The document discusses different topics related to linked lists including:
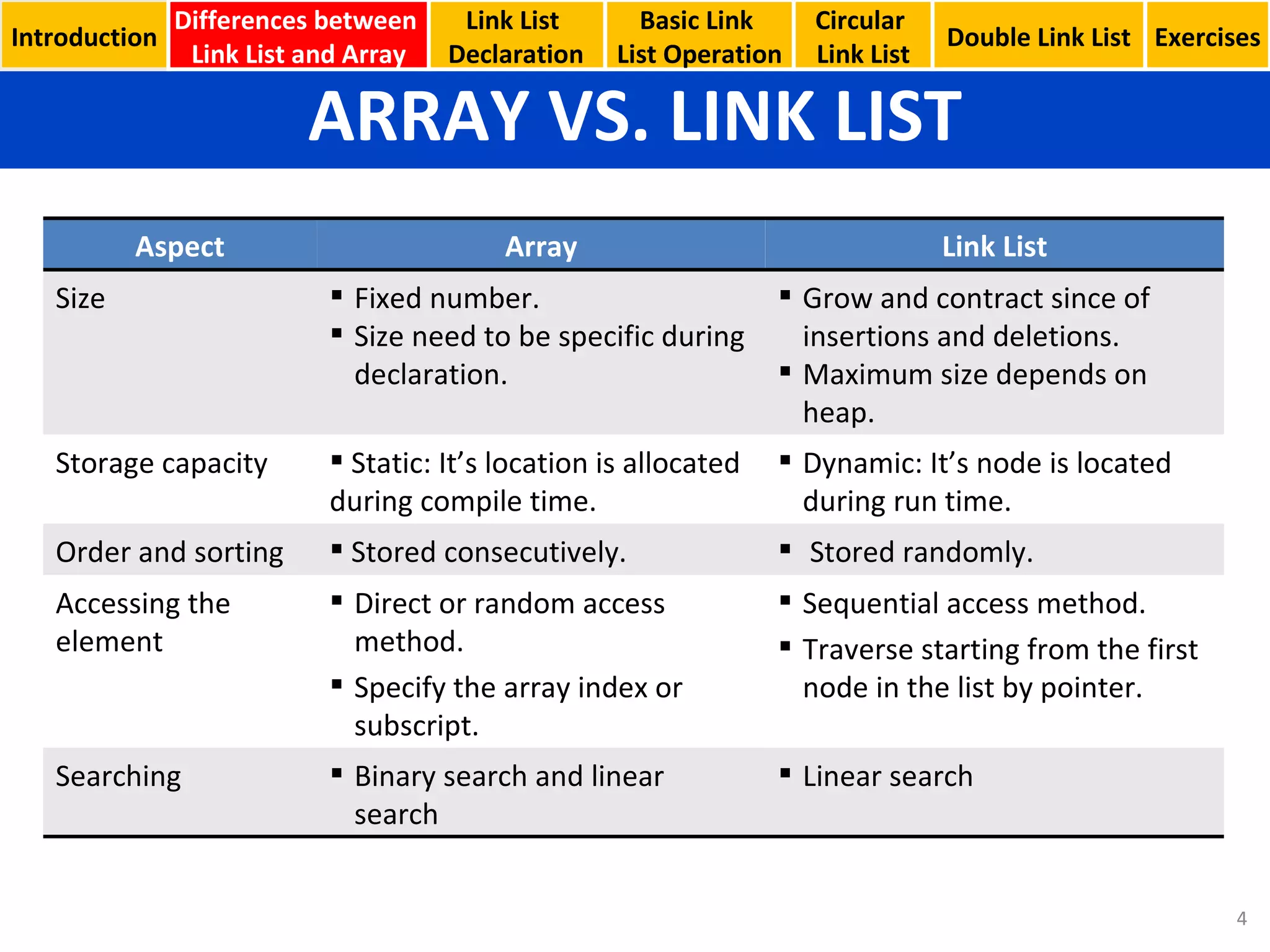
