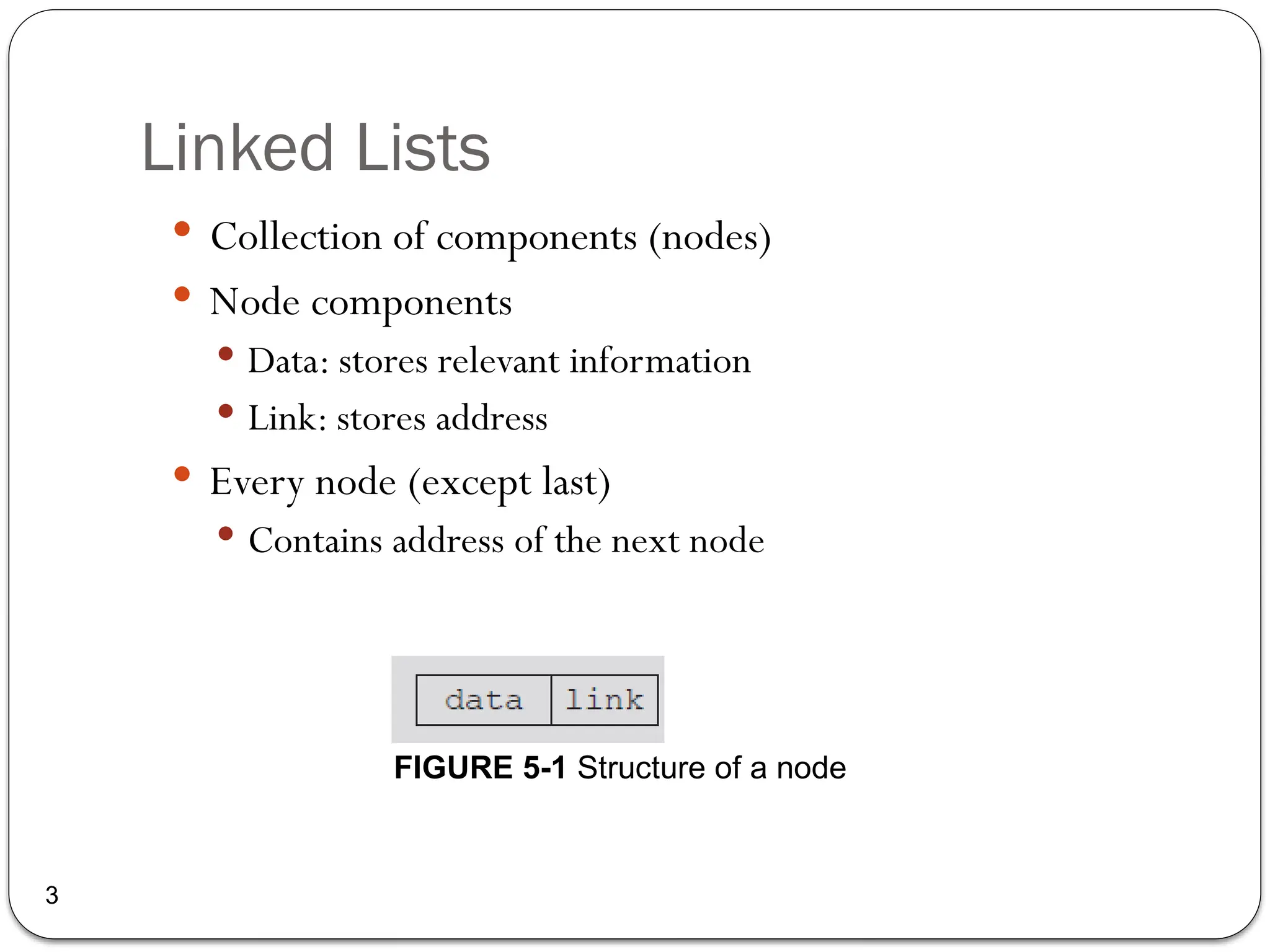
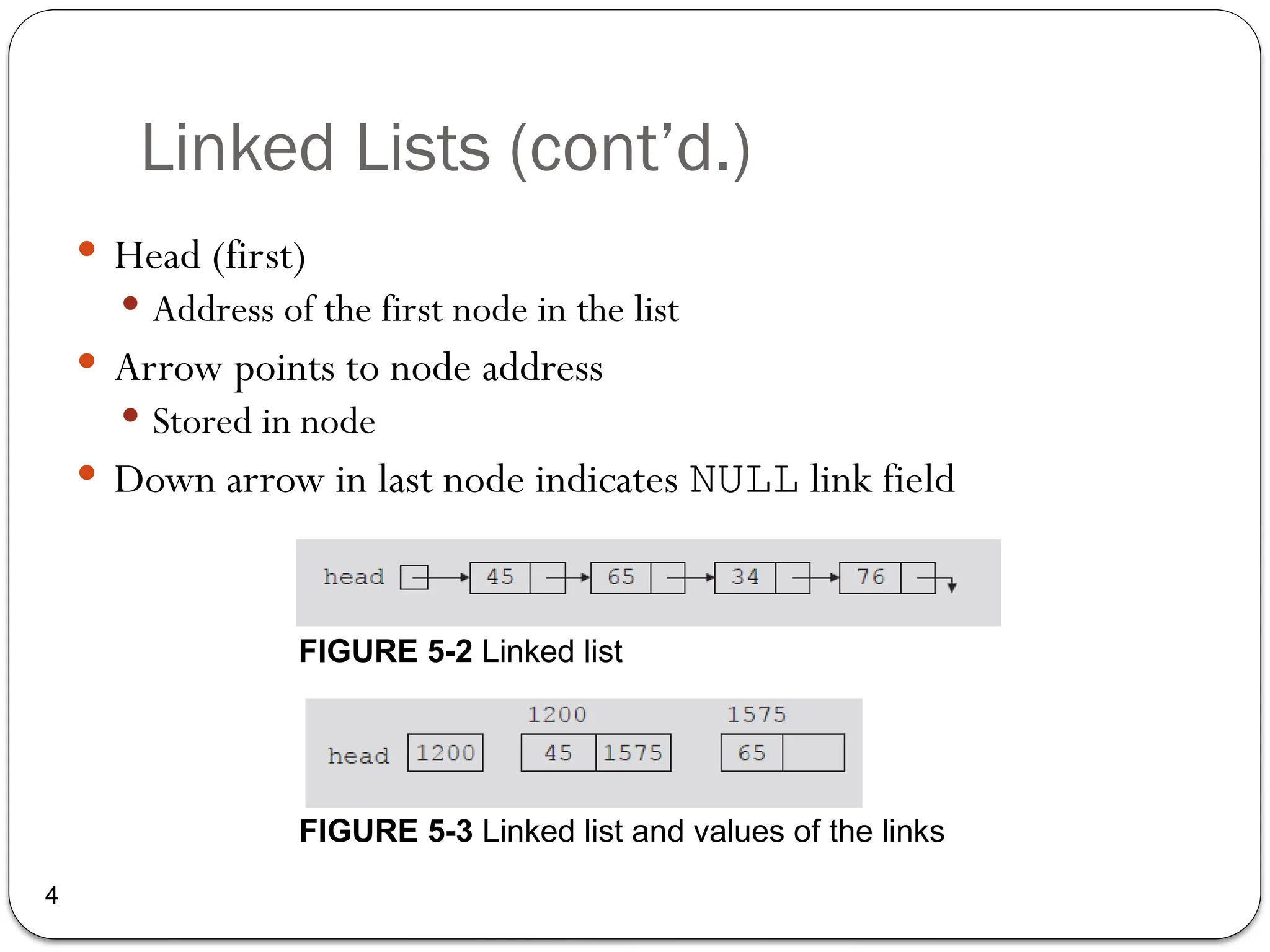
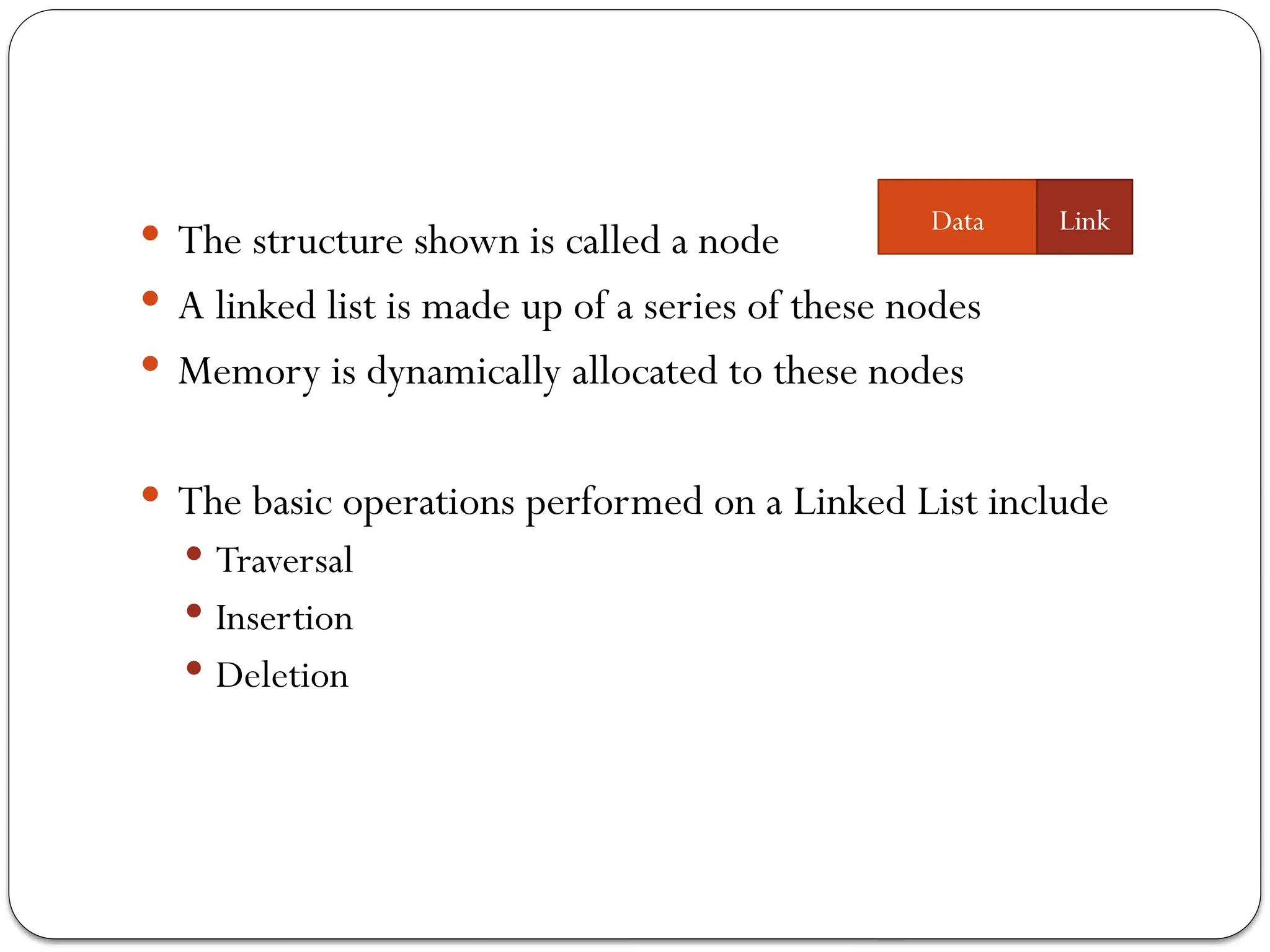
