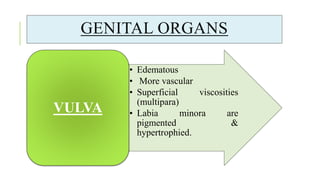
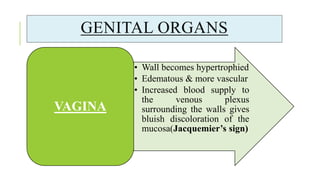
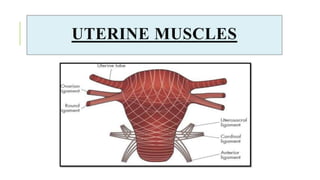
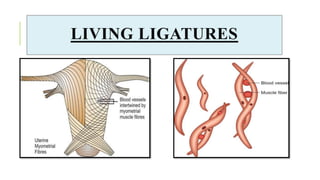
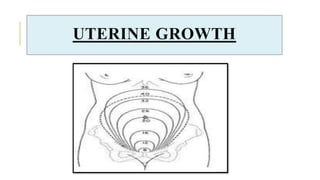
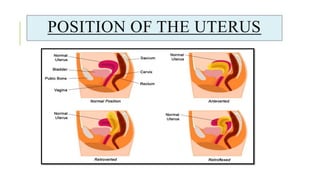
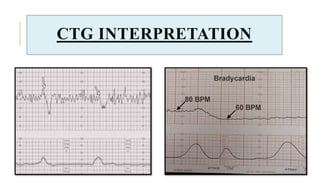
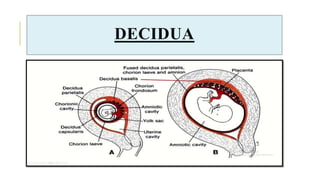
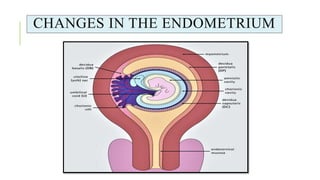
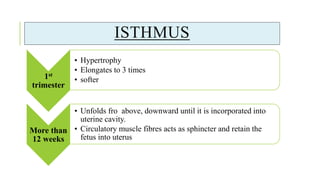
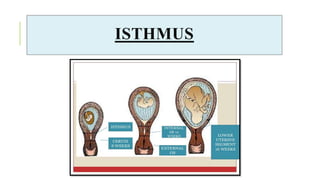
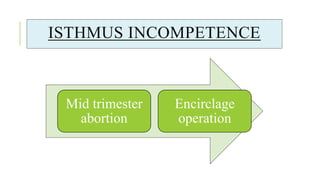
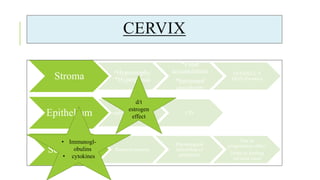
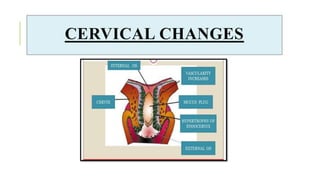
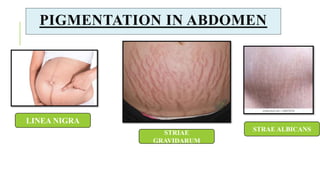
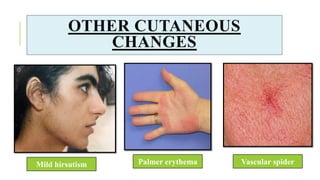
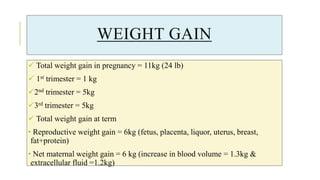
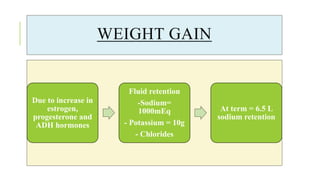
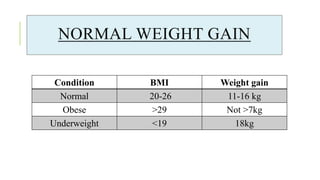
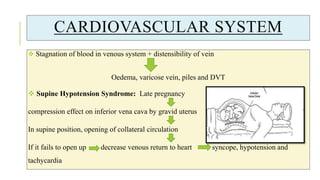
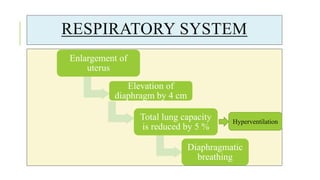
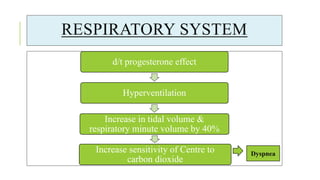
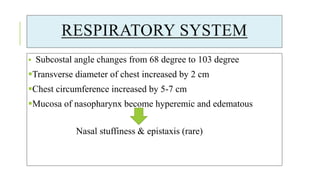
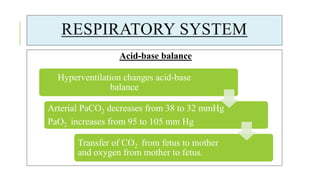
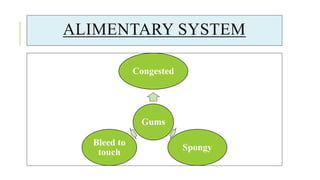
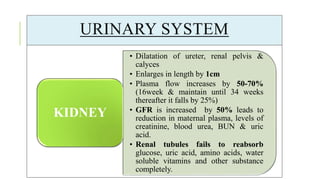
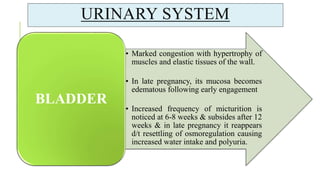
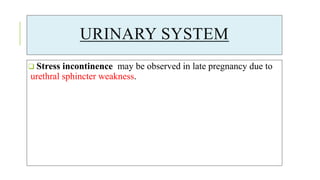
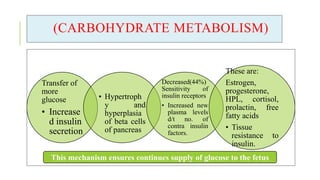
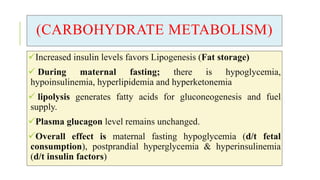
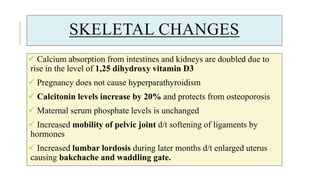
The document outlines the physiological changes that occur during pregnancy, detailing alterations in the reproductive, cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic systems. It includes specific changes in organs such as the uterus, cervix, and breasts, as well as weight gain patterns and metabolic demands of the body to support fetal growth. The information also highlights various psychological changes and the impact of pregnancy on women's health and body image.