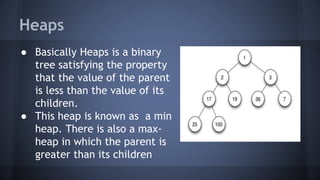
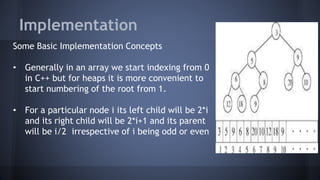
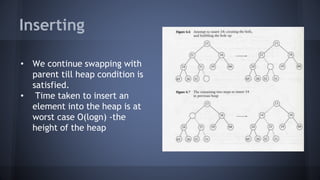
This document discusses heaps and their implementation and applications. It begins by defining heaps as binary trees where the value of each parent node is less than its children, forming a min heap. It then discusses the key properties of heaps, including finding the minimum element in O(1) time. The document goes on to describe implementing a heap using an array and the basic operations of insertion, deletion, and heapsort in O(logn) time. It concludes by discussing the advantages of heaps for fast insertion and removal and their applications in priority queues and sorting.