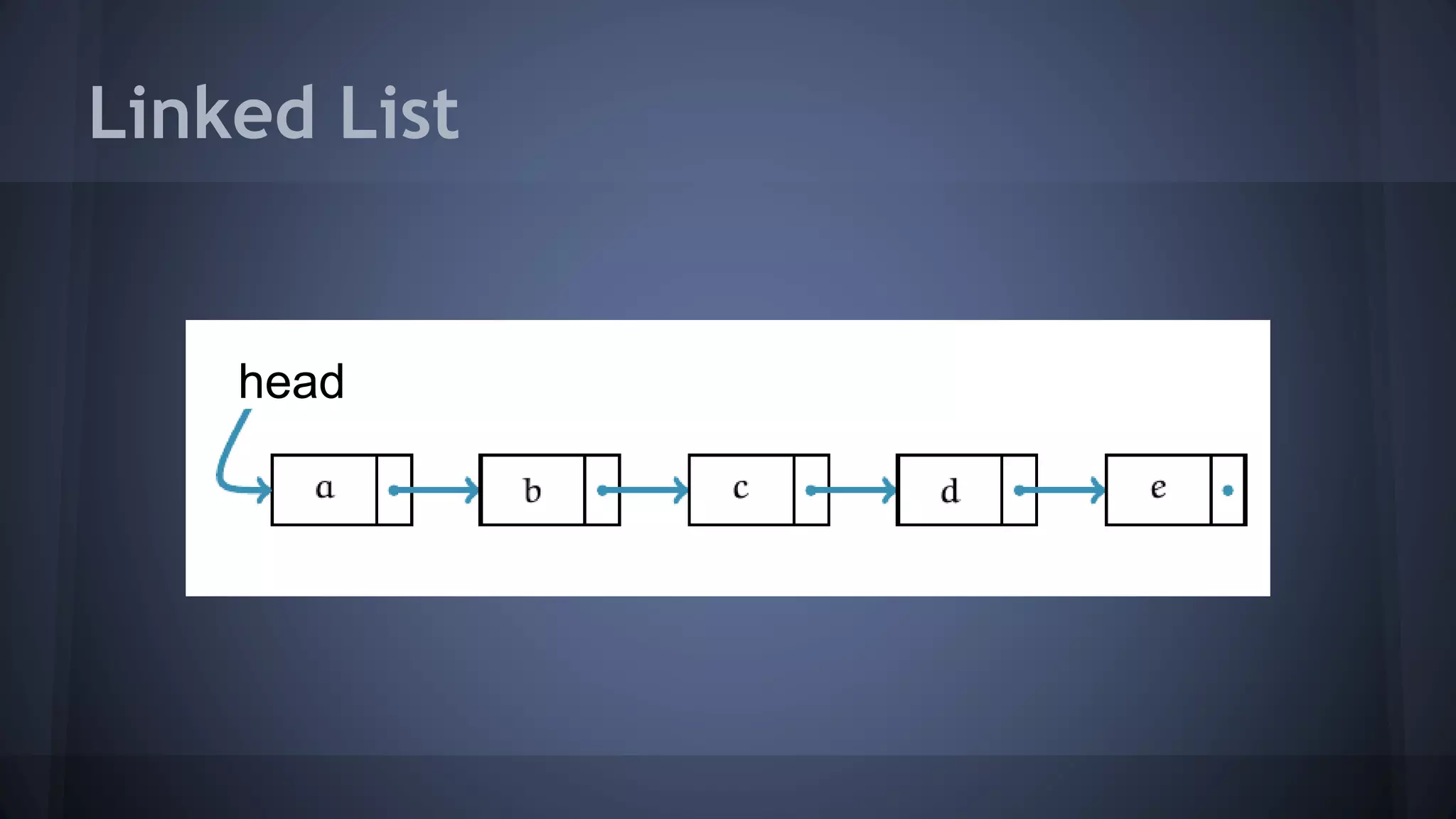
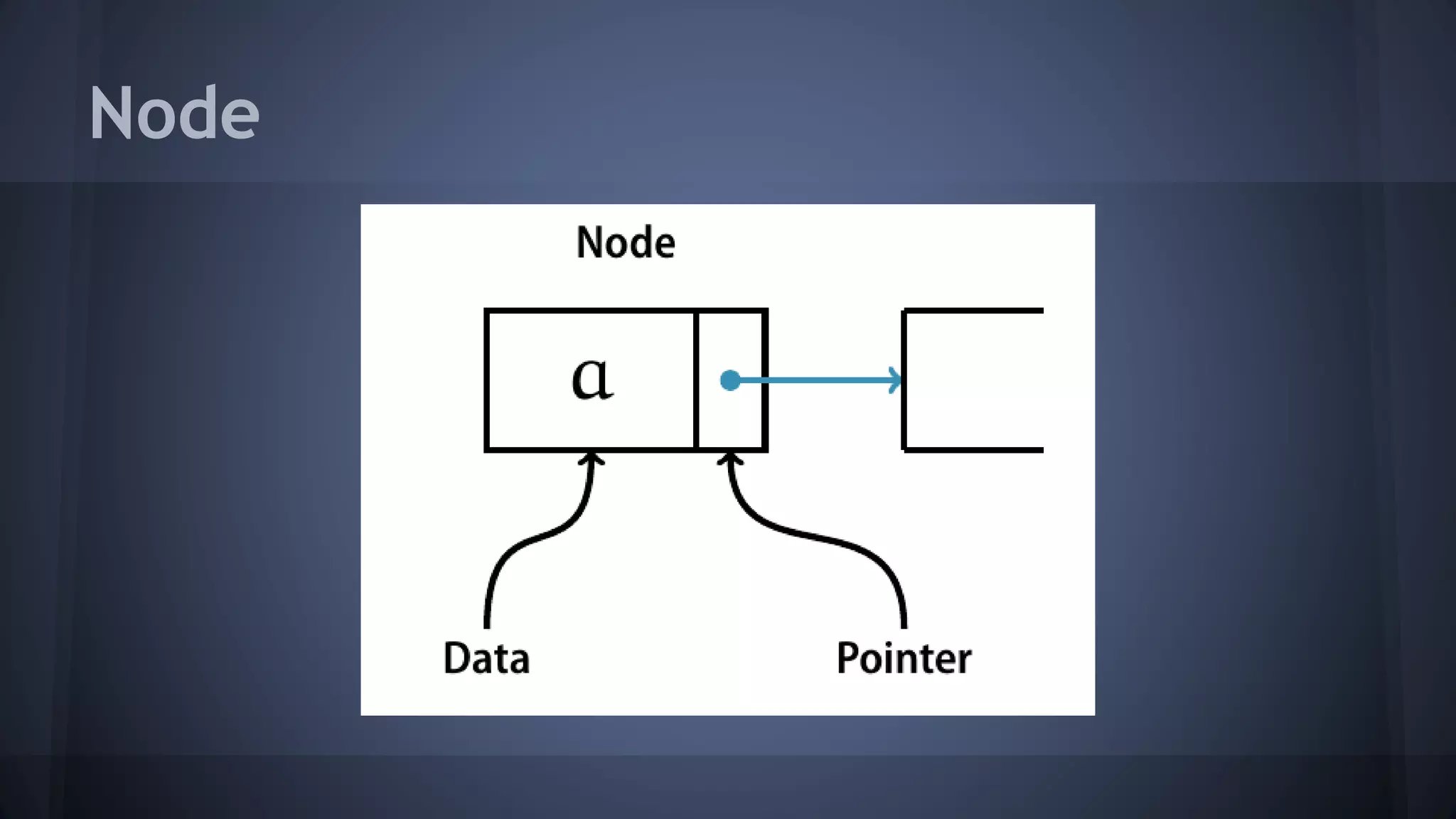
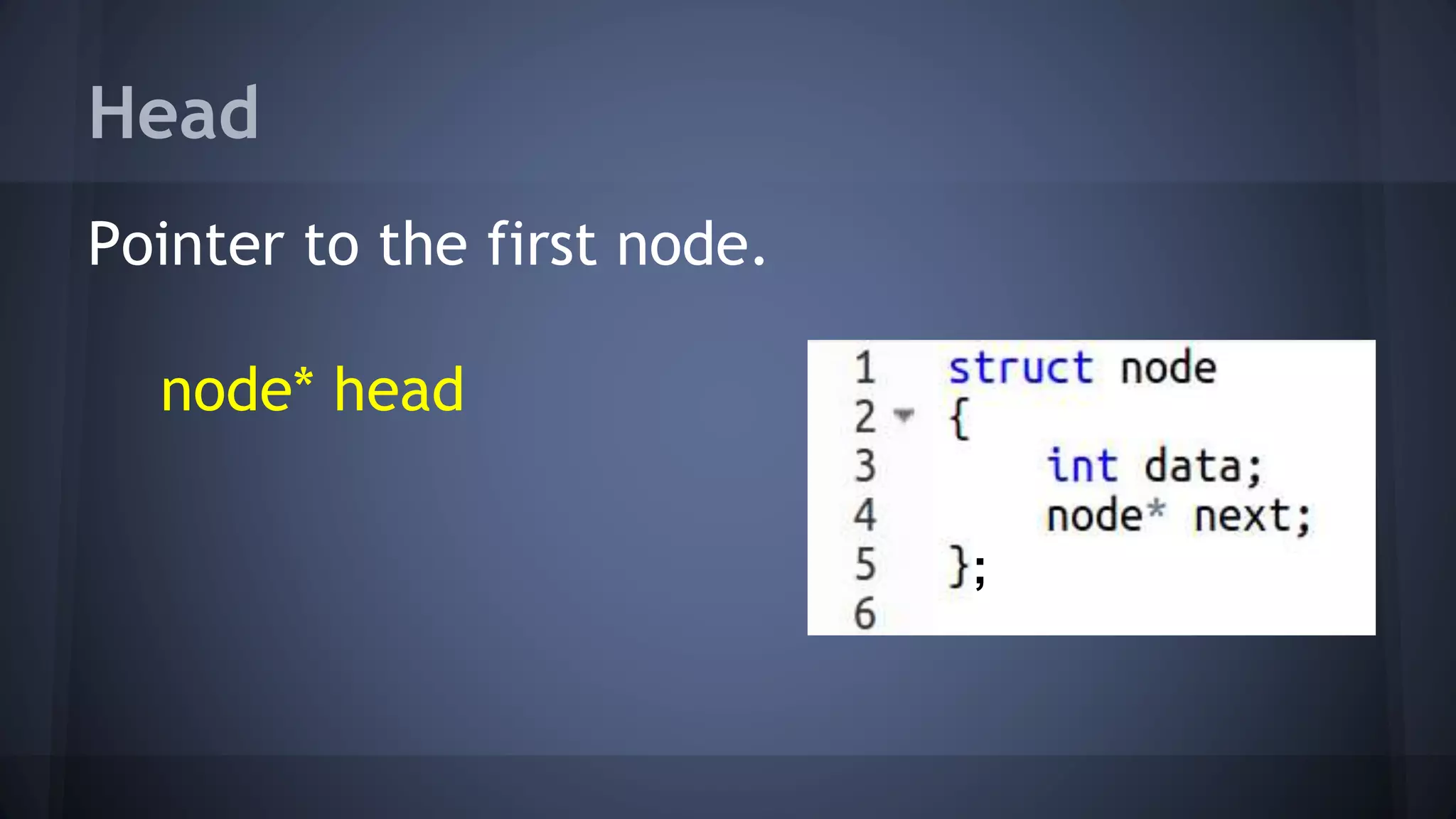
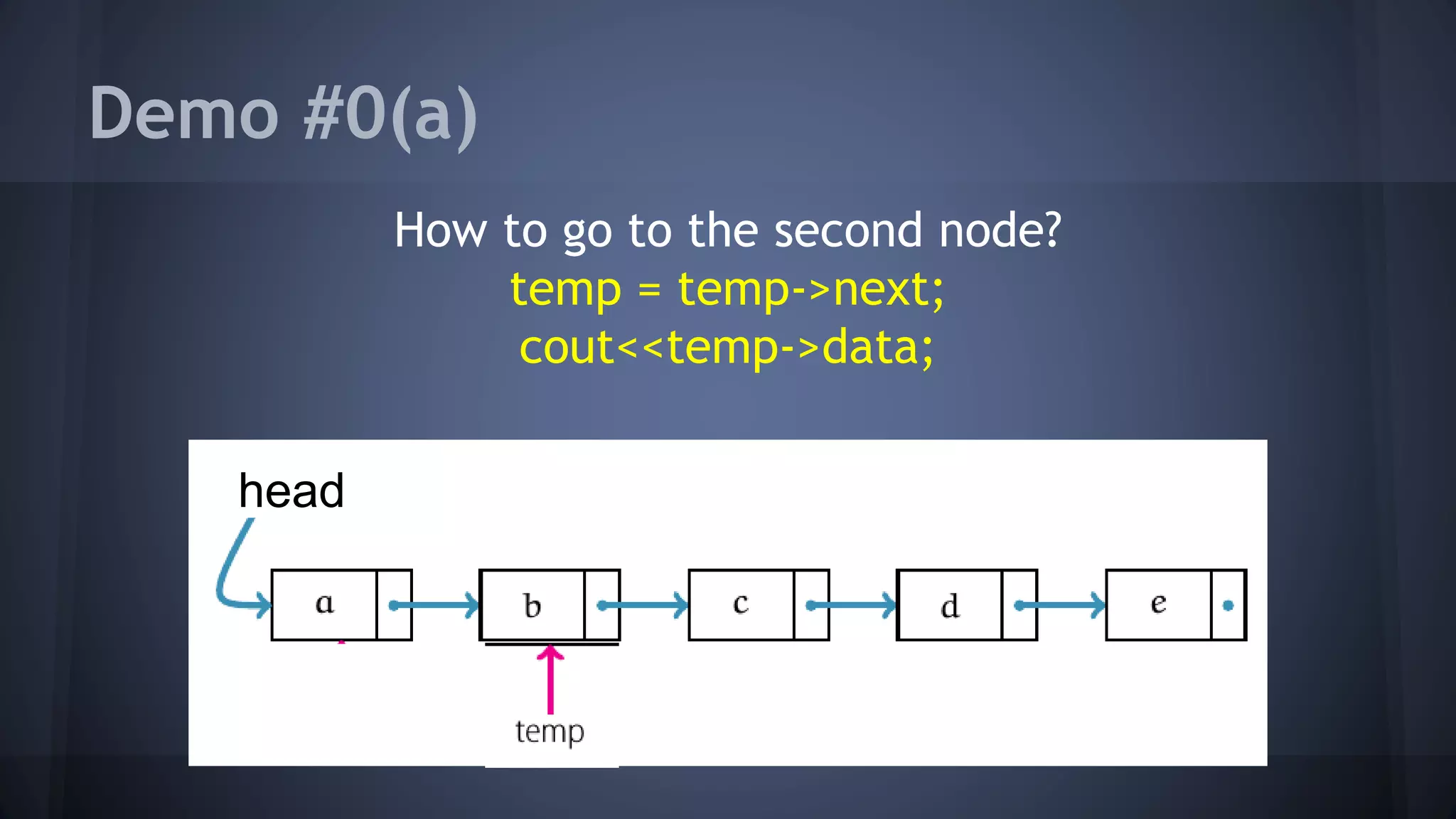