- The differences between linked lists and arrays
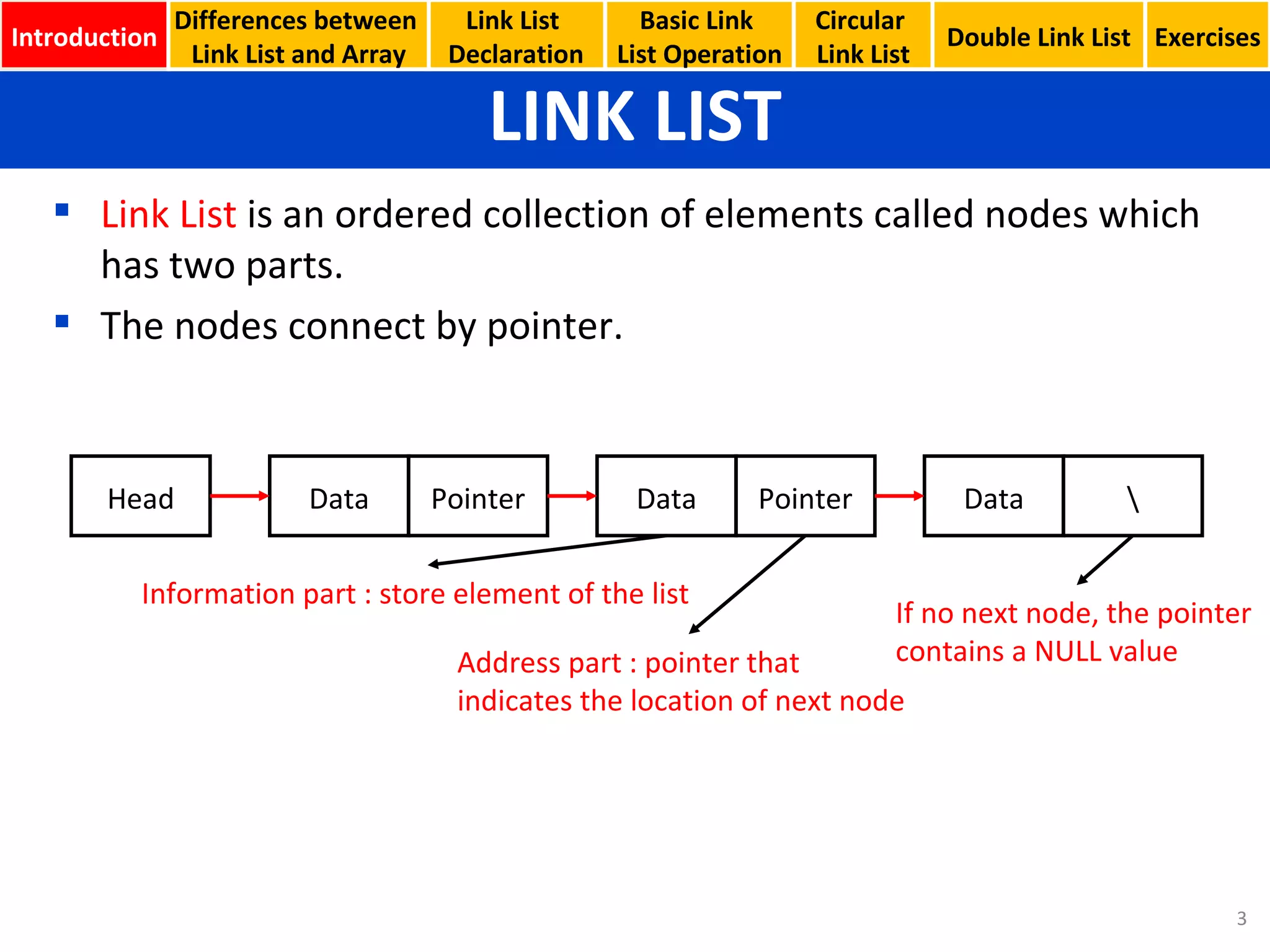