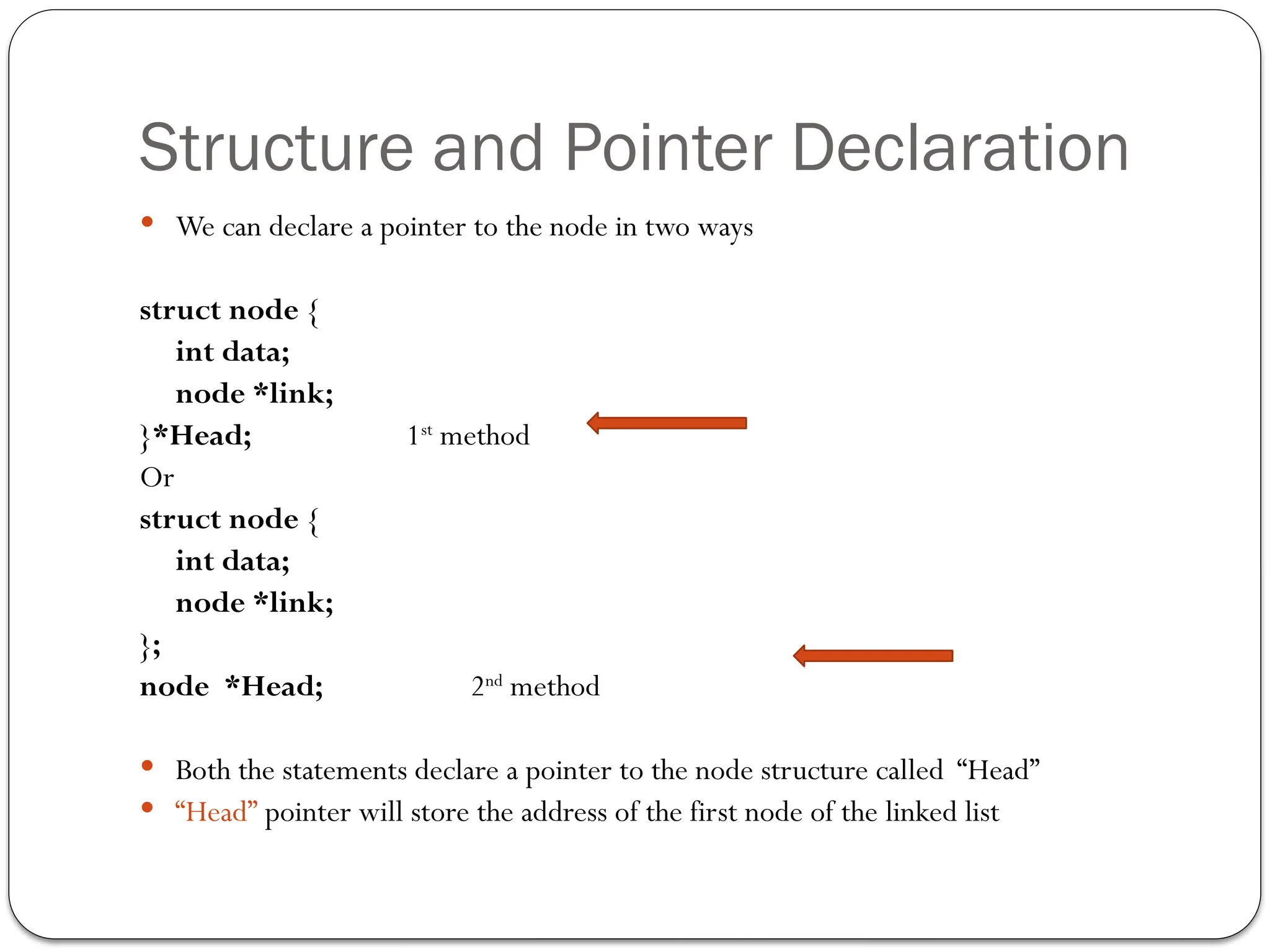
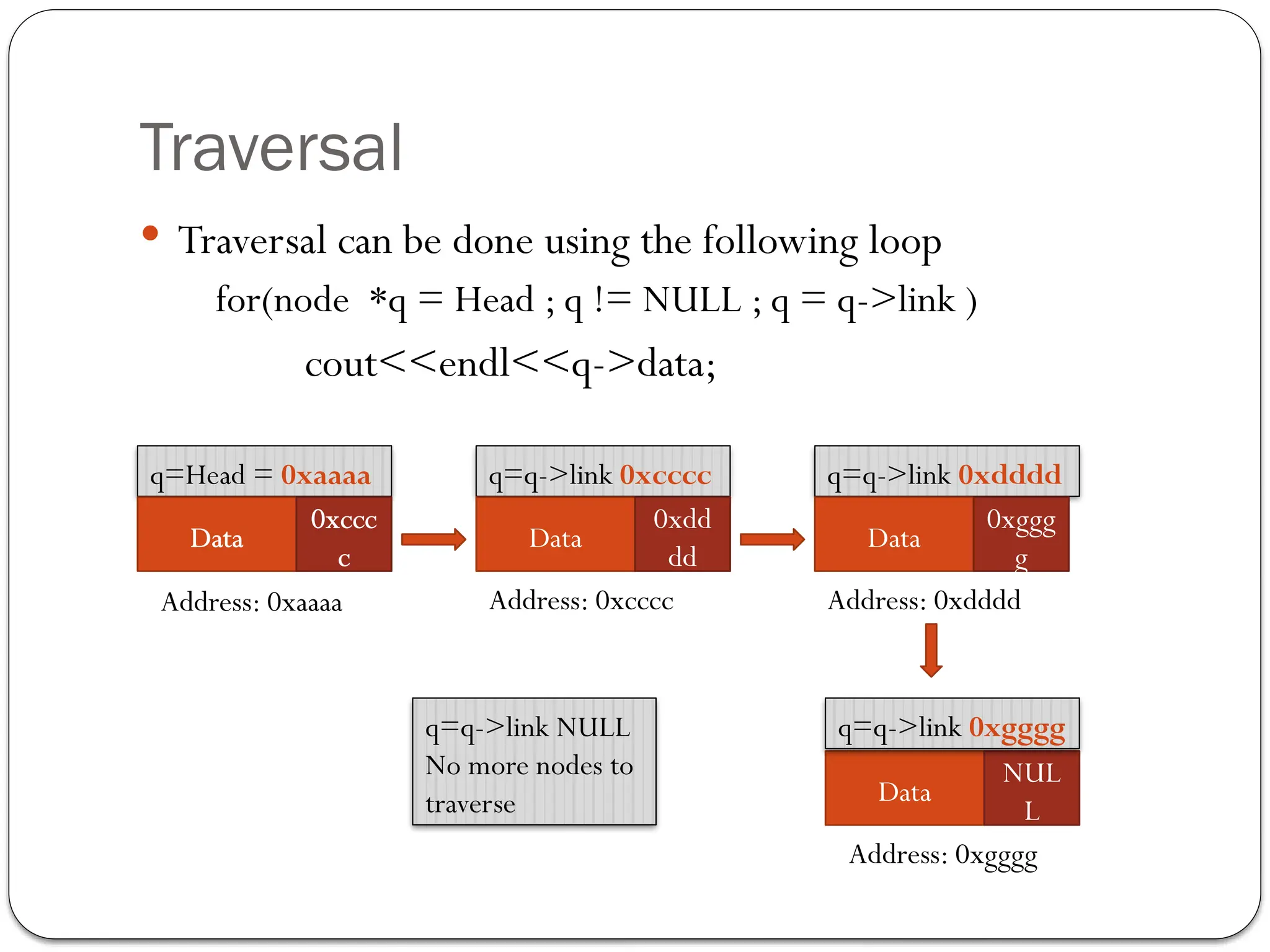