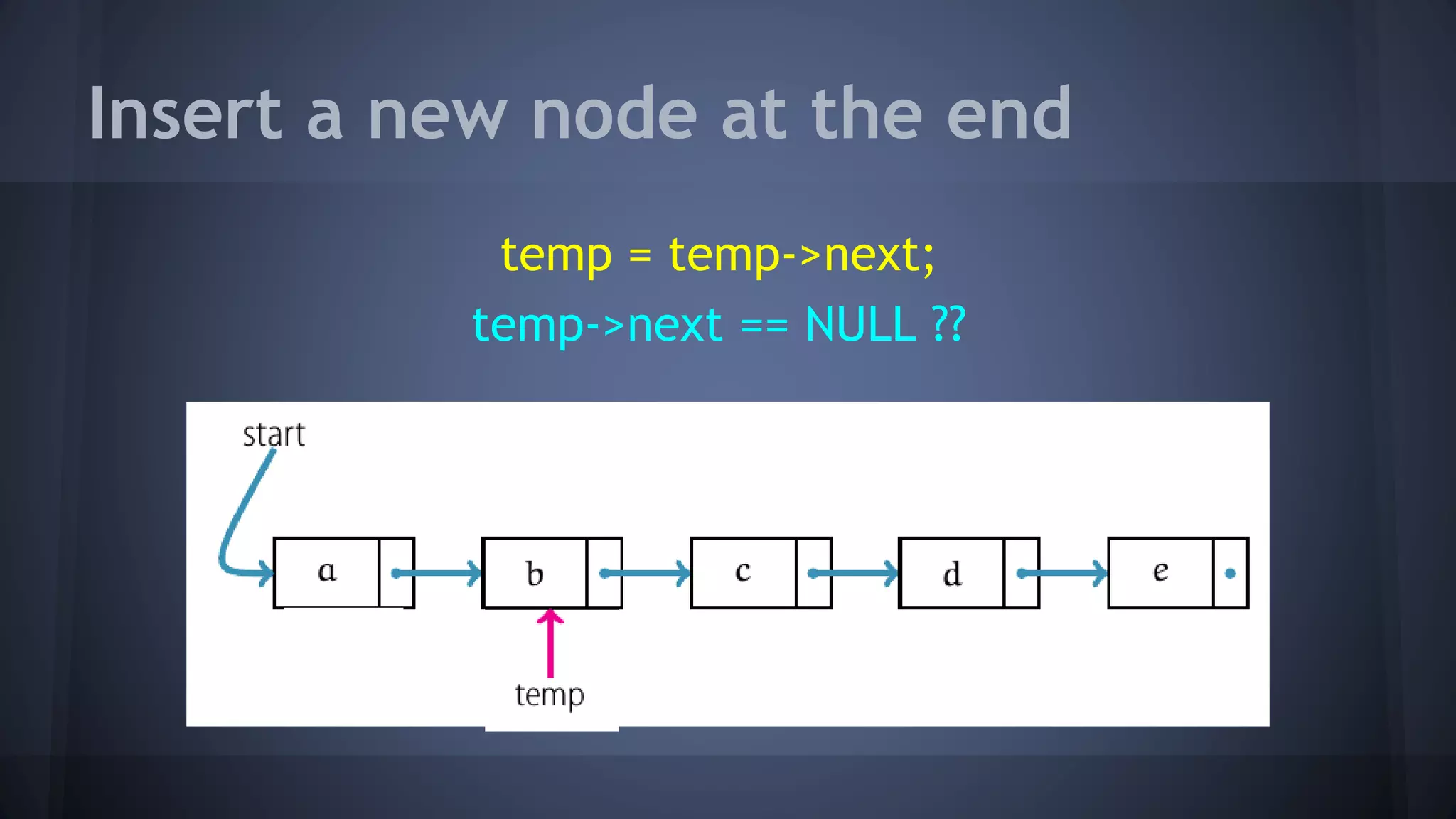
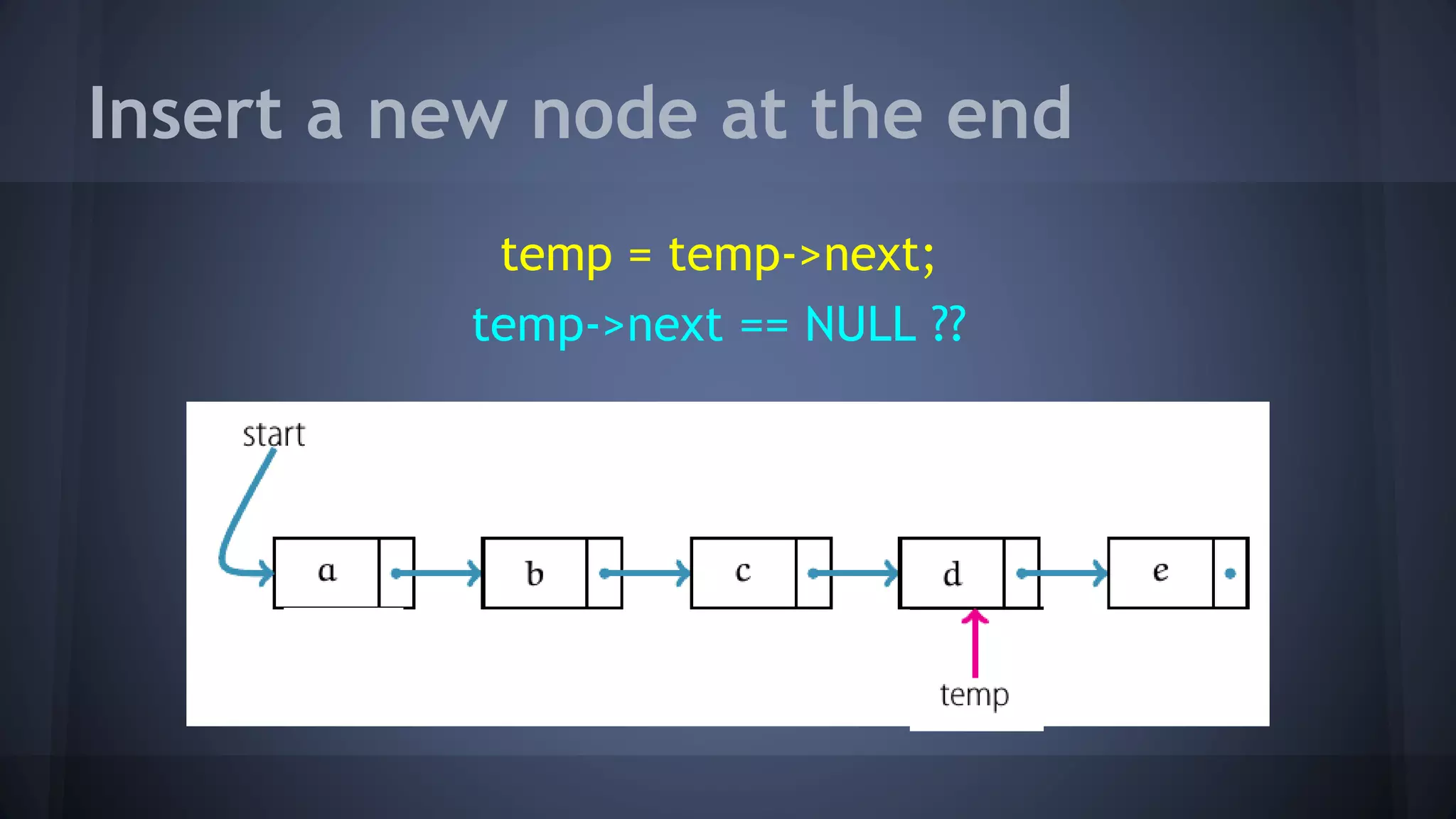
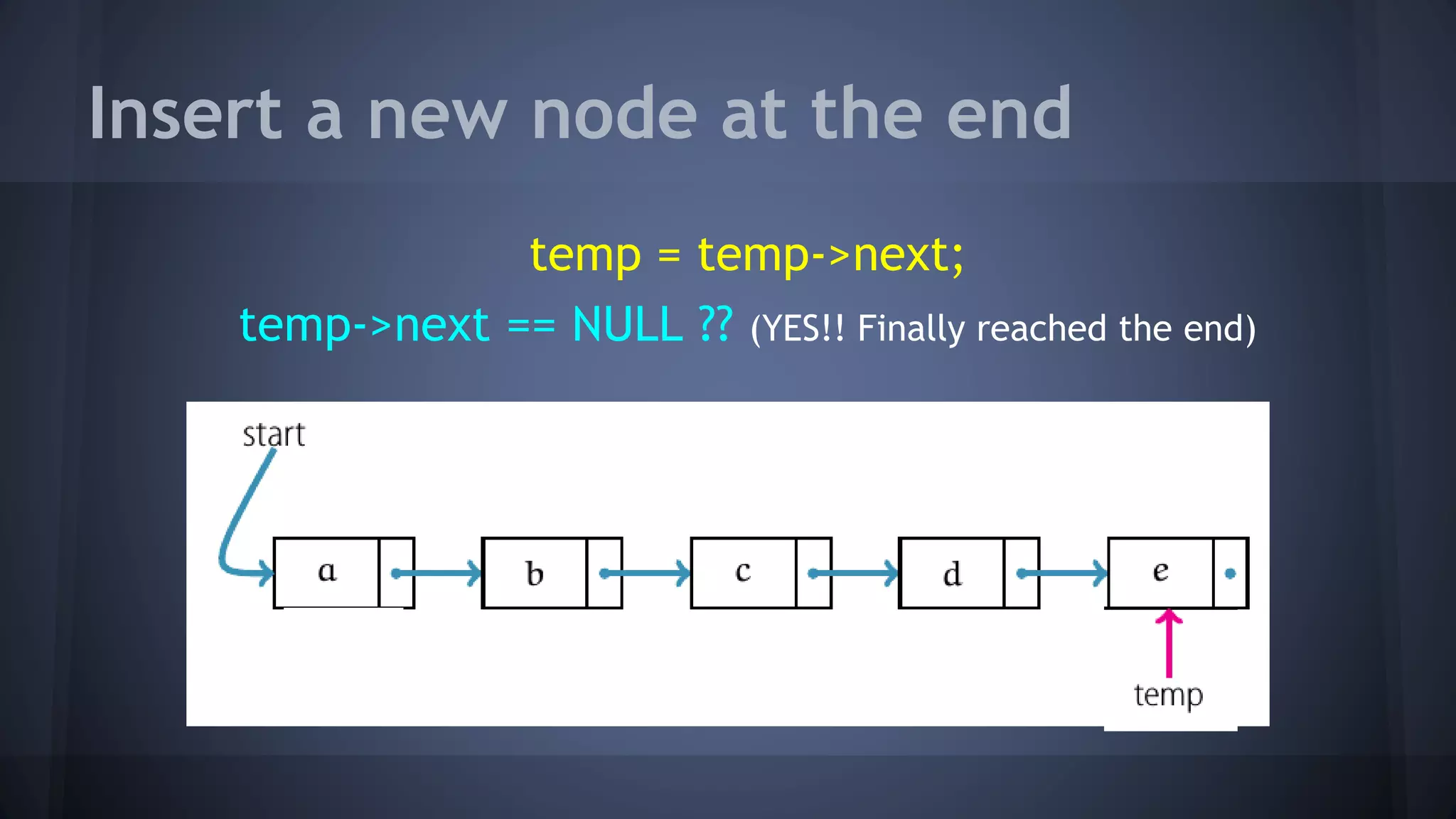
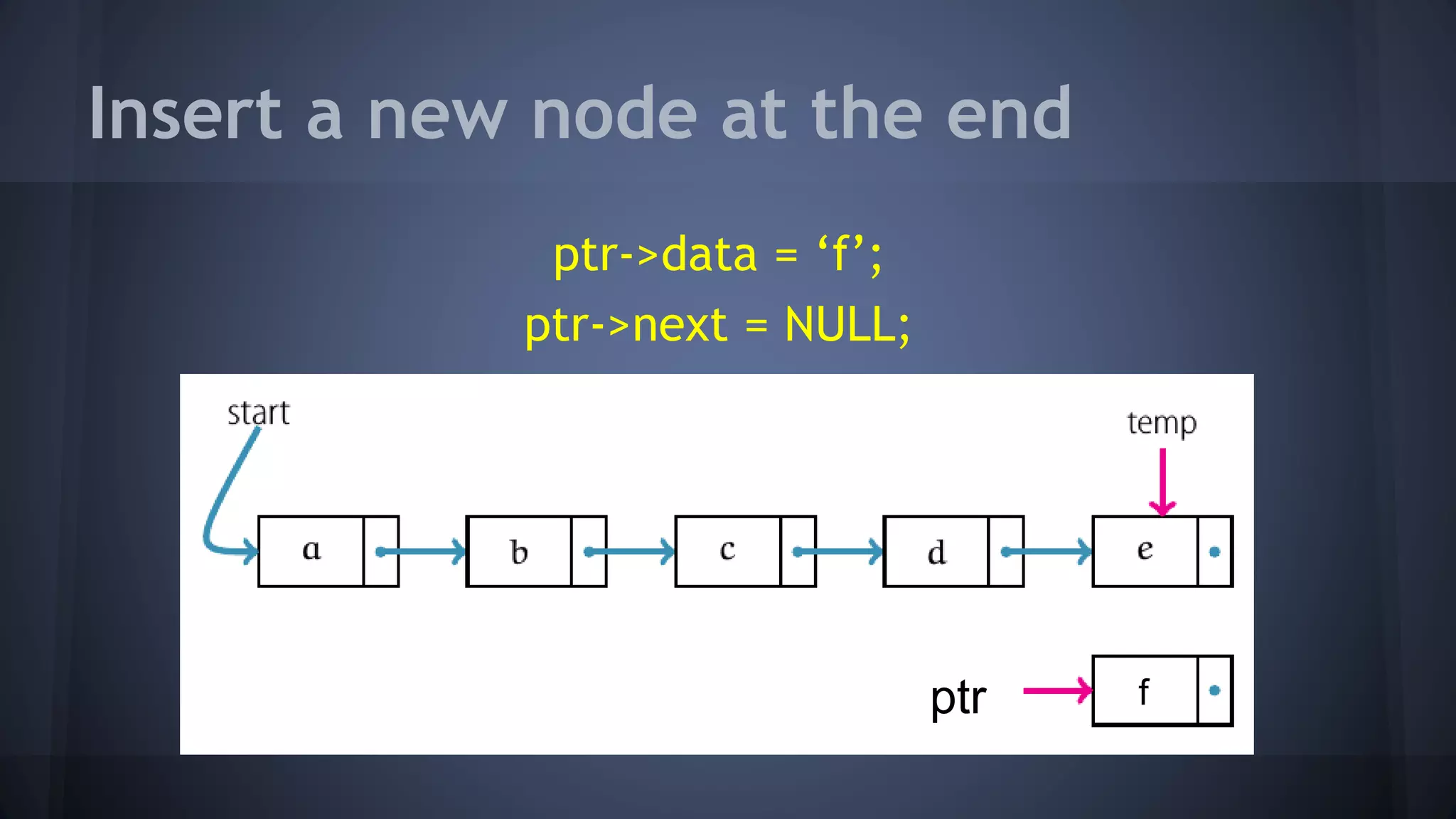