- Declaring linked list nodes
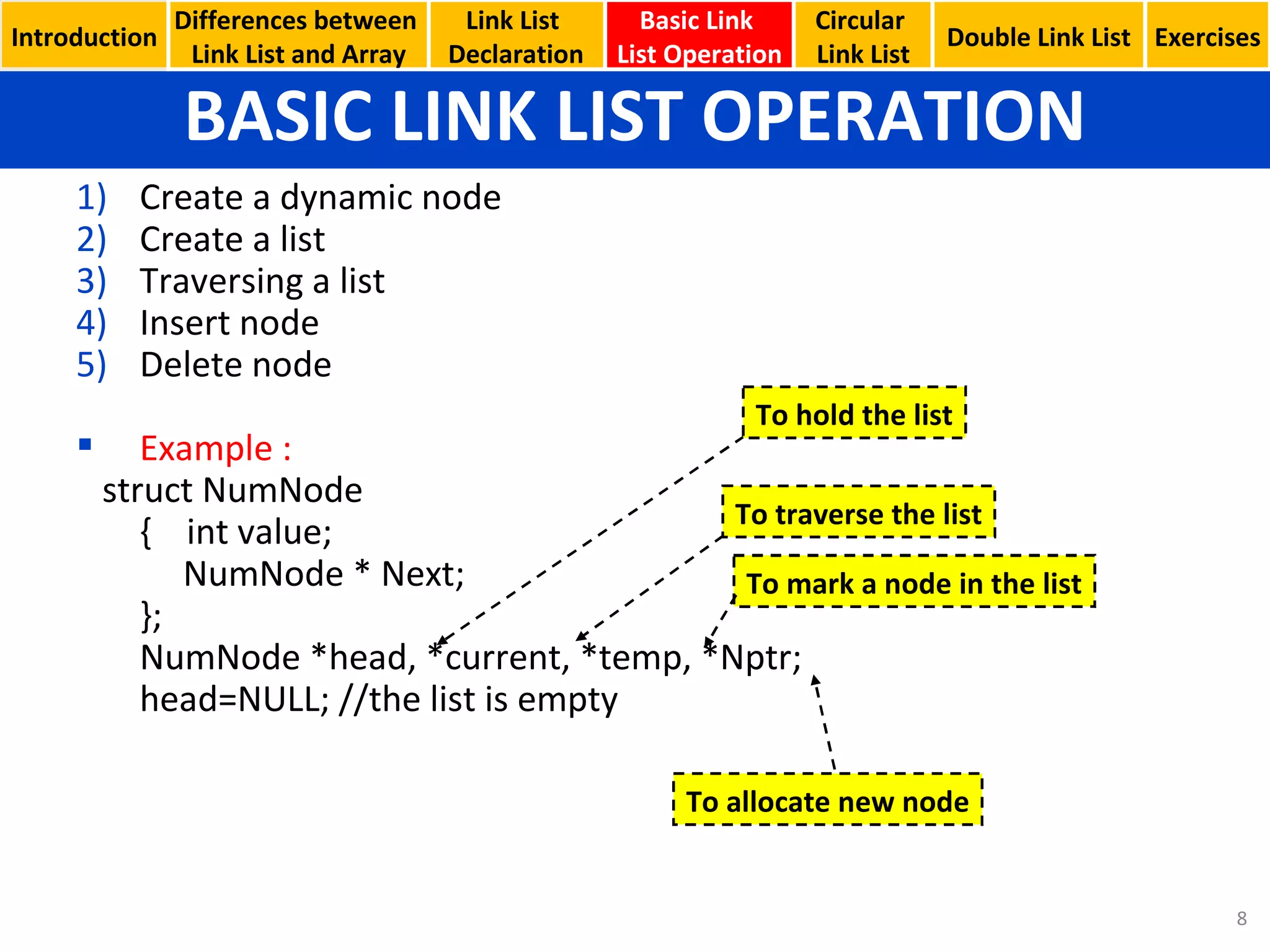
