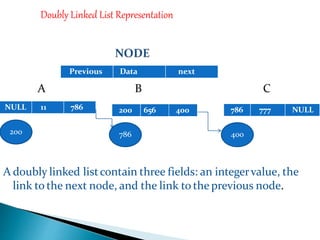
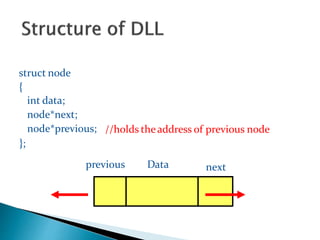
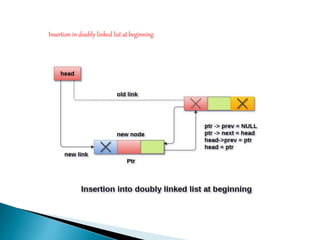
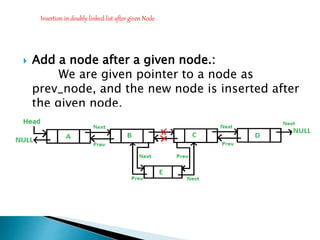
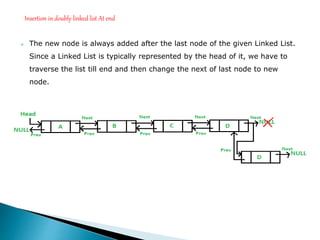
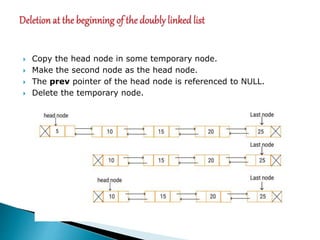
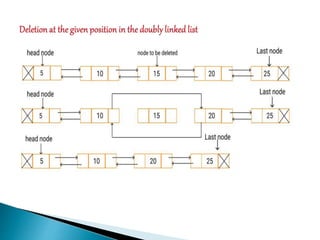
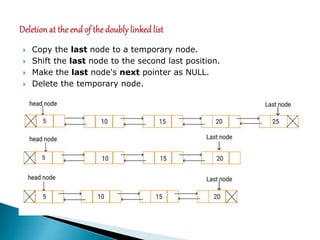
Doubly linked lists allow navigation in both directions by linking each node to both the next and previous nodes. Each node contains data and pointers to the next and previous nodes. Operations like insertion and deletion are more complex than with singly linked lists since both next and previous pointers must be updated. However, elements can be easily accessed from either direction. Basic operations on doubly linked lists include insertion and deletion at the beginning, end, or at a specified position in the list by adjusting the relevant next and previous pointers.