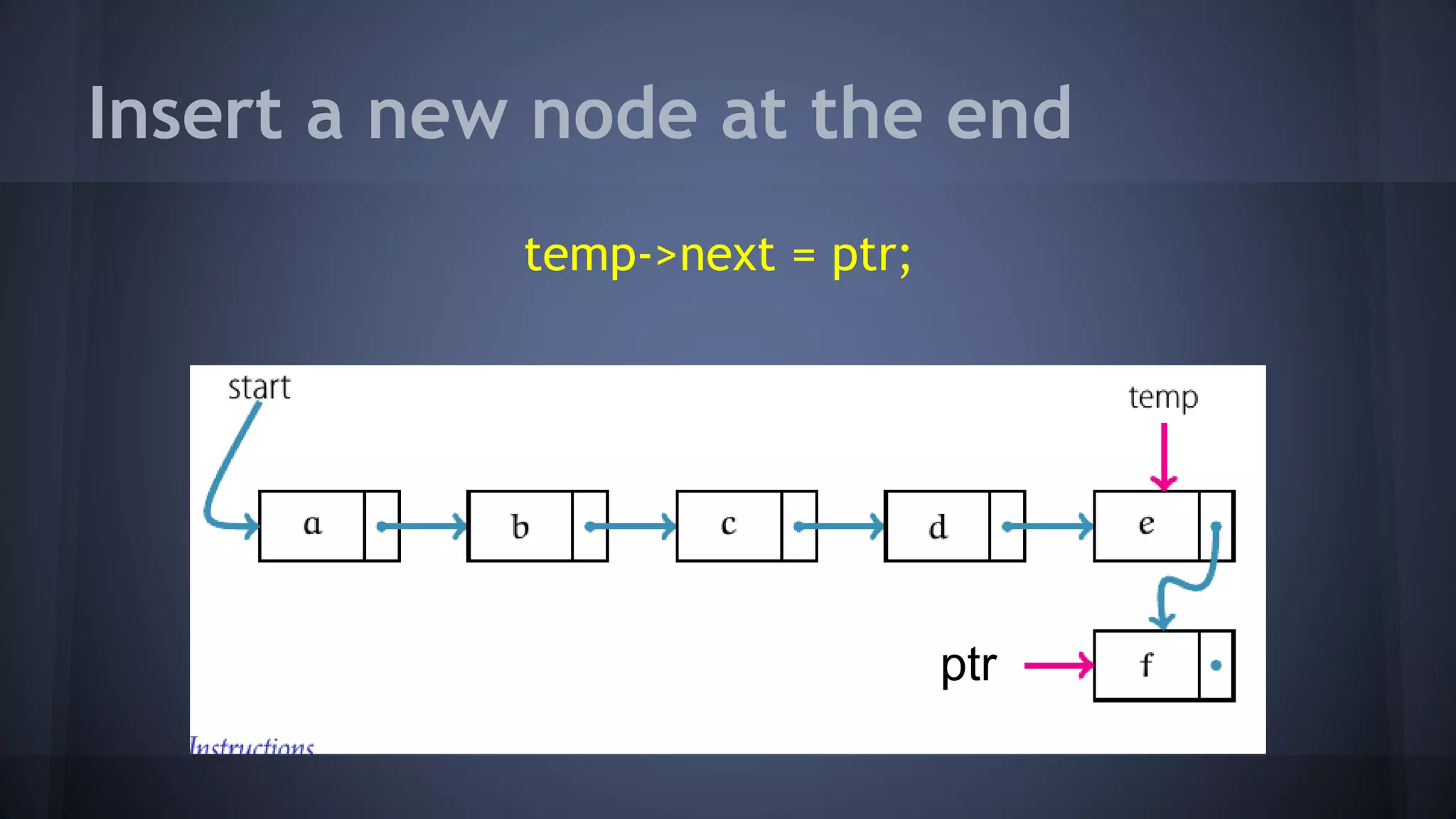
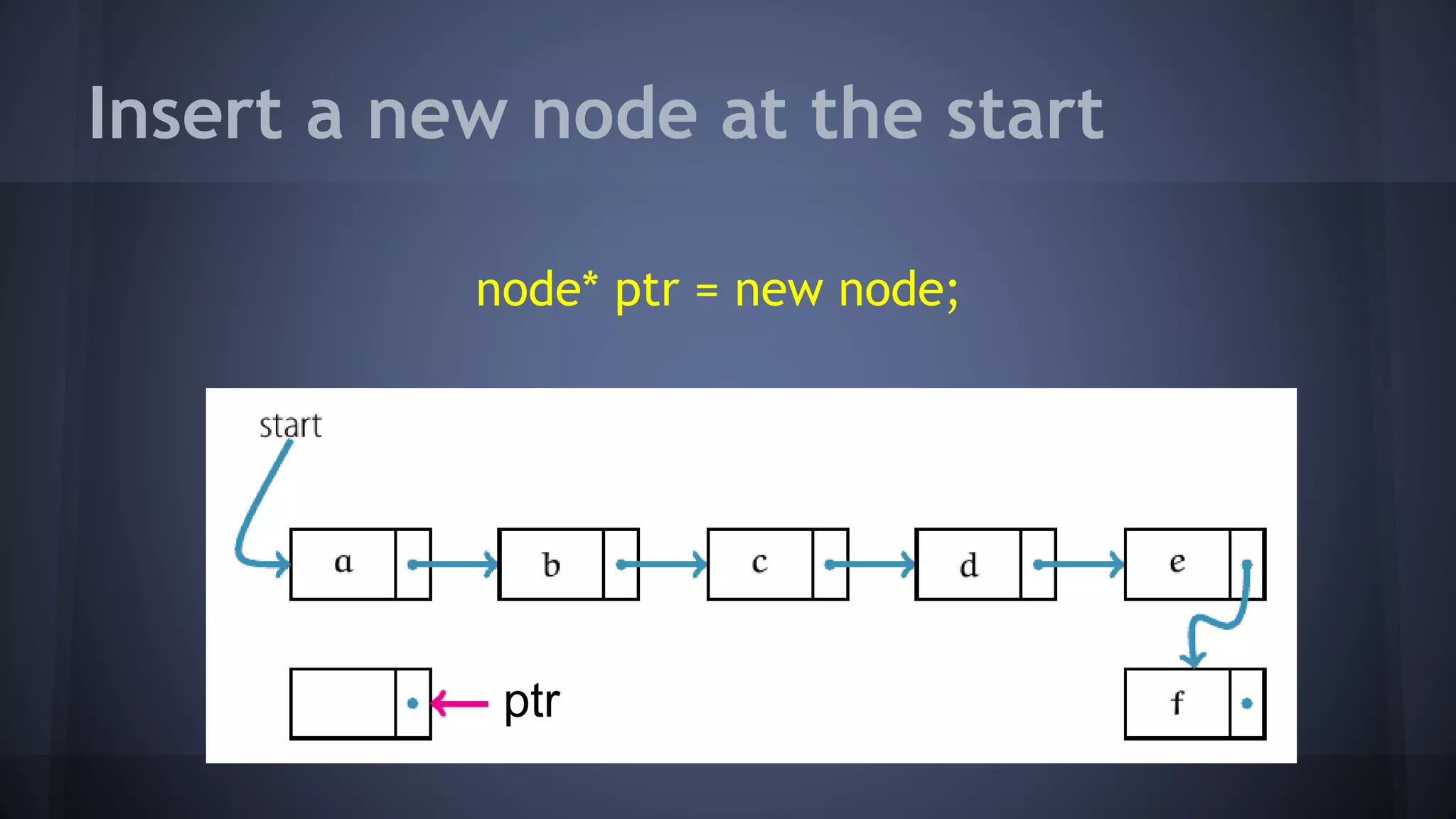
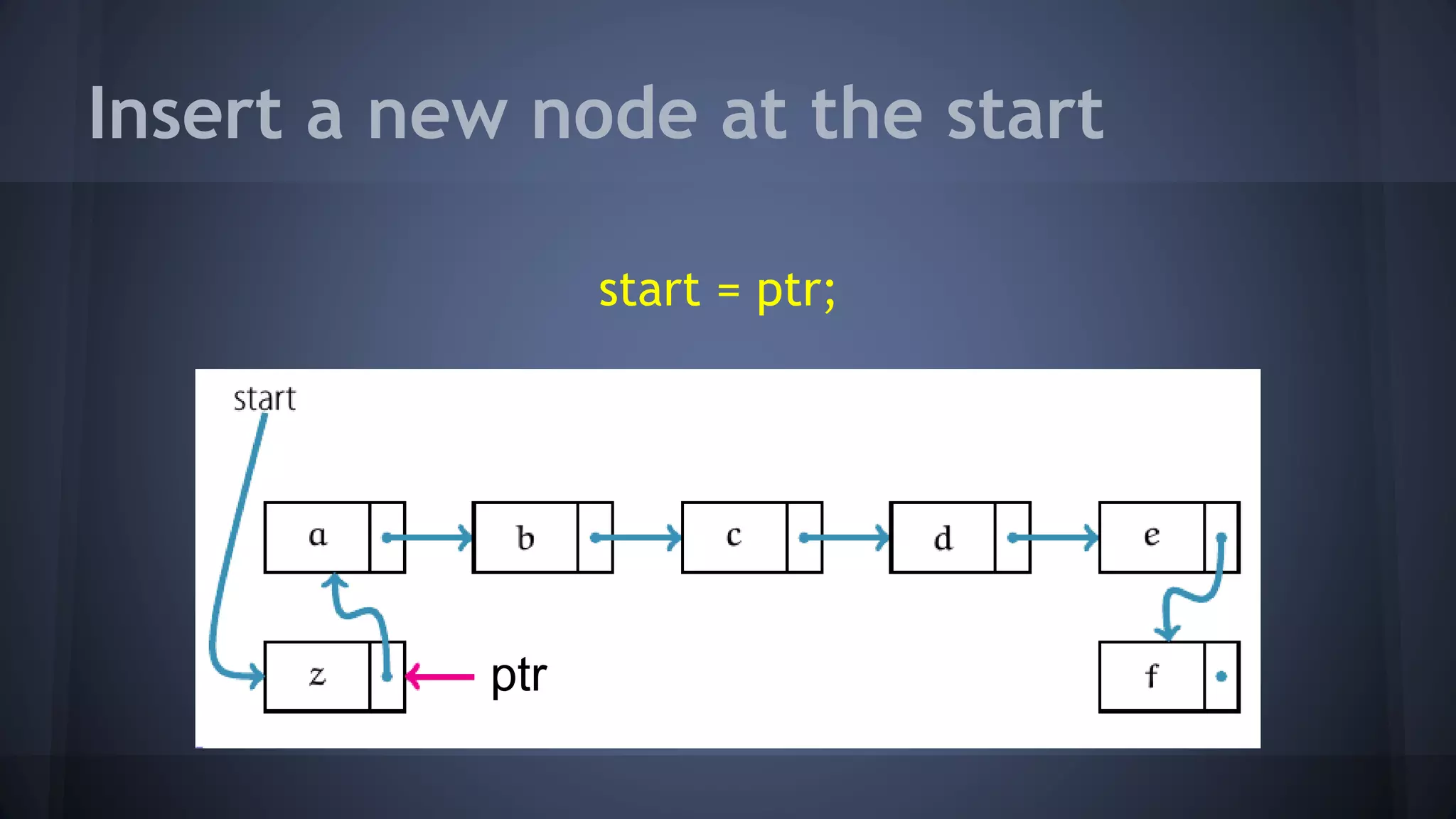
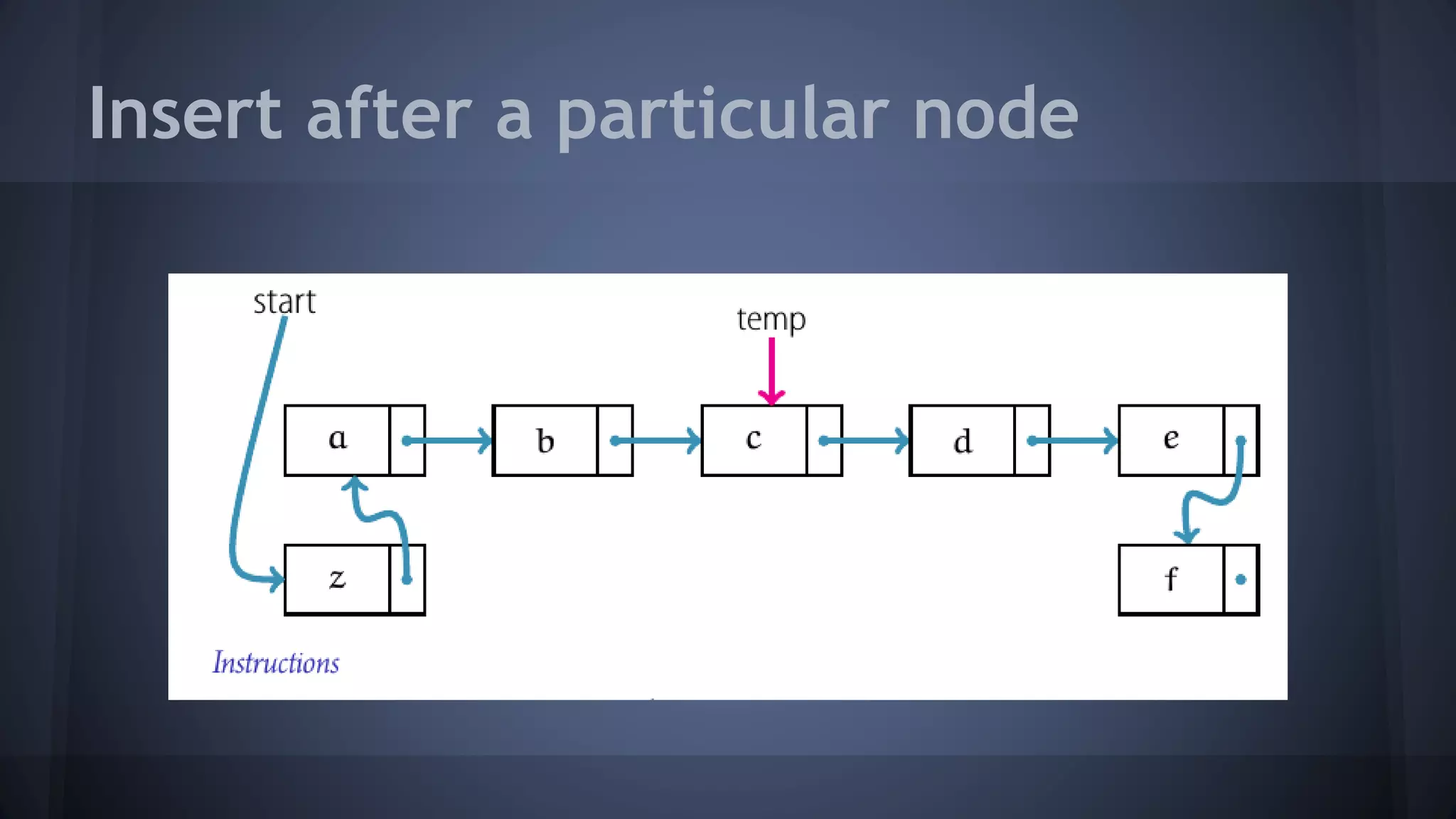