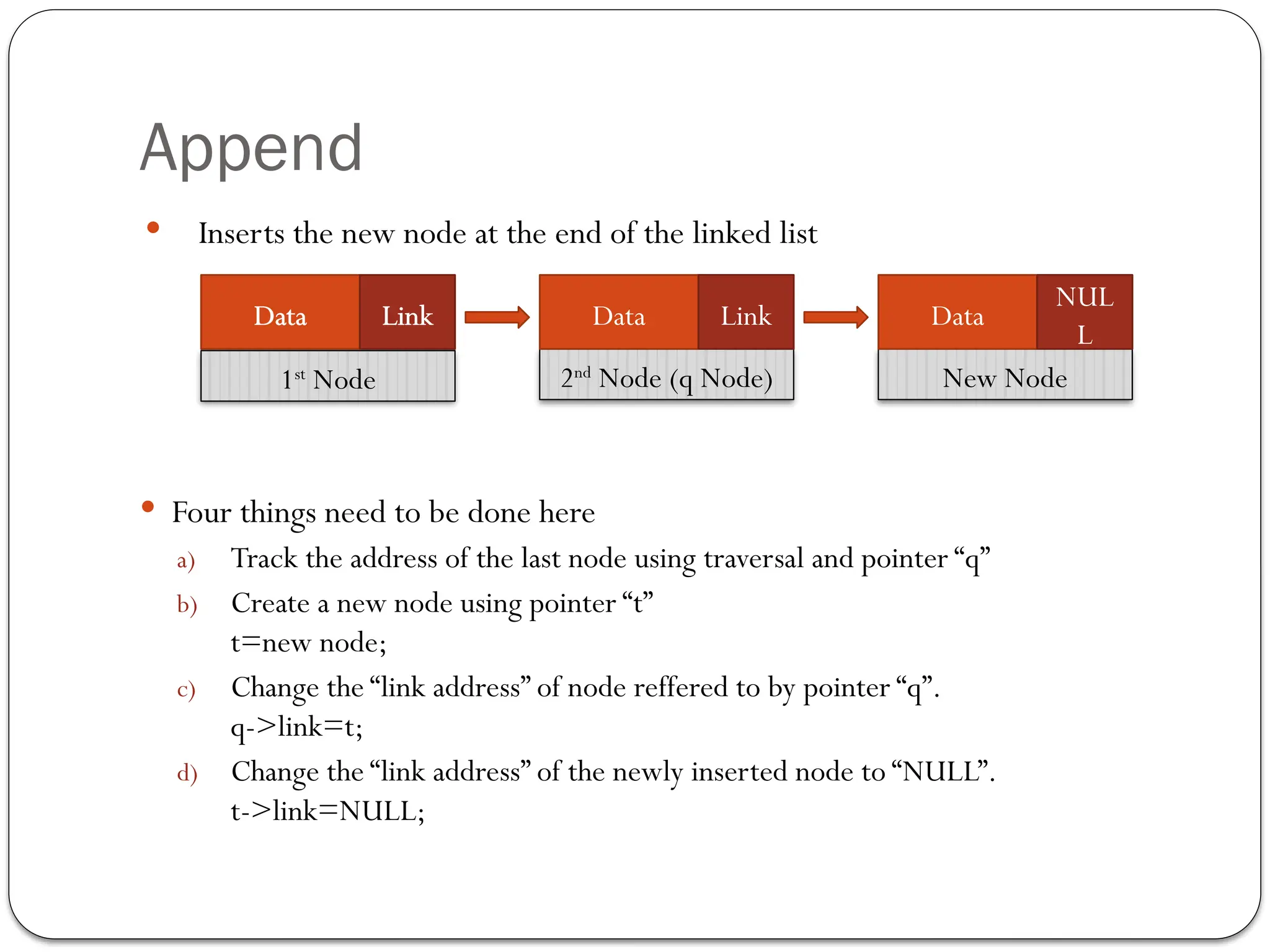
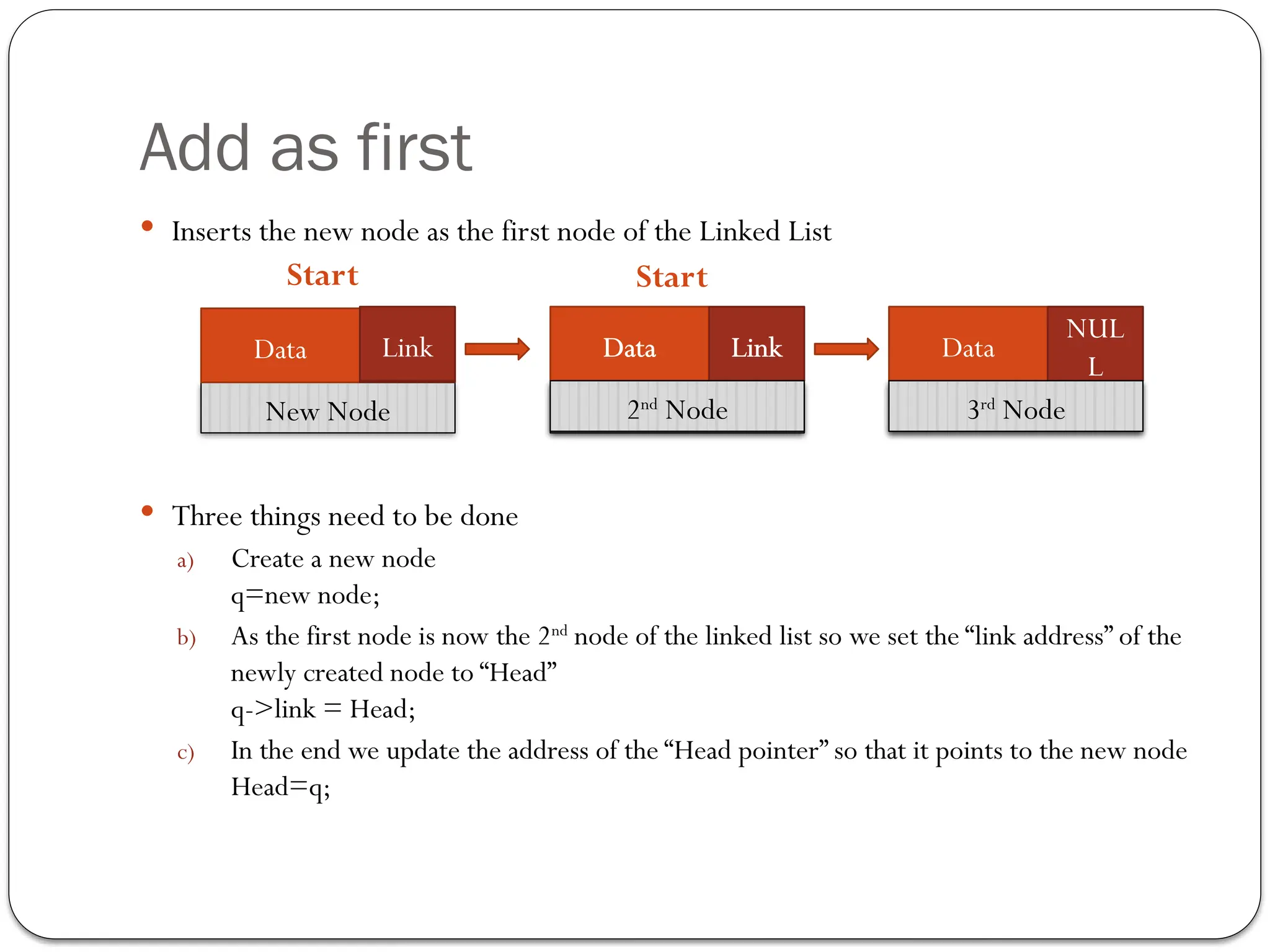
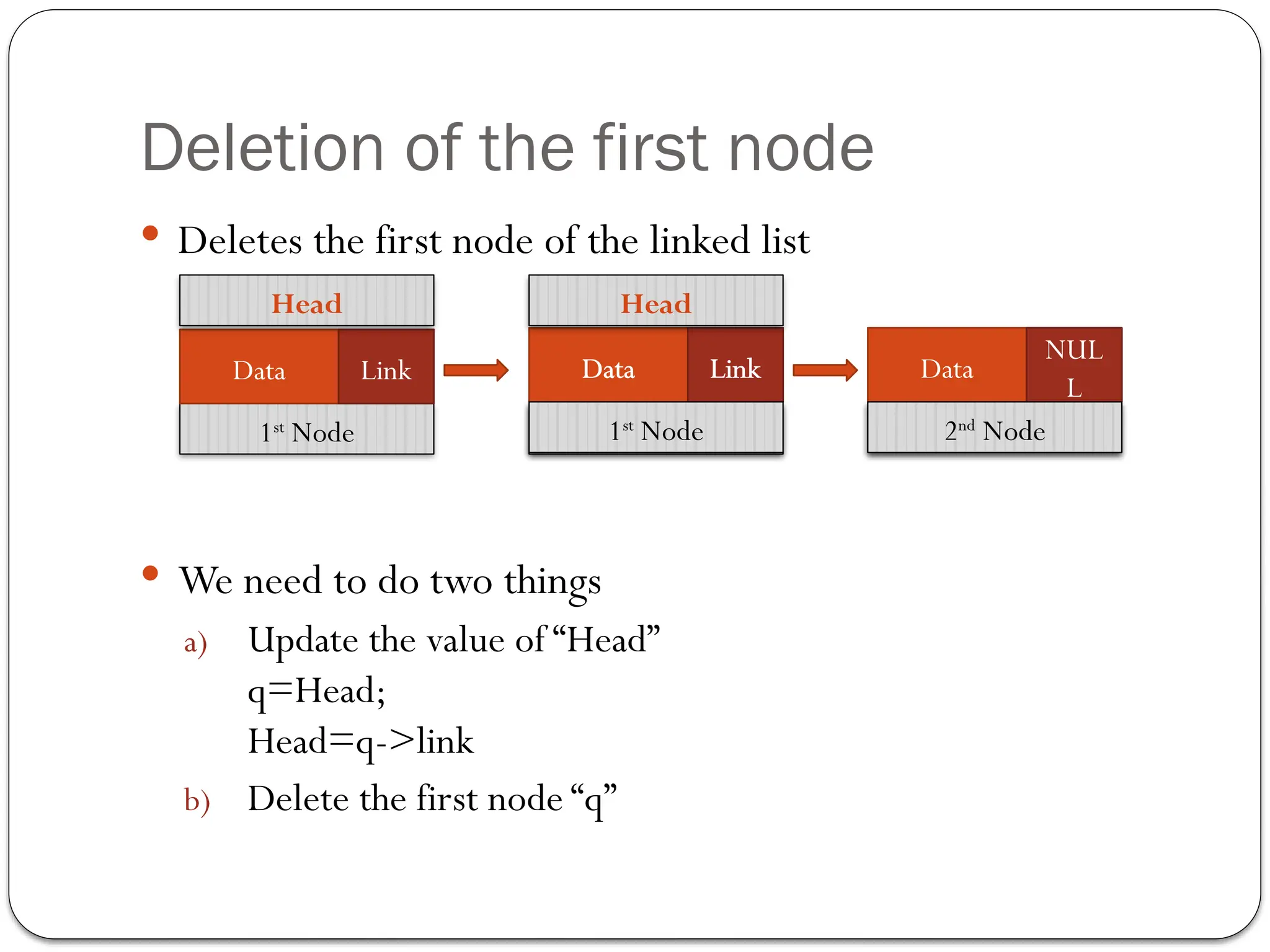
