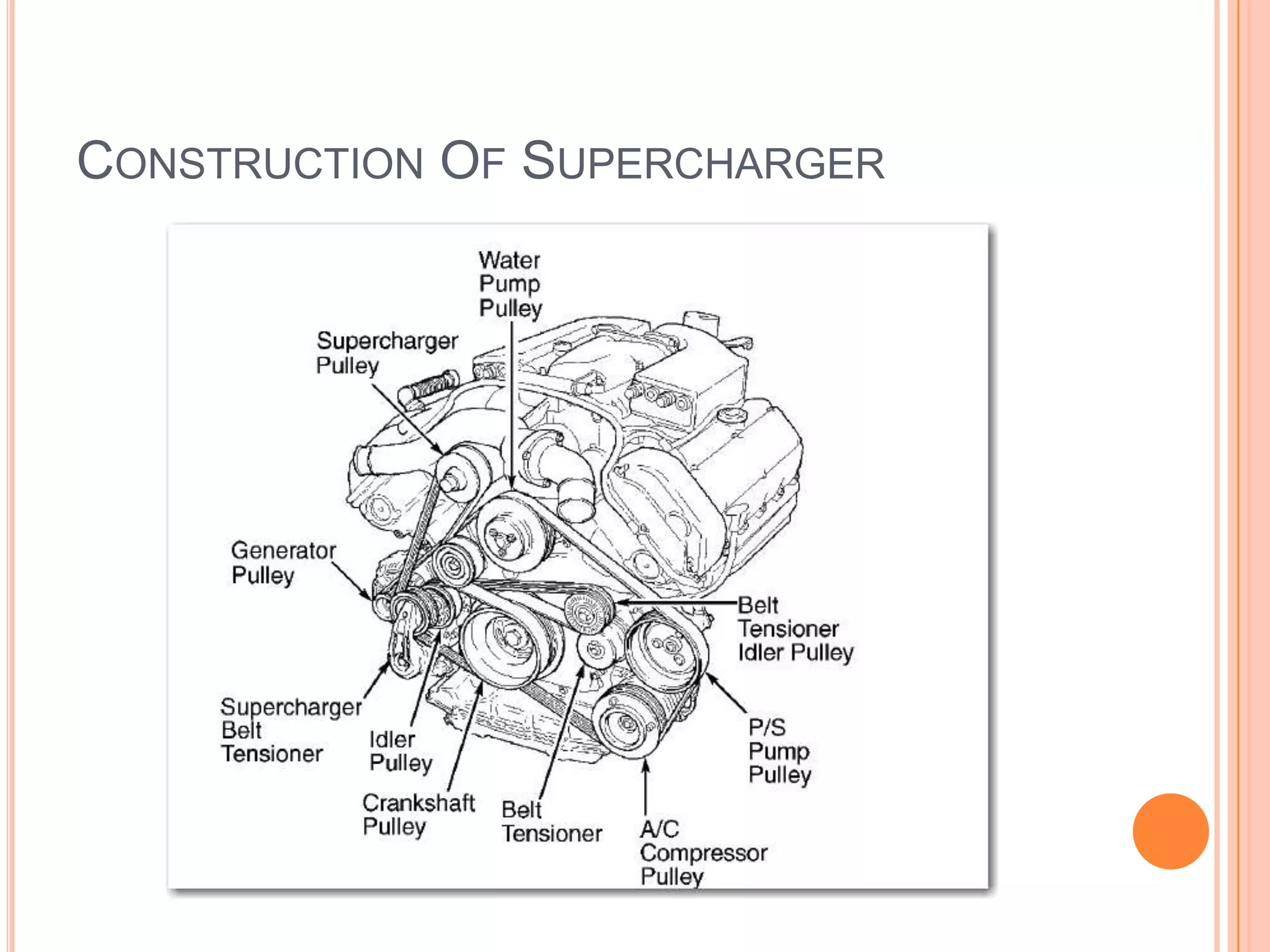
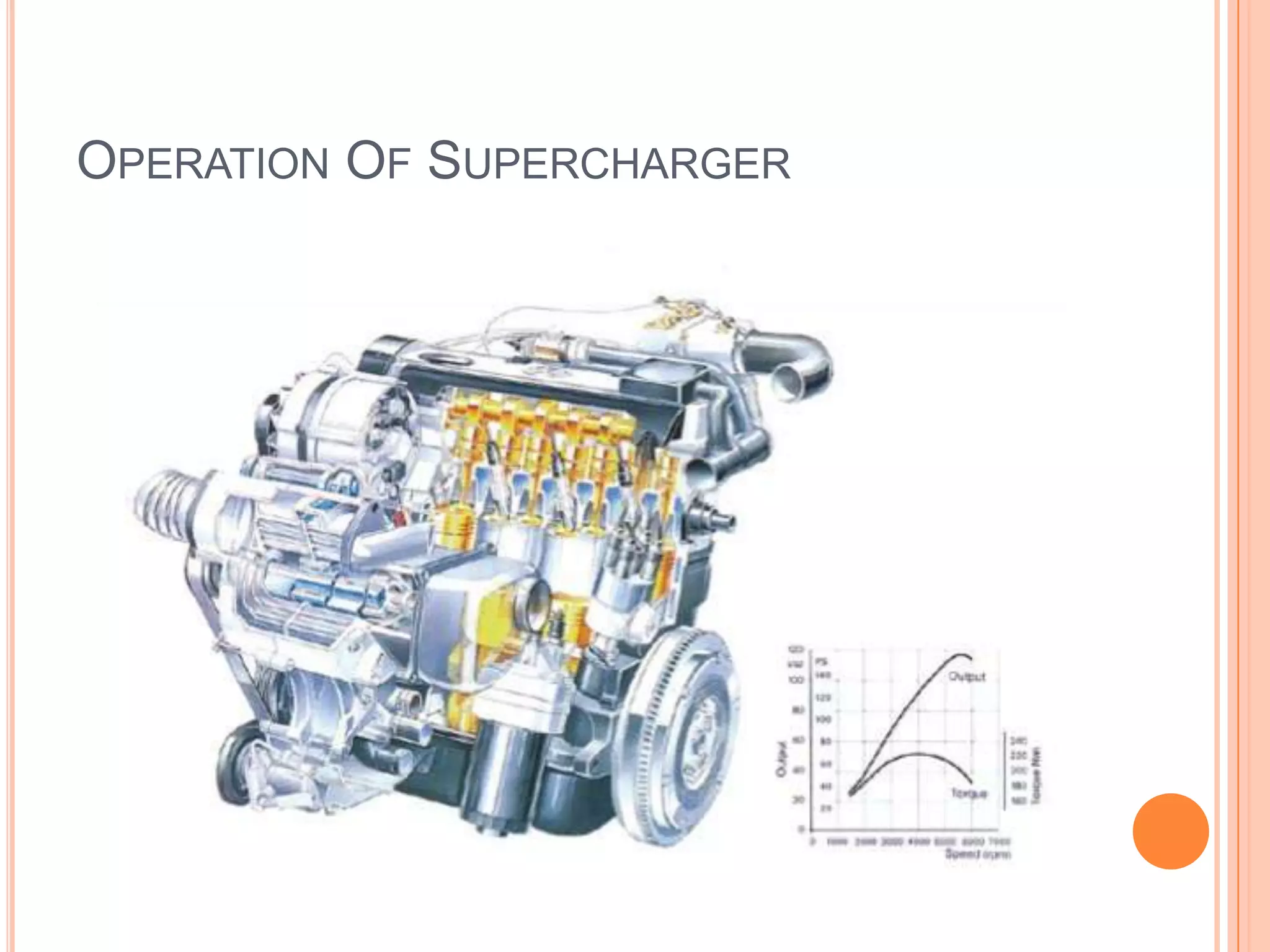
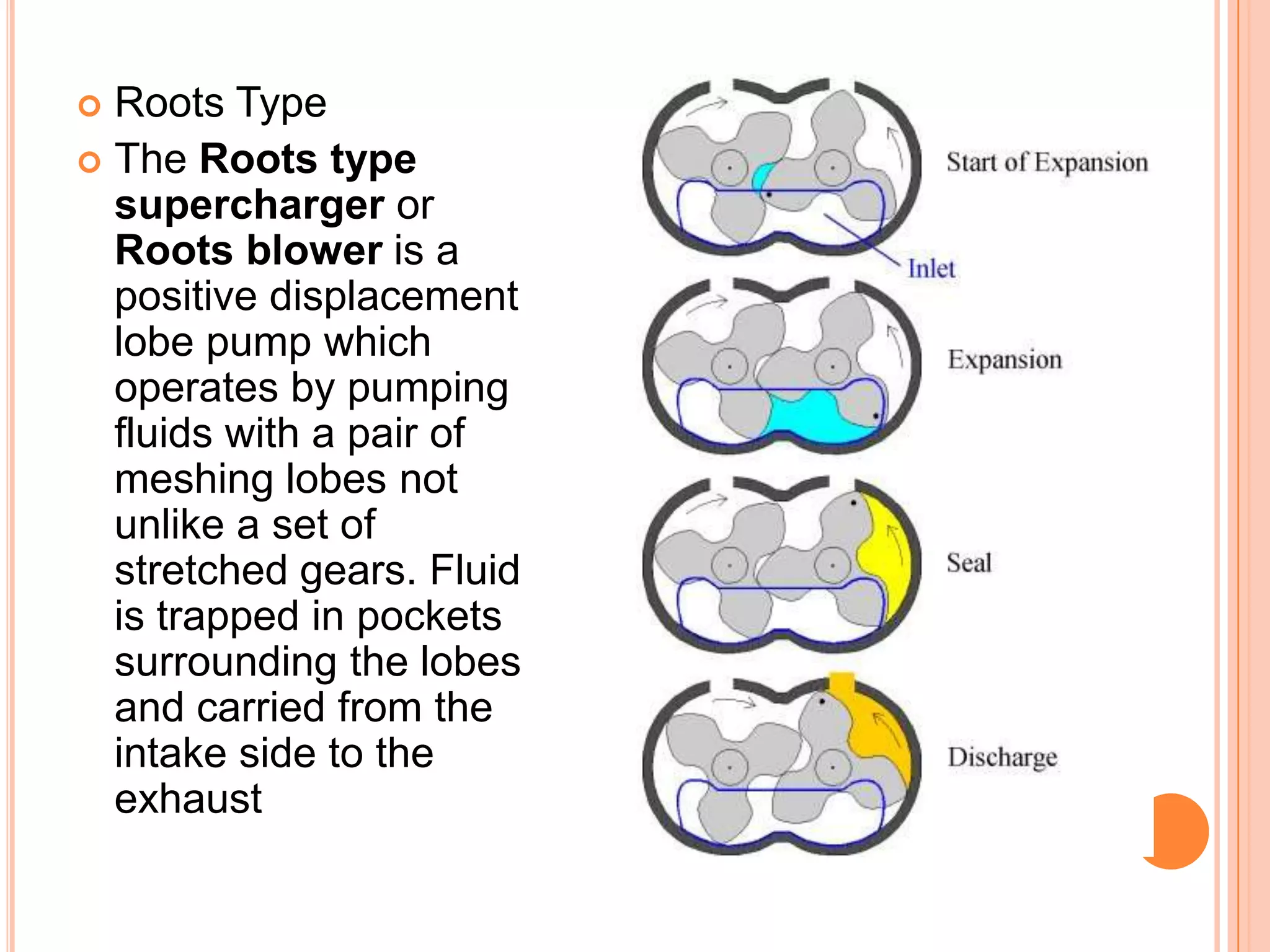