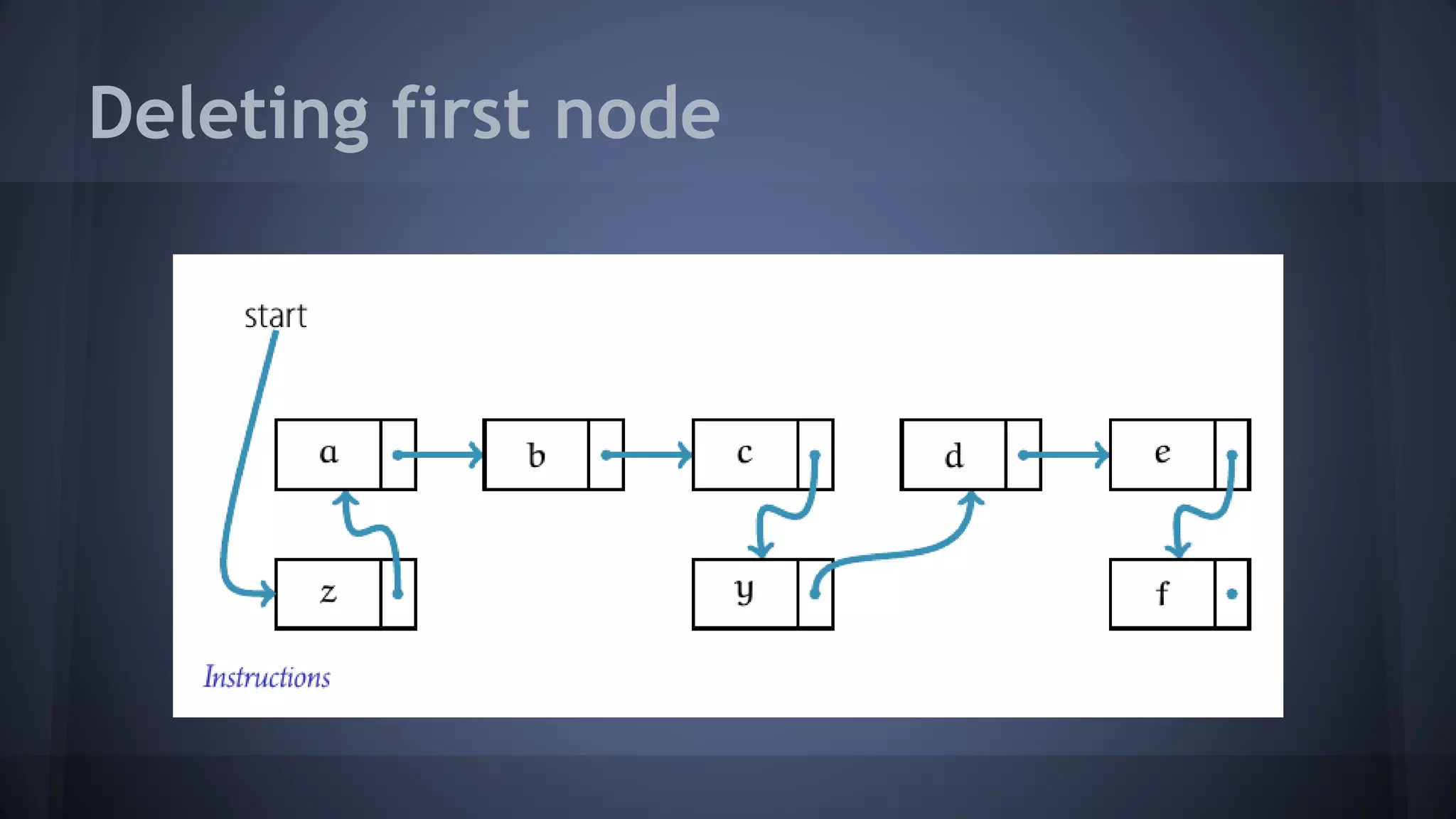
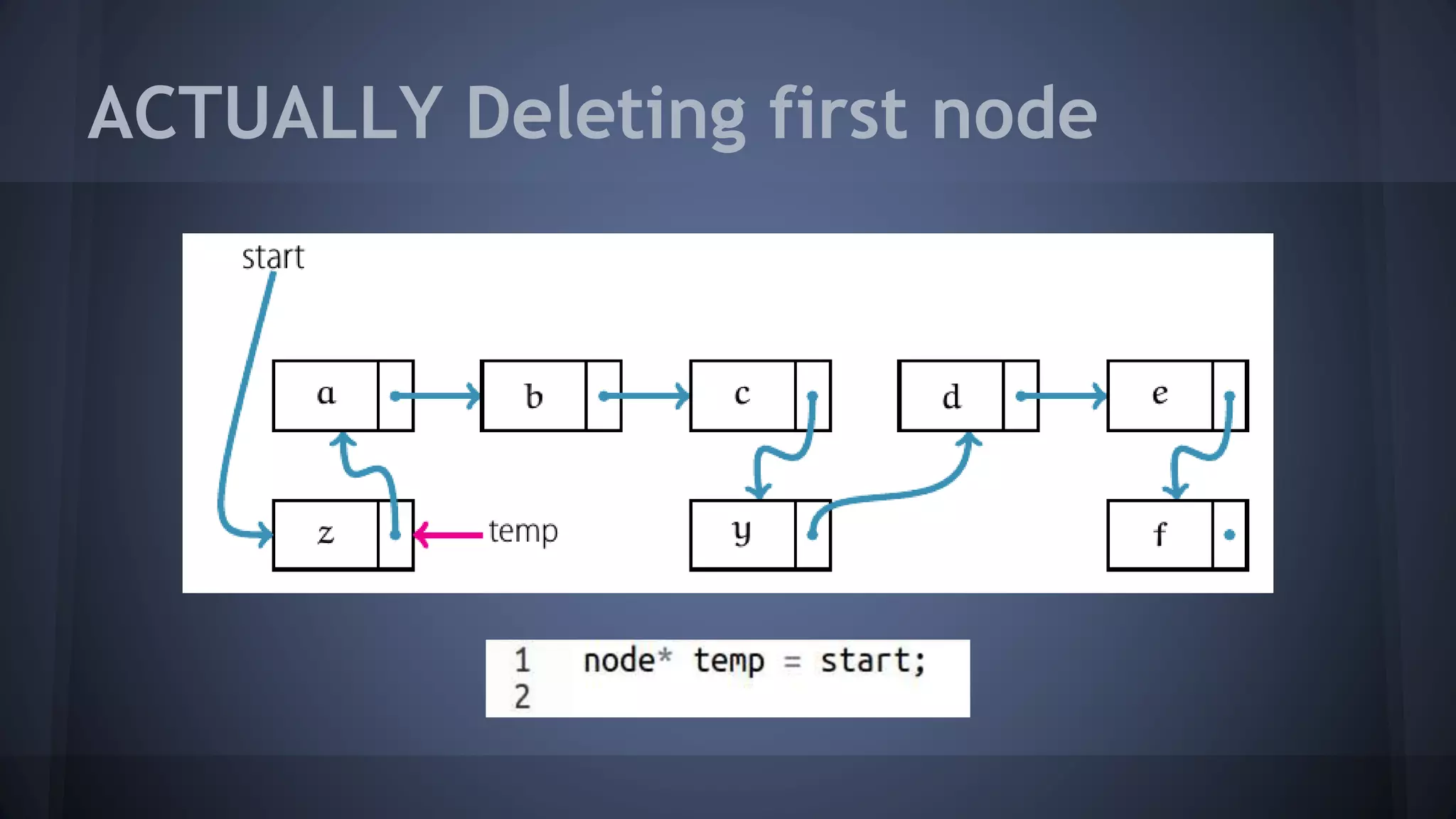
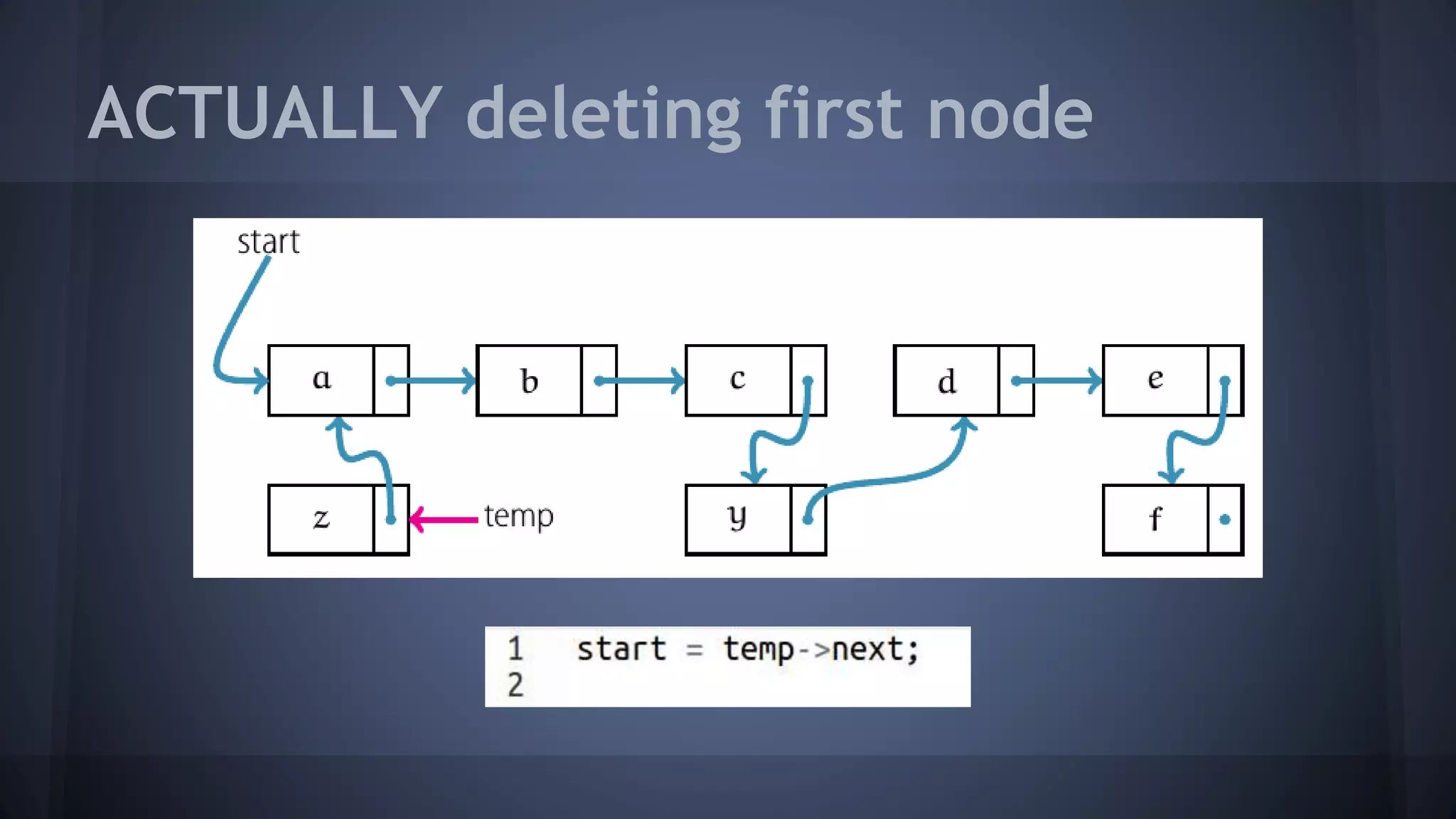
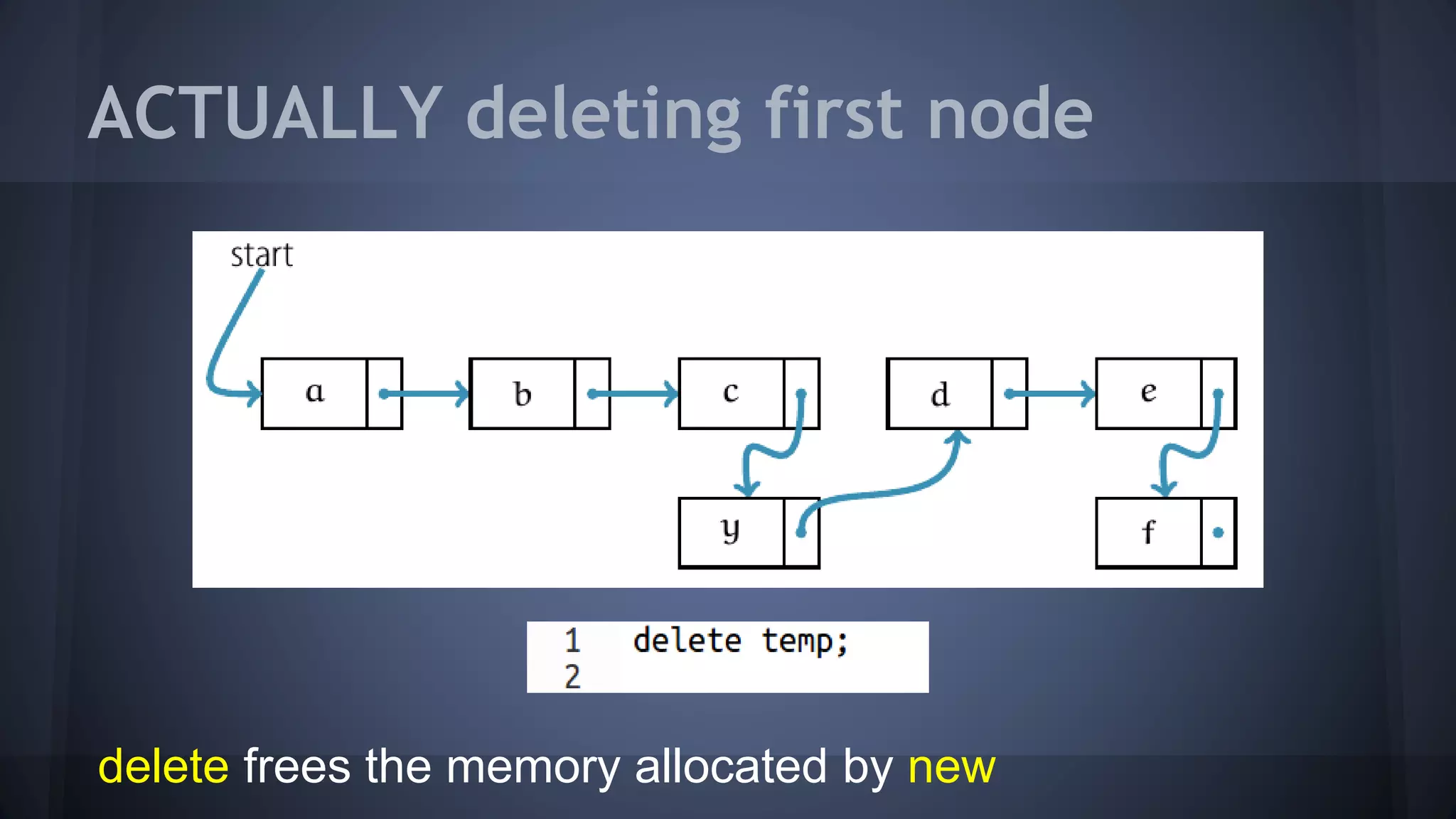
