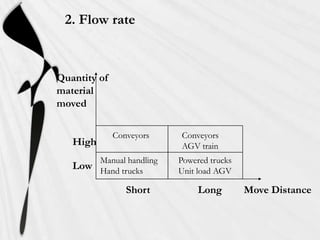
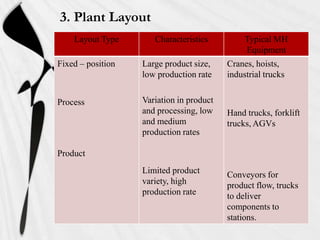
Material handling involves the movement, storage, and control of materials throughout the manufacturing process. It aims to reduce costs and improve efficiency. The document discusses various types of material handling equipment like conveyors, industrial trucks, cranes, and automated guided vehicles. It also outlines objectives like minimizing costs and distances materials are handled. Key considerations in designing material handling systems include the material characteristics, flow rates, and plant layout.