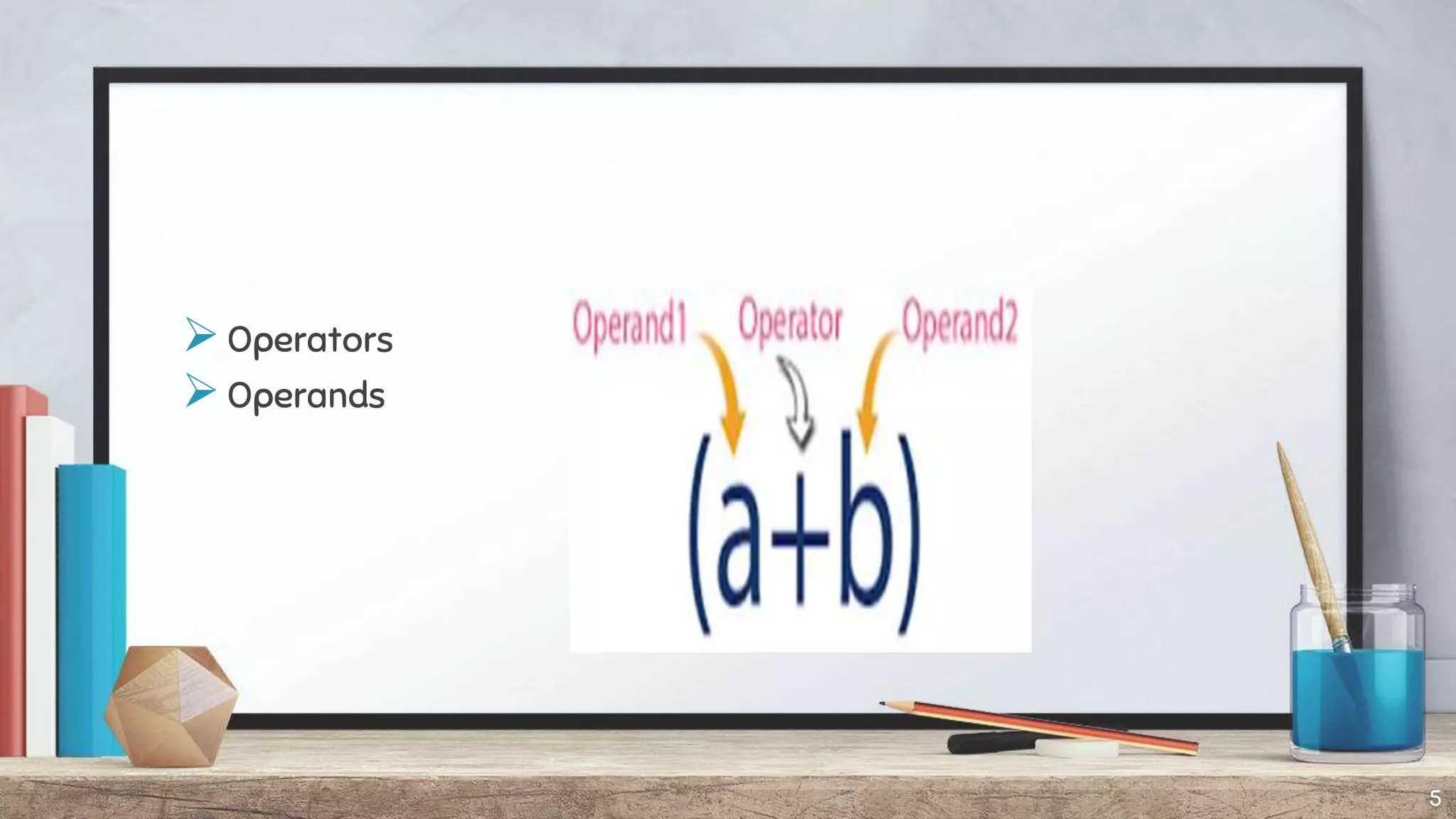
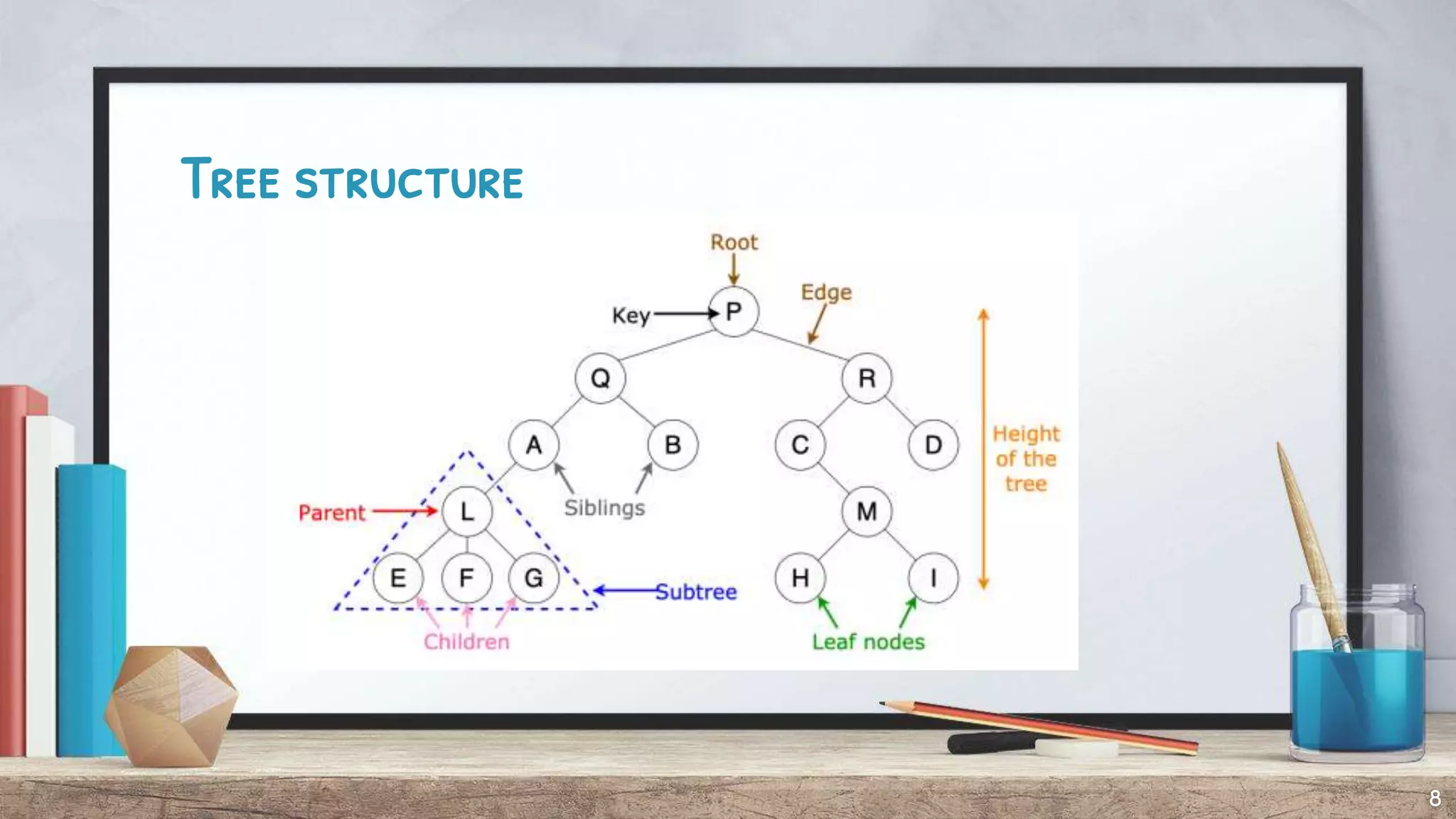
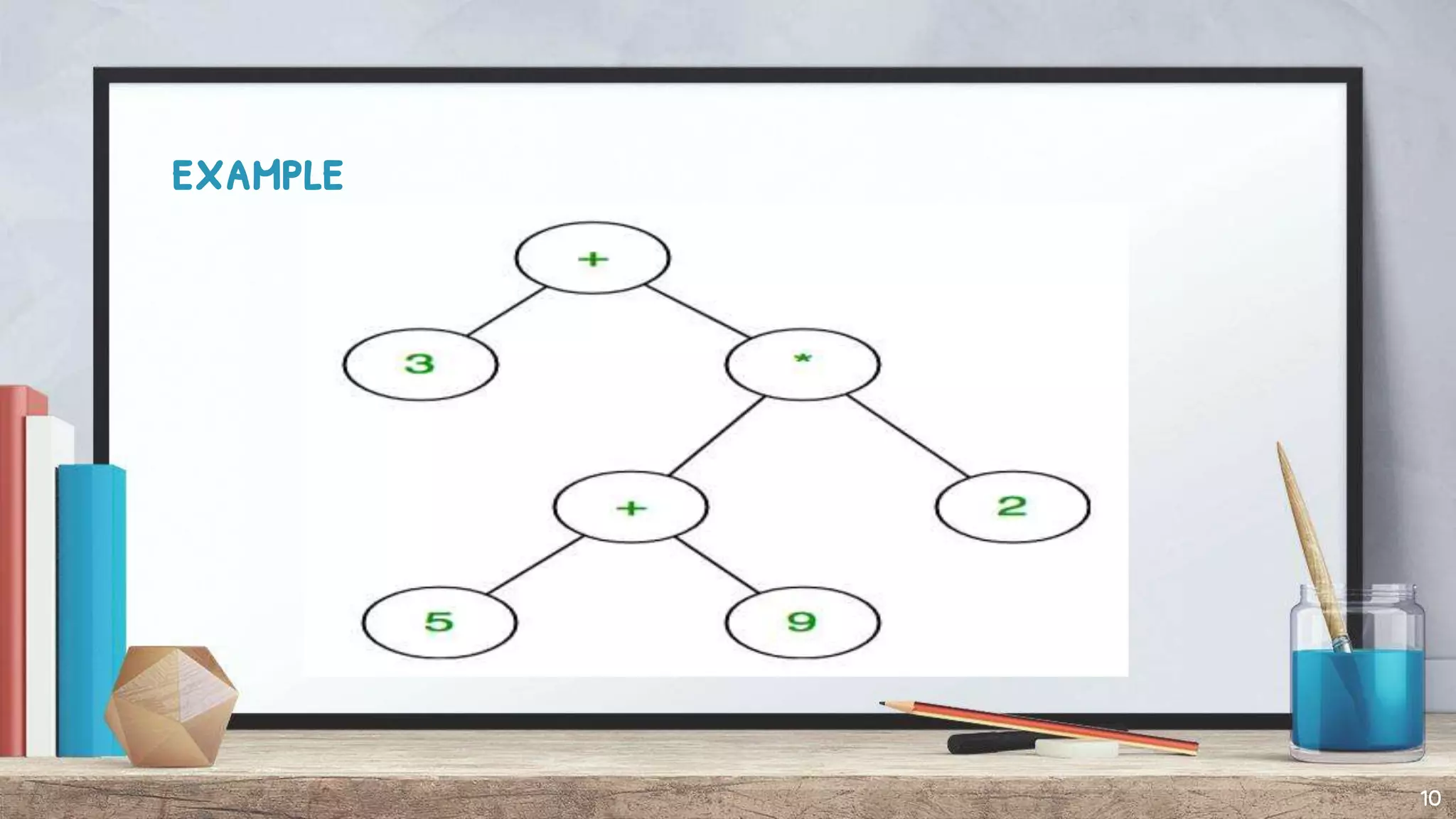
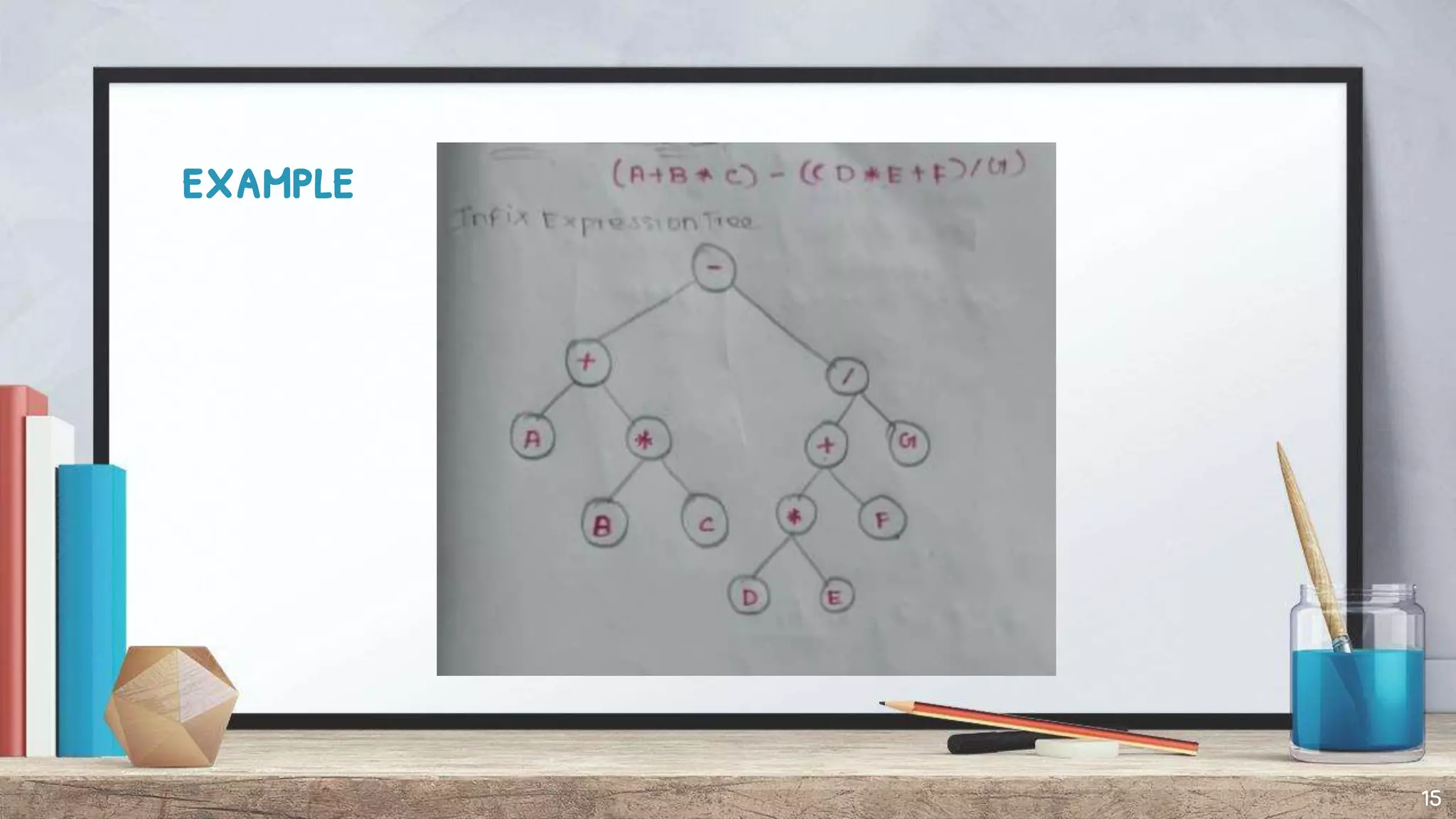