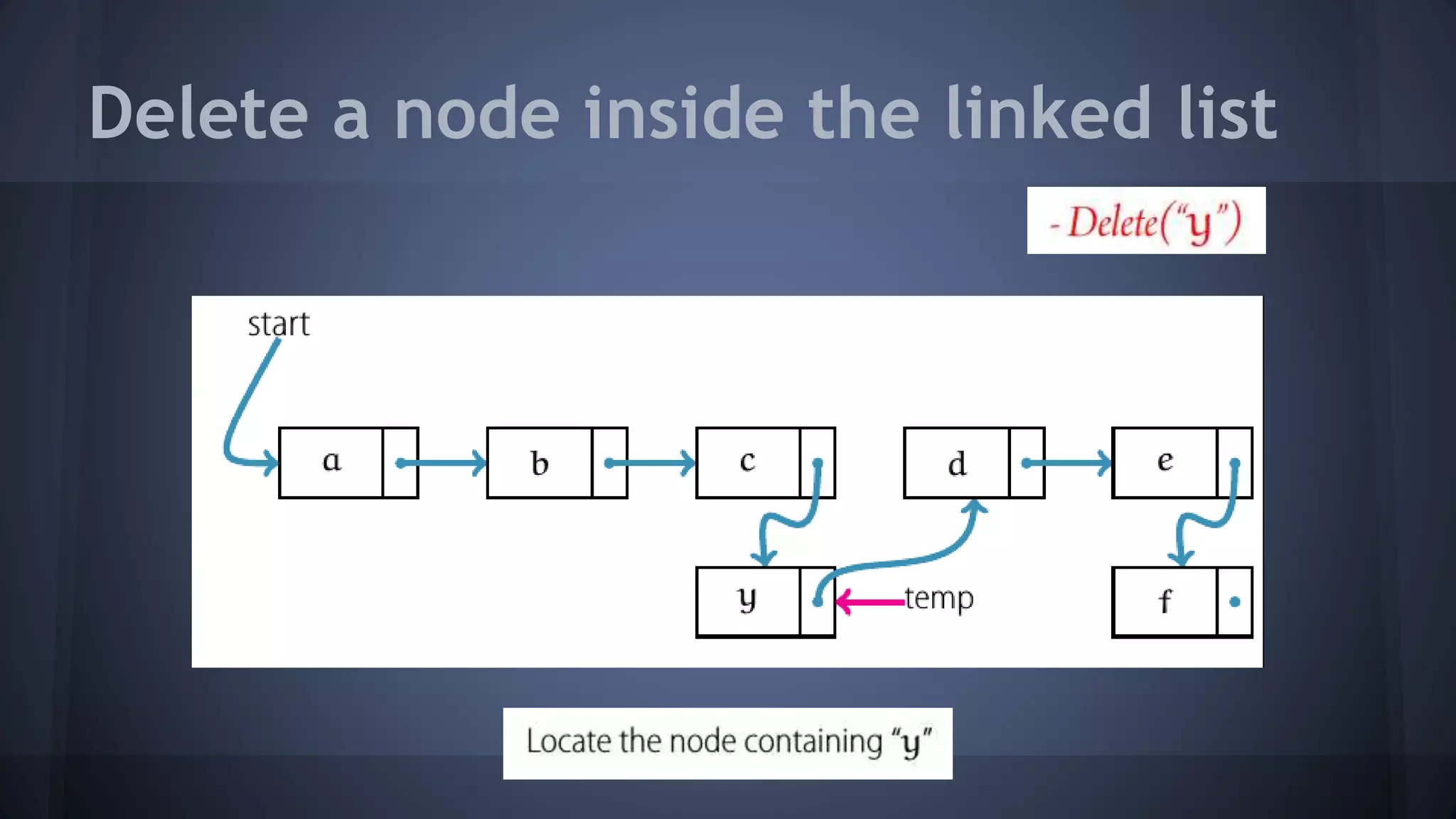
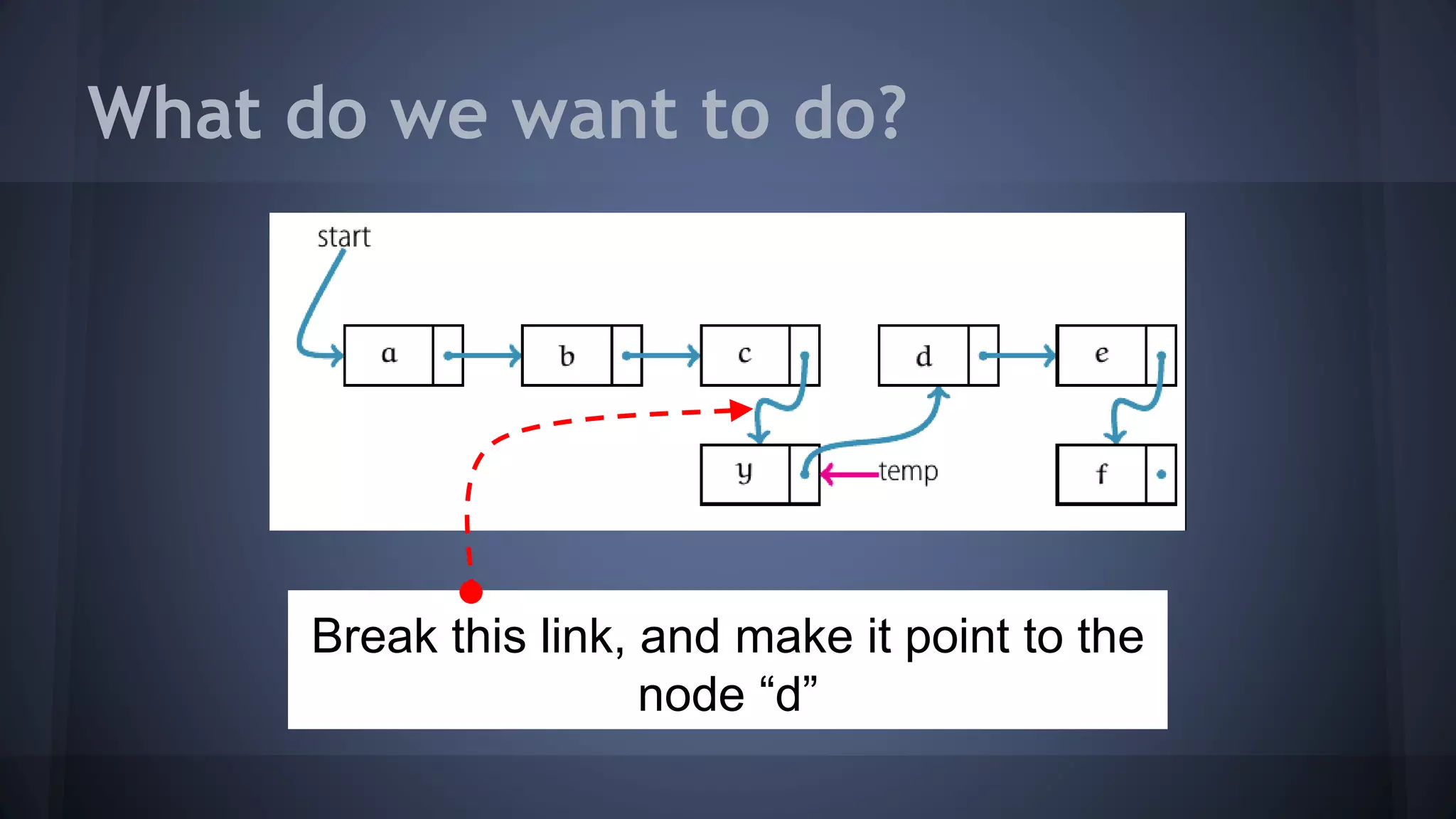
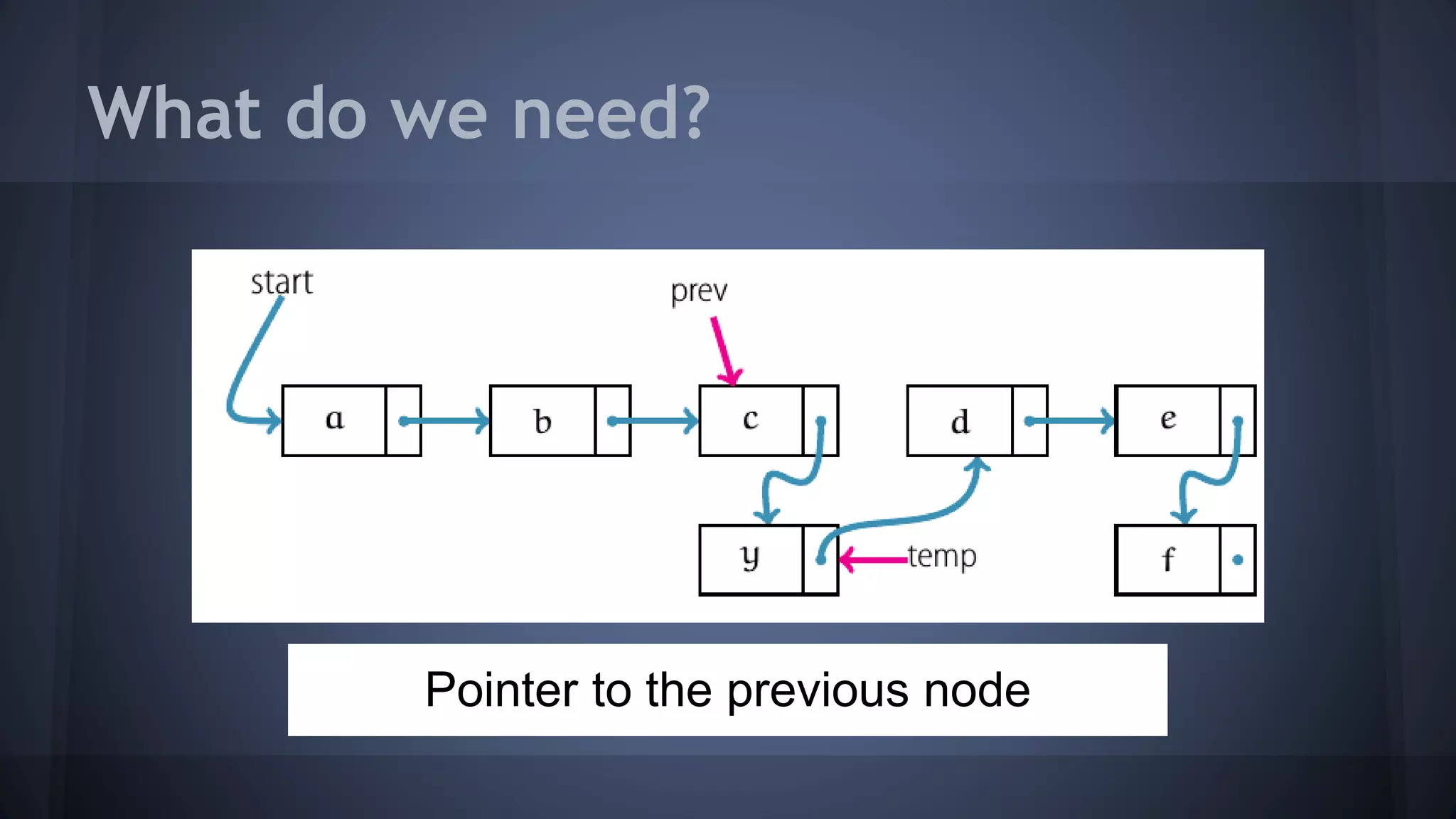
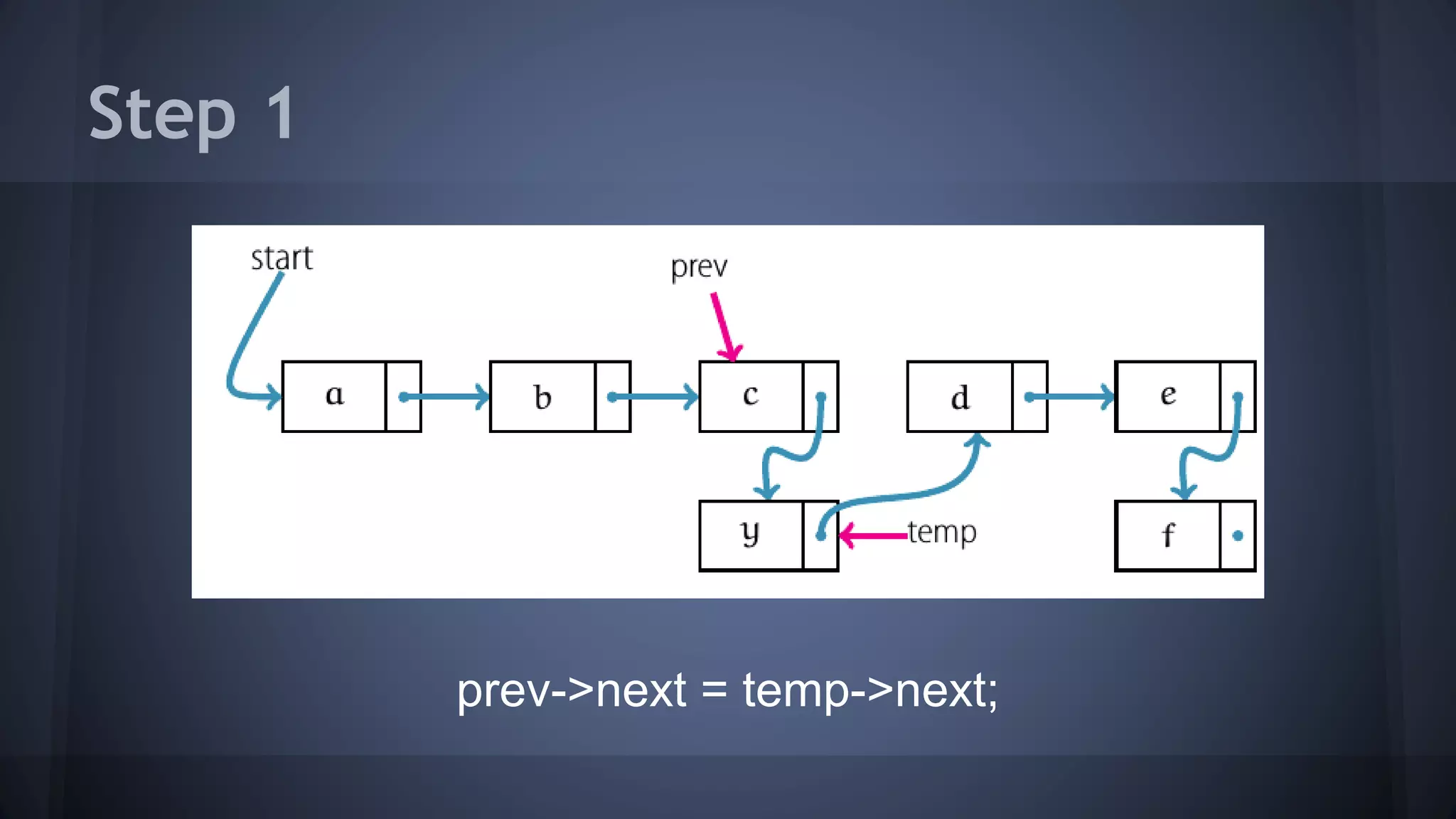
