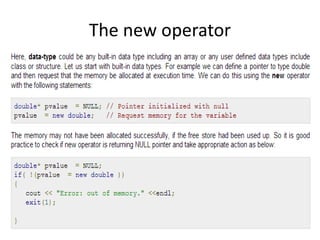
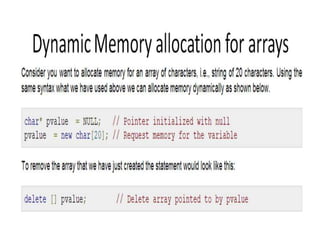
C++ strings are different from C strings and have additional functionality. Some key differences are that C++ strings can be initialized without needing strcpy, concatenated using +, and their length checked using length() or size(). Memory for C++ strings is automatically allocated and handled, unlike in C where memory must be manually allocated and managed.