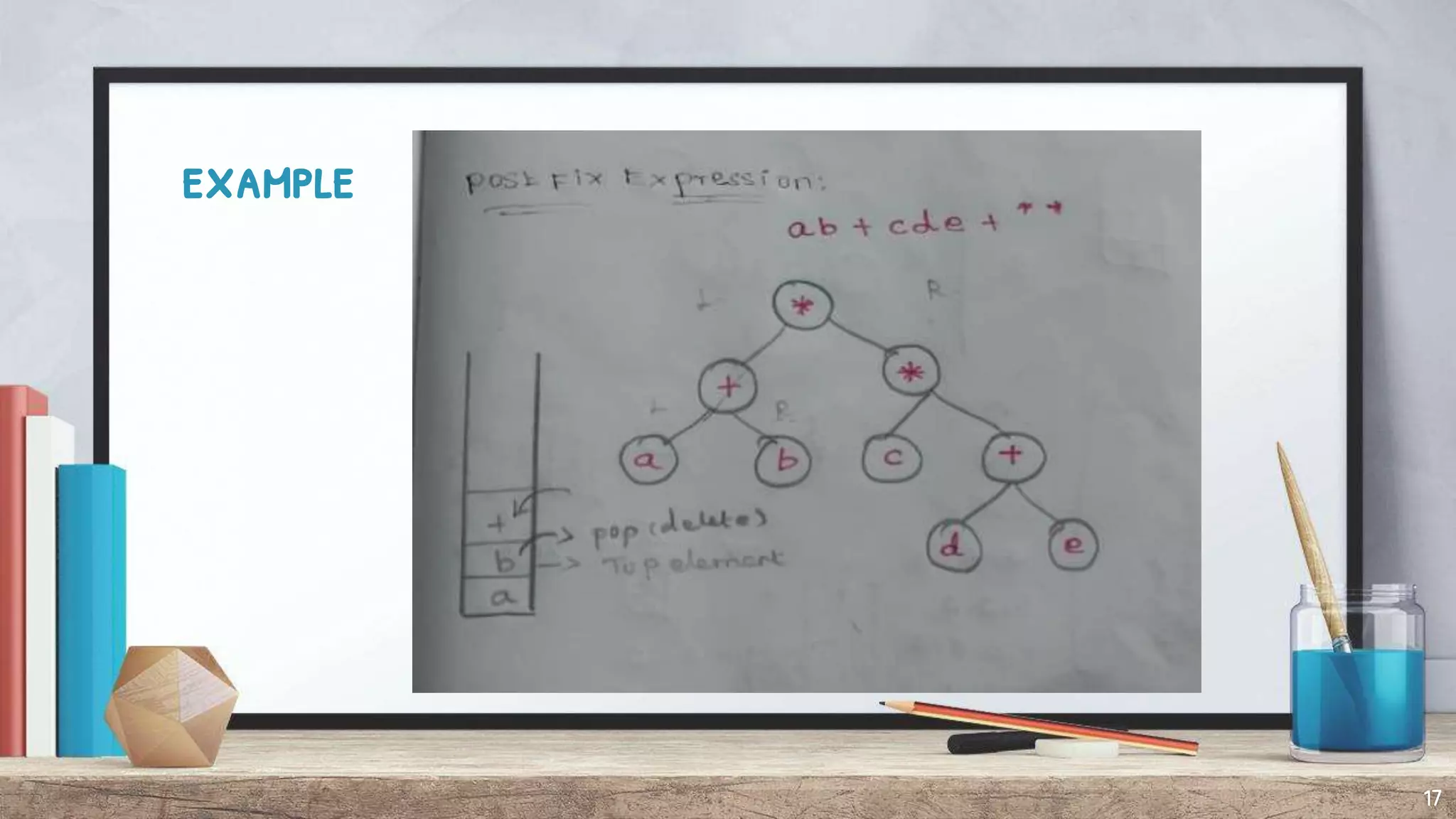
The document discusses expression trees, which are binary trees used to represent expressions. Each node in an expression tree contains either an operator or operand. There are three types of expressions - arithmetic, character, and logical/relational - which evaluate to a number, character, or true/false value. The document describes how to construct an expression tree using a stack, and provides examples of algebraic and Boolean expression trees. It also discusses traversing expression trees using infix, postfix, and prefix notation and provides examples of each.