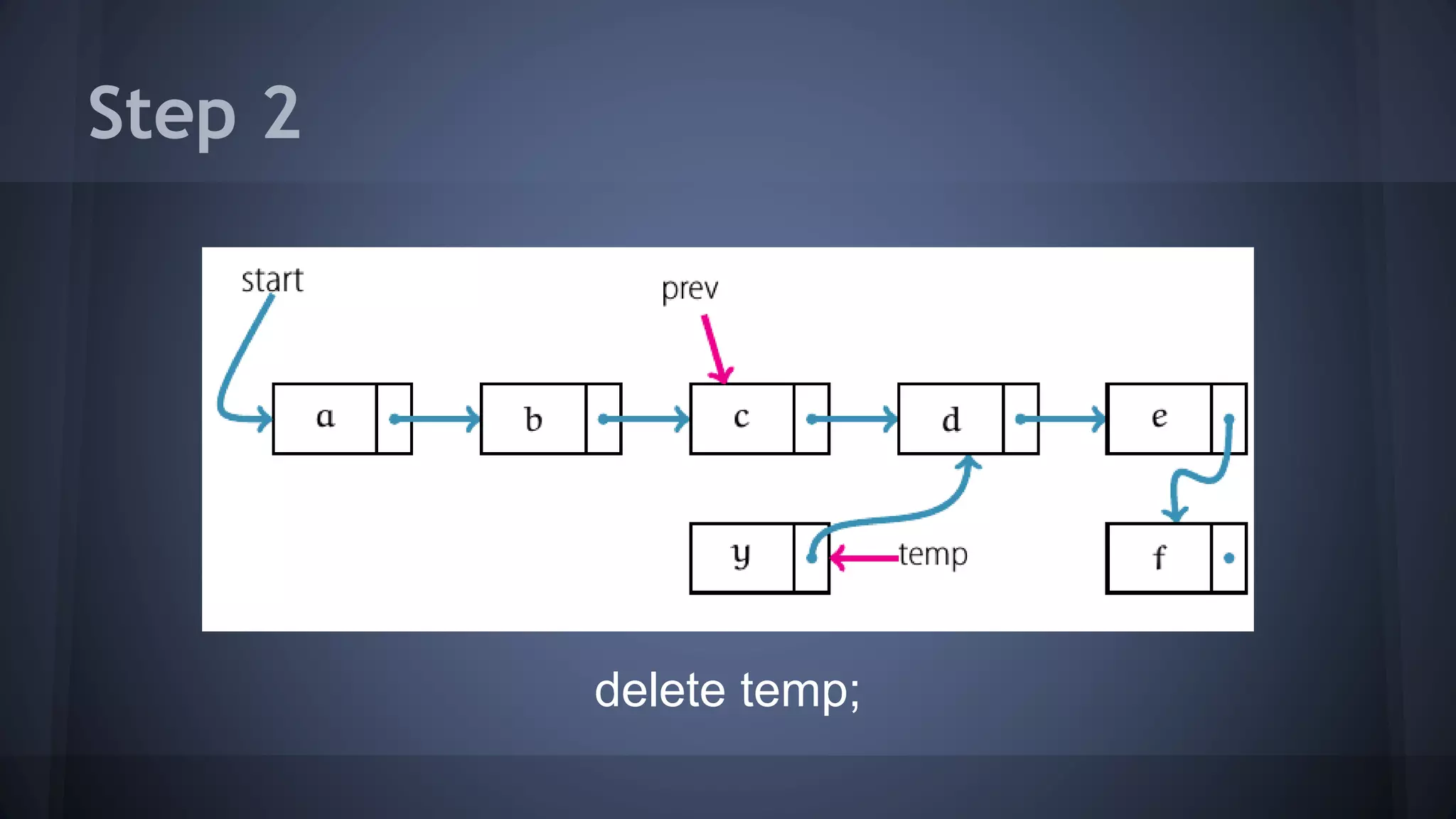
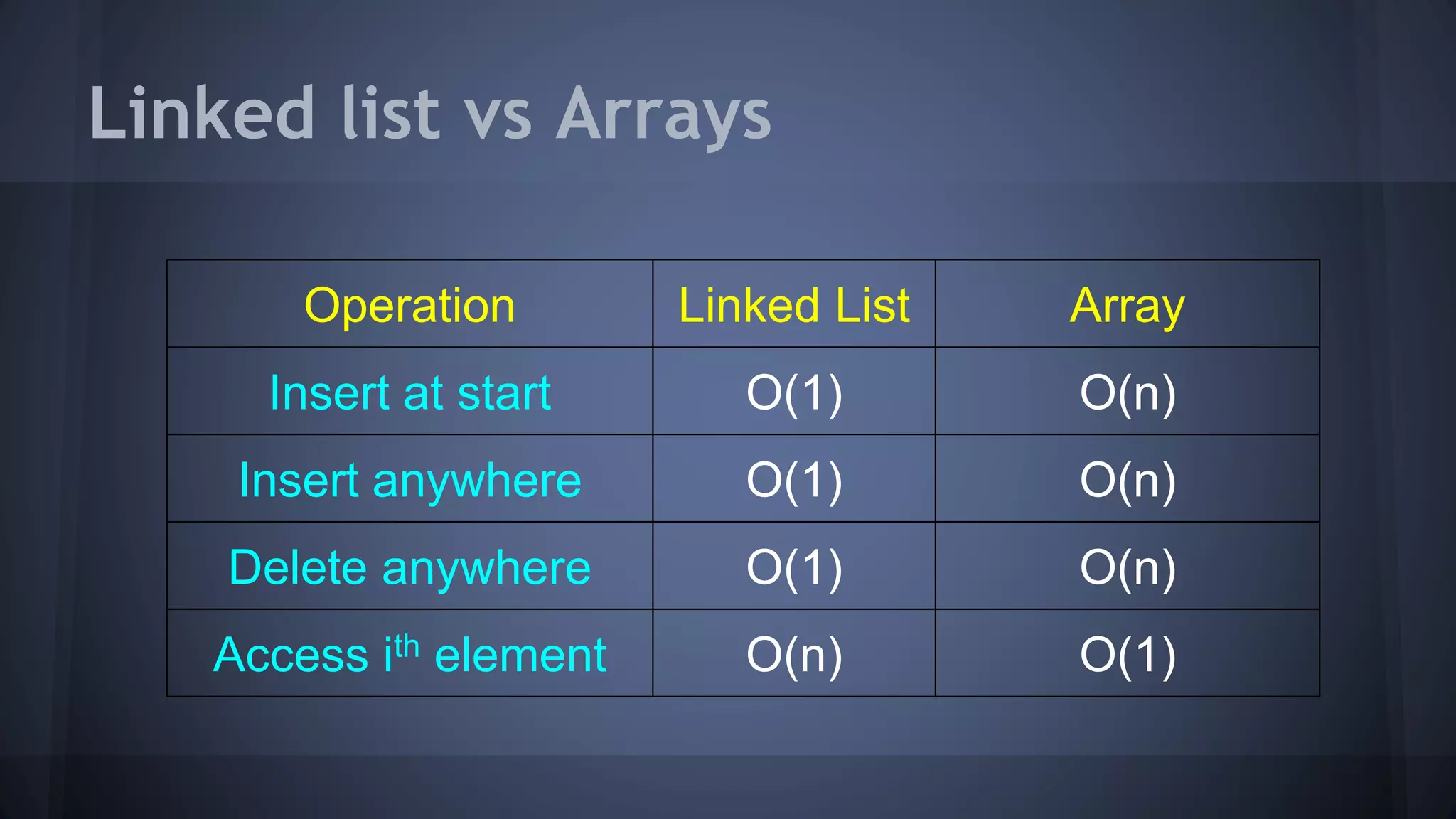
This document provides an overview of linked lists in C++. It discusses how to represent a linked list node using a struct with a data field and pointer to the next node. It demonstrates how to traverse a linked list by accessing the data and next fields of each node. Several examples are provided for linked list operations like inserting and deleting nodes at different positions within the list.