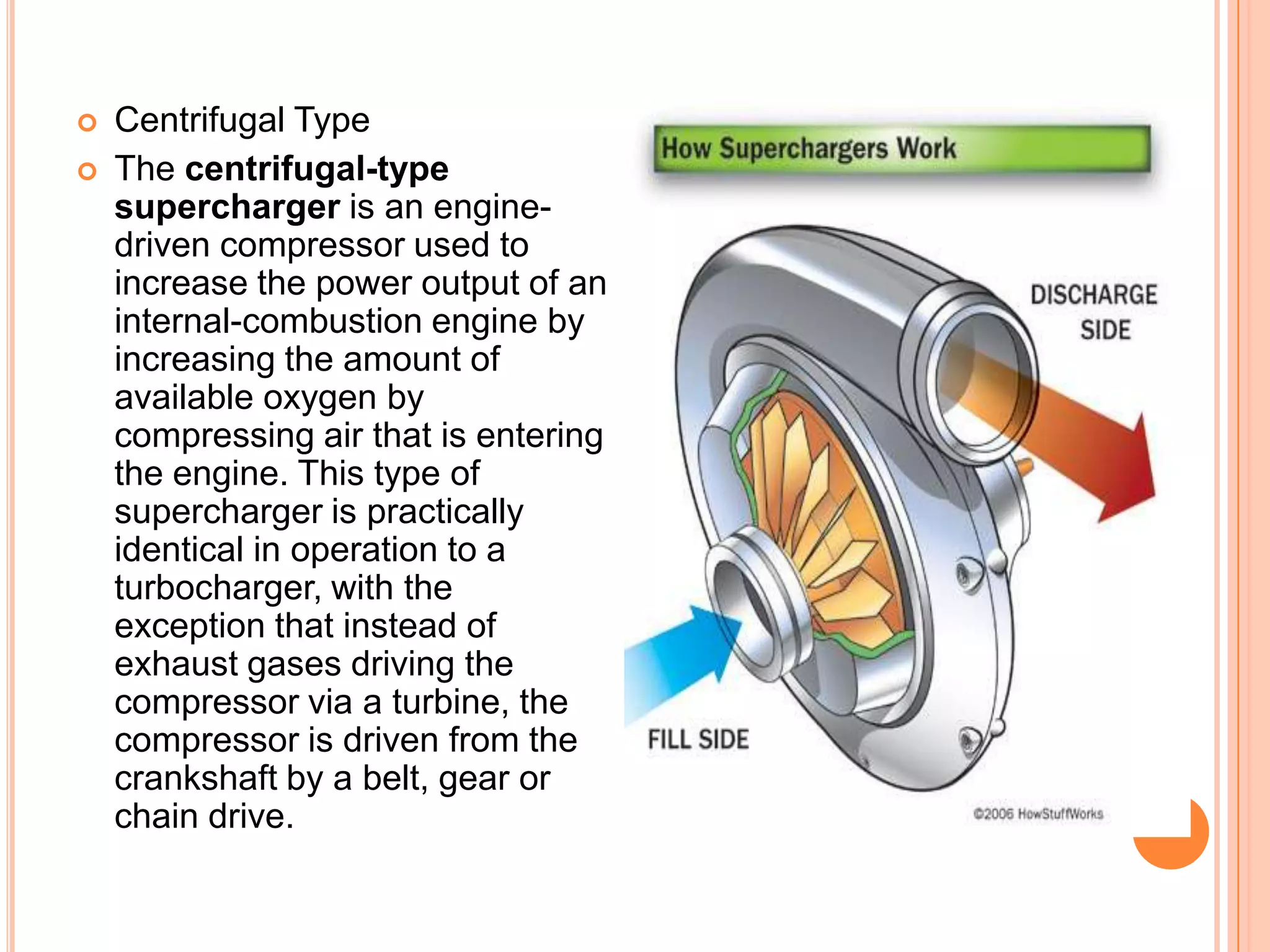
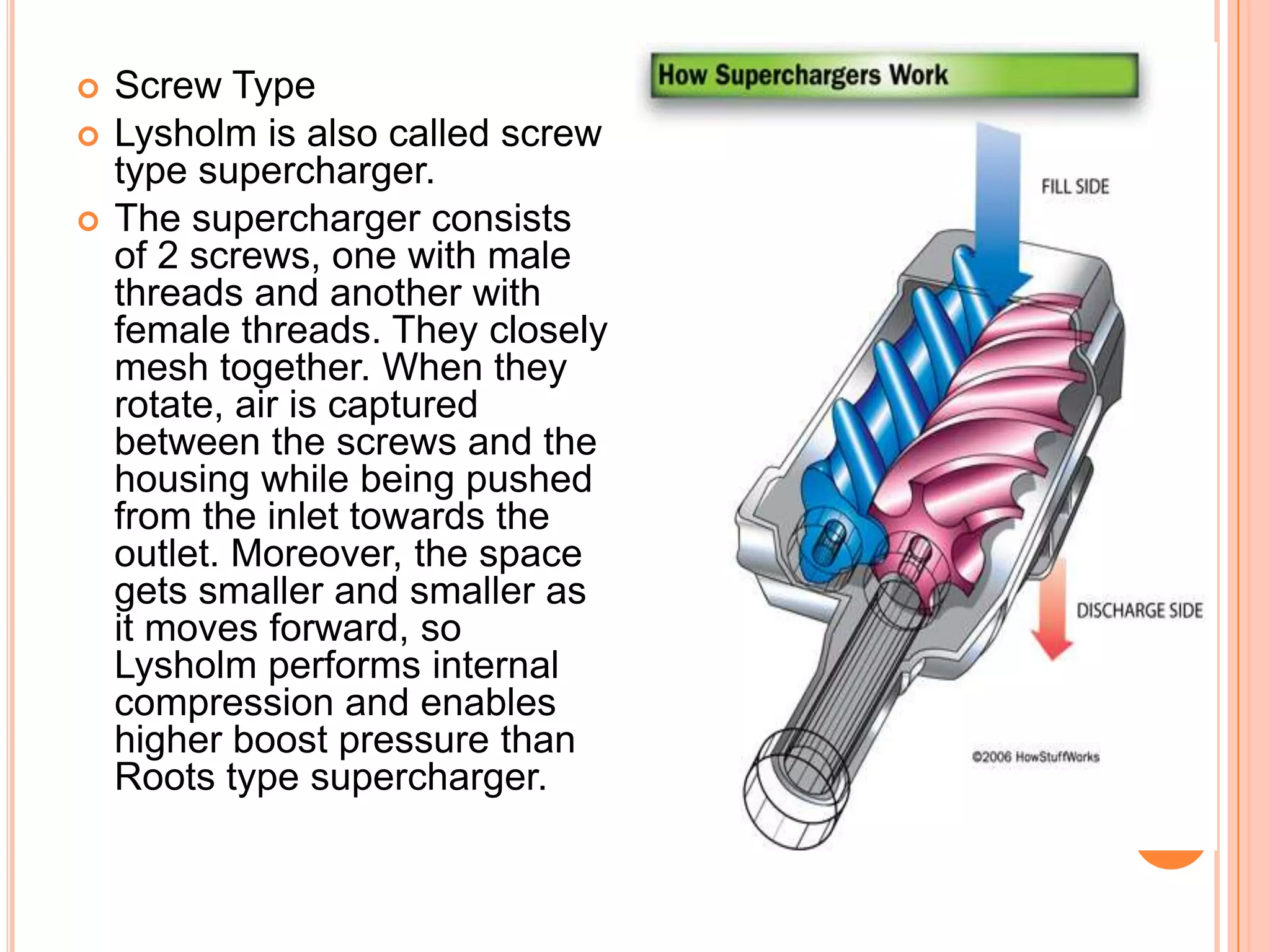
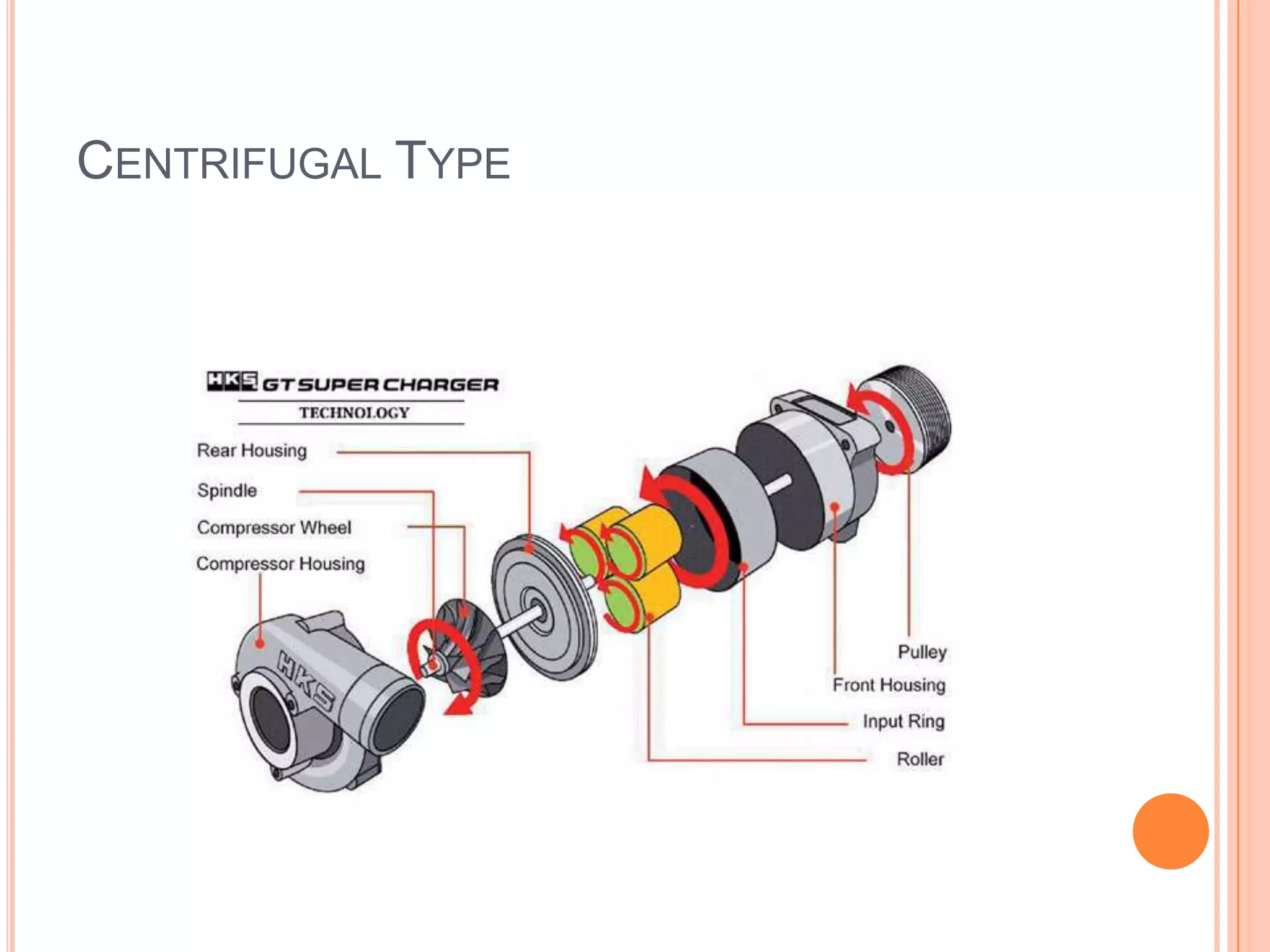