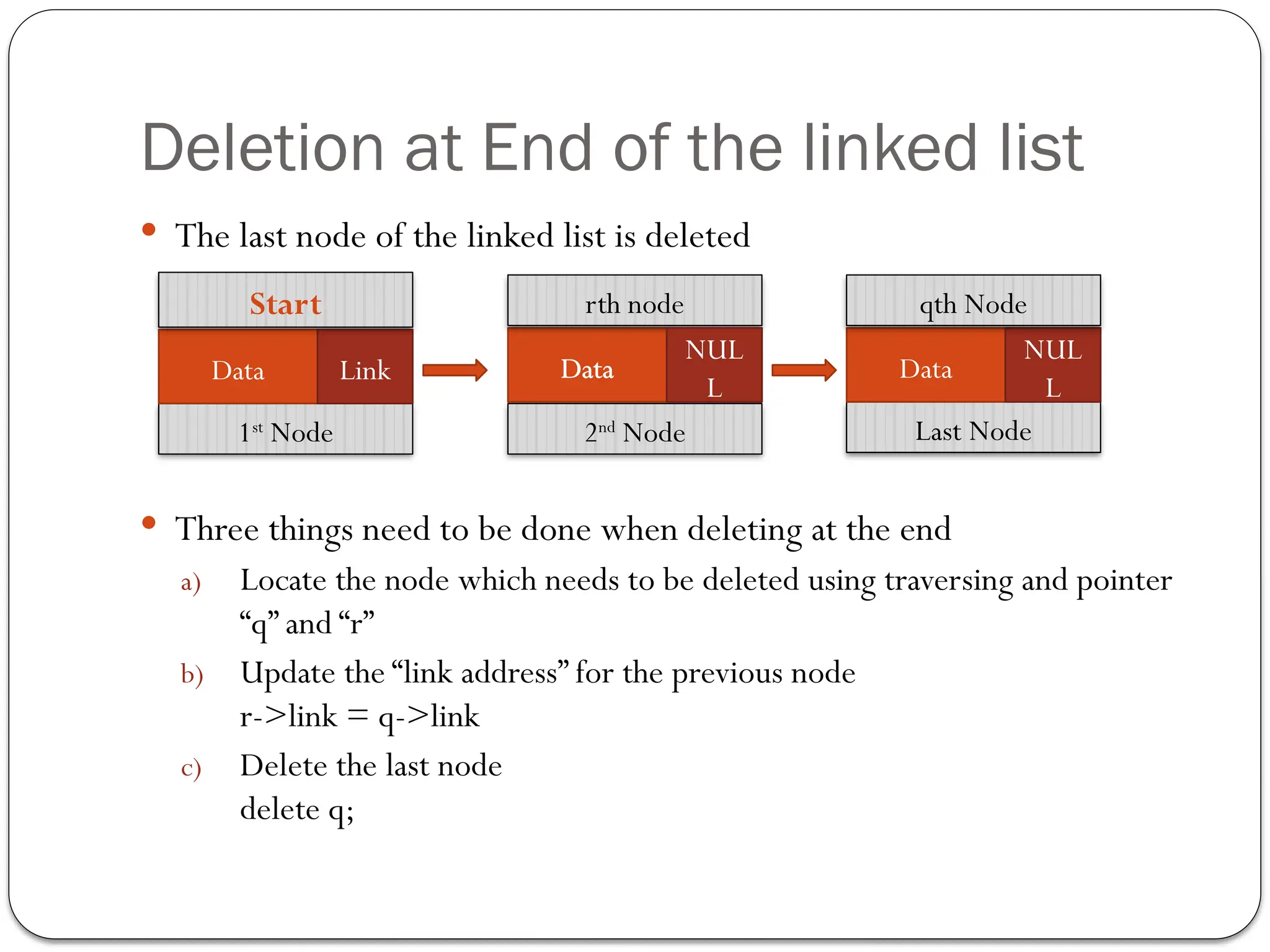
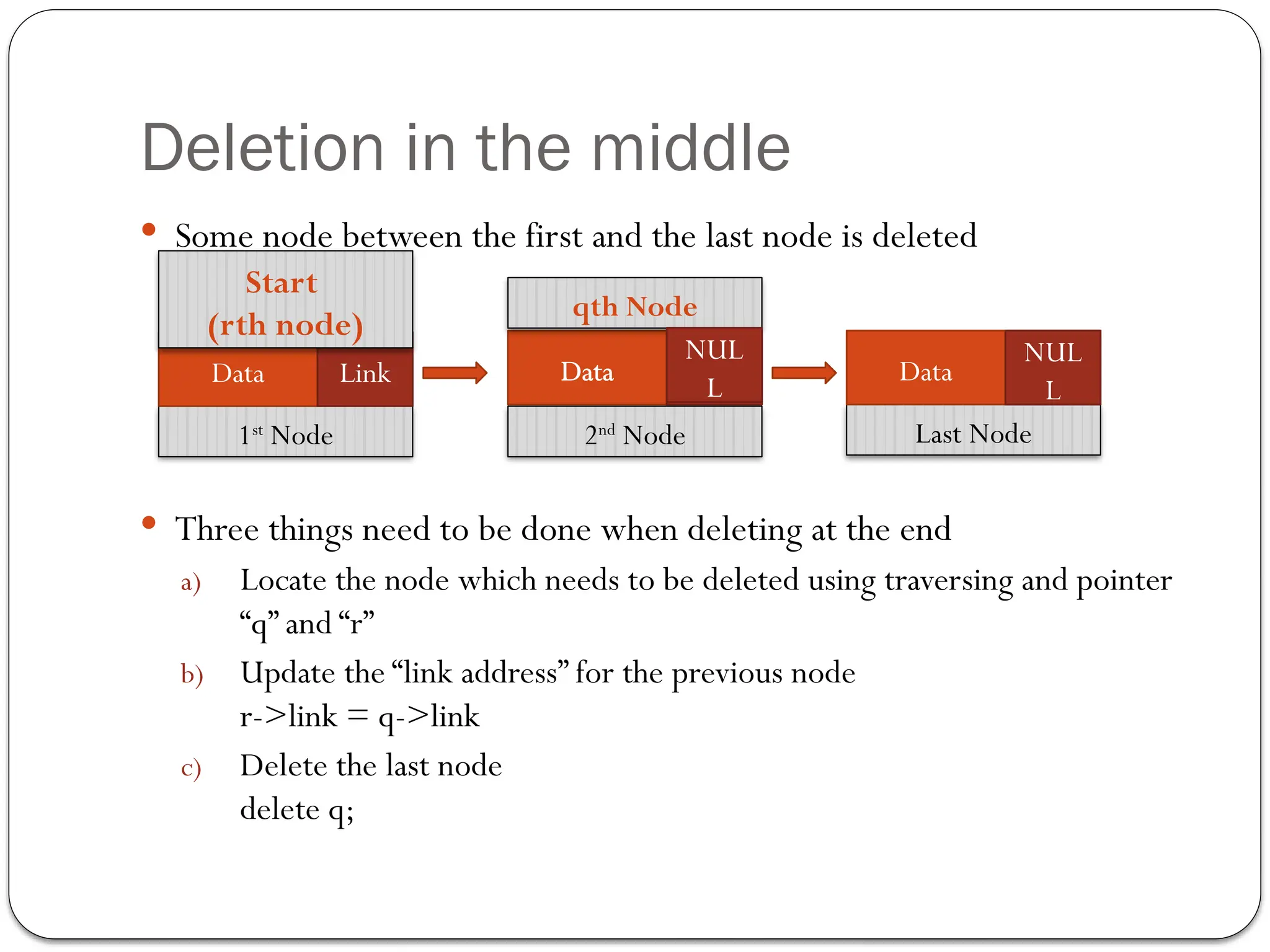
The document provides an overview of linked lists, explaining their structure, operations, and various methods for adding and deleting nodes. It describes the node components, including data and link pointers, and outlines basic operations like traversal, insertion (append, add as first, add after), and deletion (of first, middle, last nodes). The document also includes code examples for implementing these operations in C++.