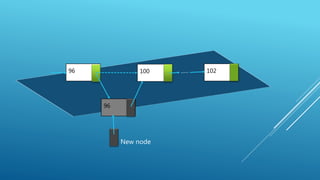
- Linked lists are linear data structures made up of nodes that contain data and a pointer to the next node. This allows them to be linked together to form a list.
- There are two types of linked lists: singly linked lists where each node has a pointer to the next node, and doubly linked lists where each node has pointers to both the next and previous nodes.
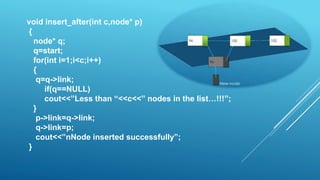
- Basic operations on linked lists include creating and inserting nodes, deleting nodes, searching the list, and reversing the list. Nodes are created dynamically and inserted at the beginning, end, or after a specified node using pointer manipulation.