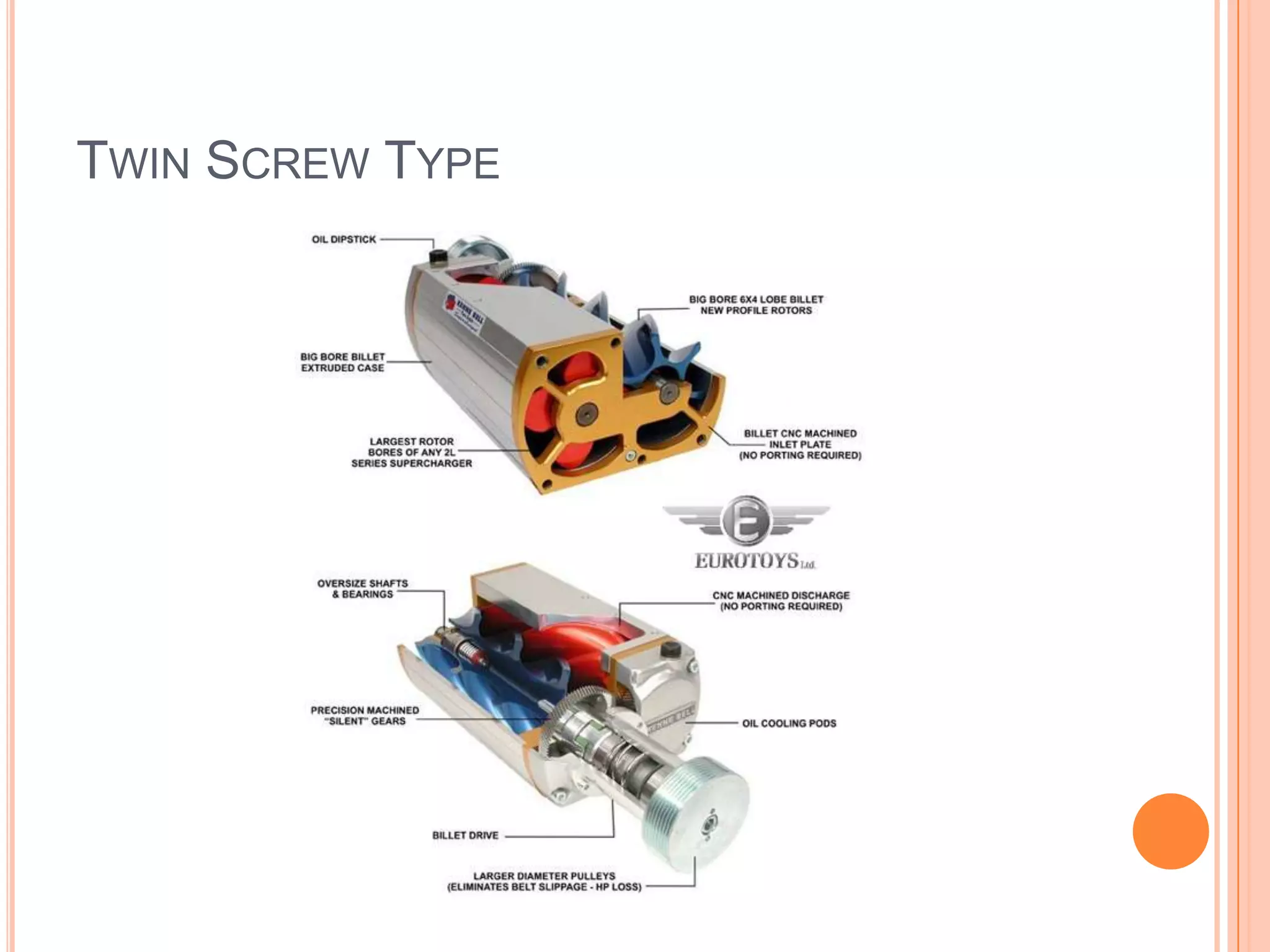
This document summarizes different types of superchargers, including their construction, operation, components and advantages/disadvantages. It describes three main types - Roots, centrifugal, and screw (twin screw) superchargers. The Roots type uses a pair of meshing lobes to pump air from intake to exhaust. The centrifugal type increases boost via an engine-driven compressor wheel. The screw type uses two meshing screws to compress air as it moves from inlet to outlet. Key components of each type are identified. Advantages include increased power without lag, while disadvantages include reduced efficiency and increased engine strain.