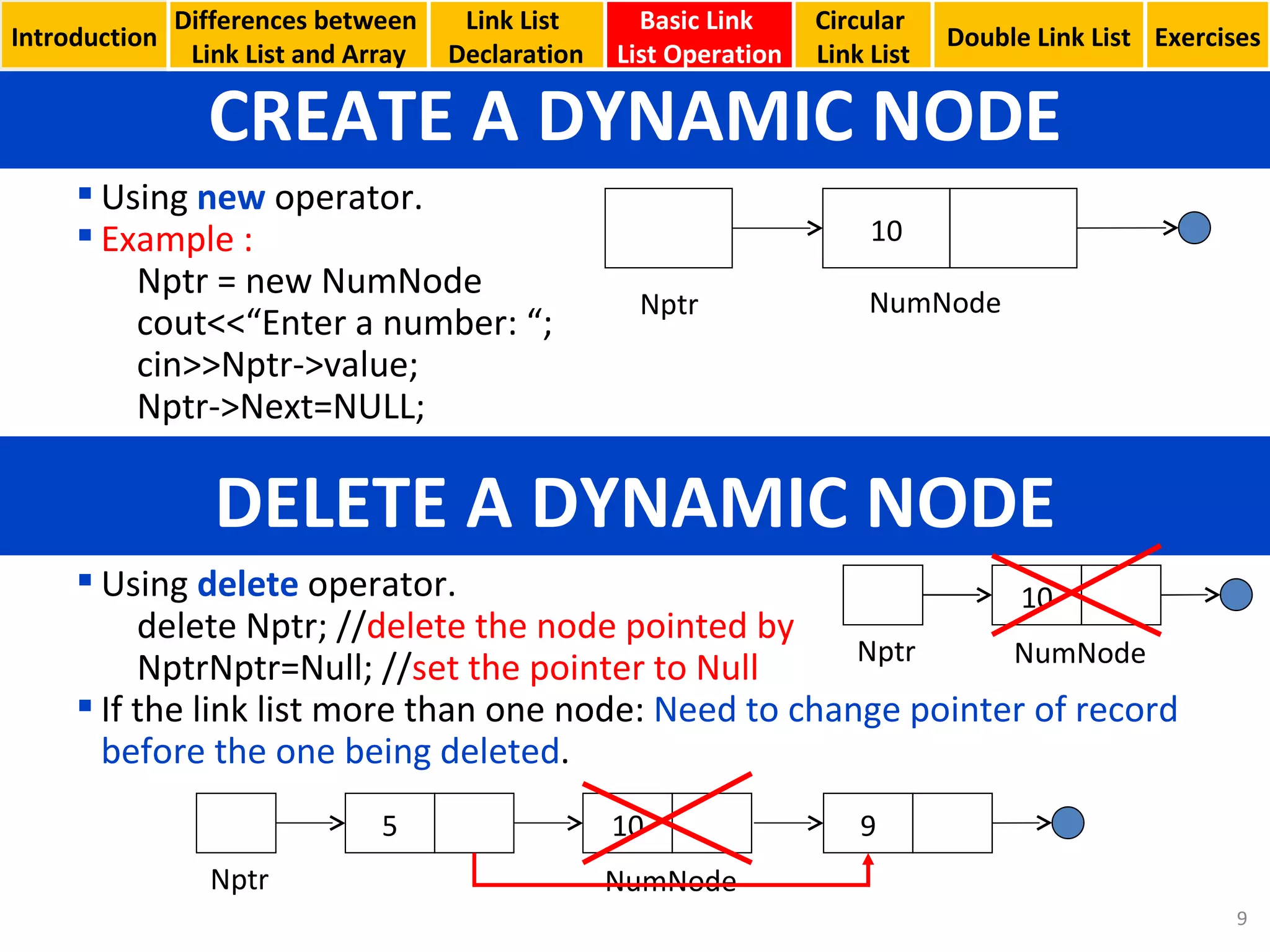
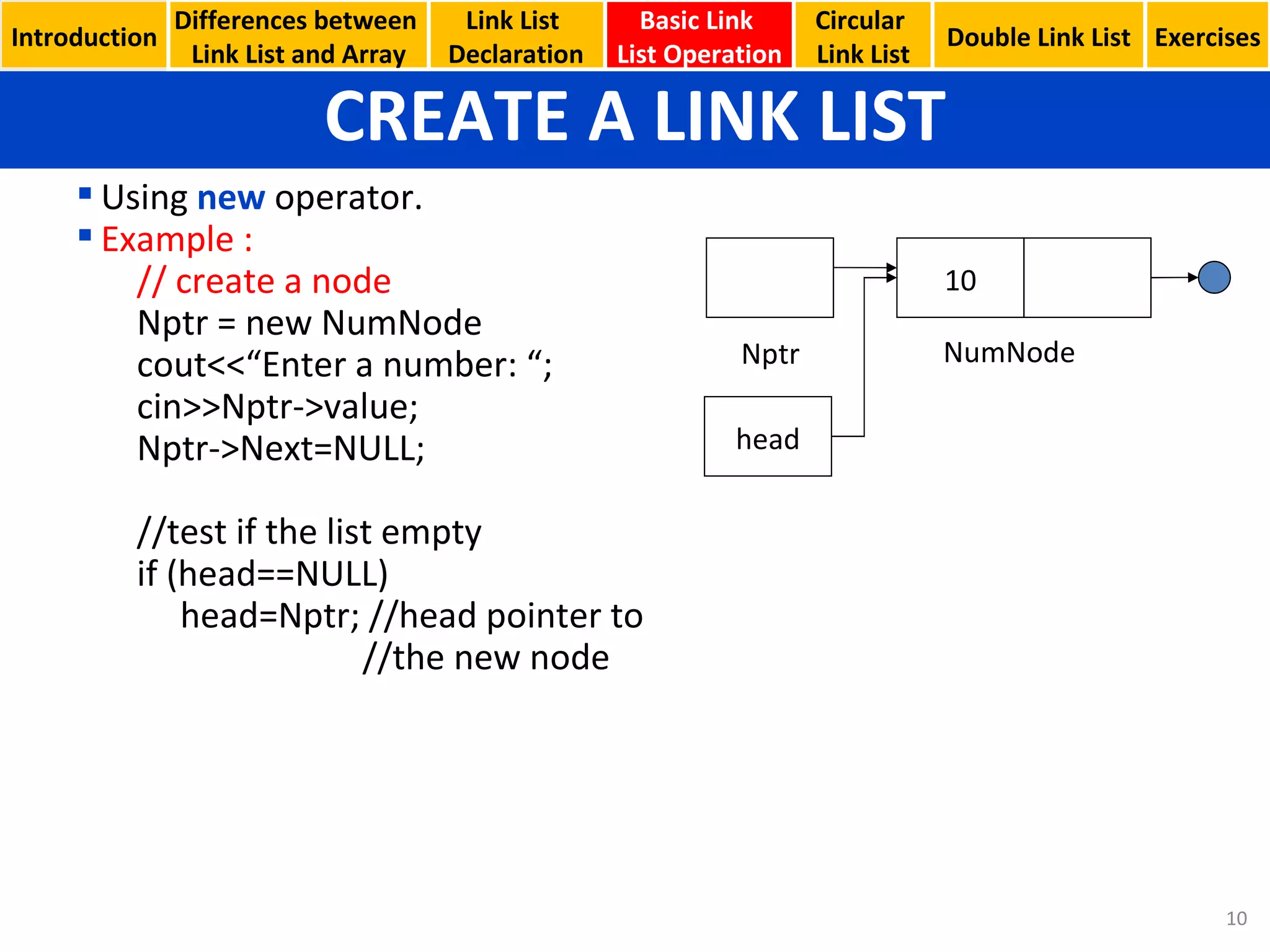
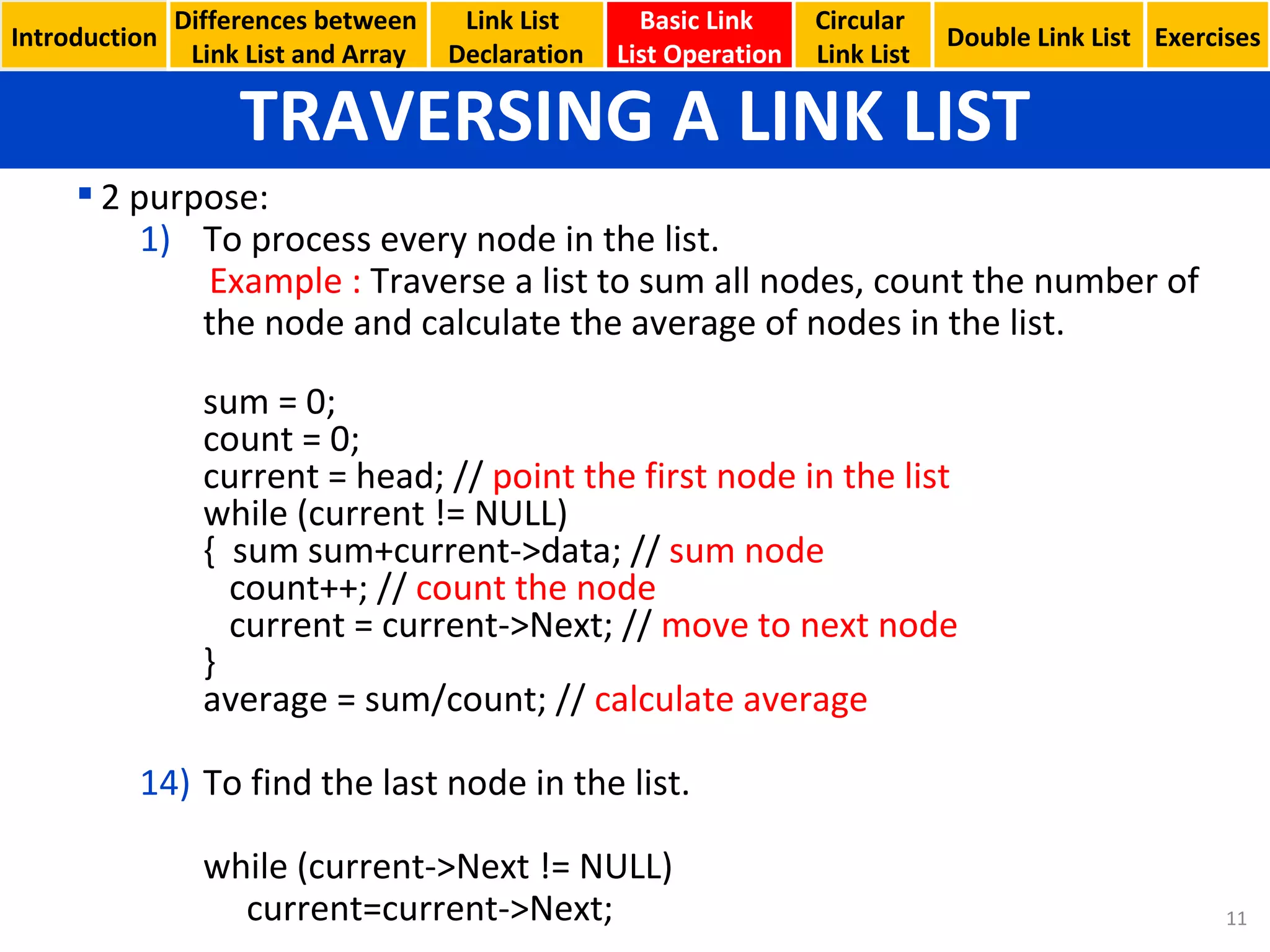
- Basic linked list operations like creating nodes, traversing the list, inserting and deleting nodes
- Using external pointers to reference the head, current and new nodes
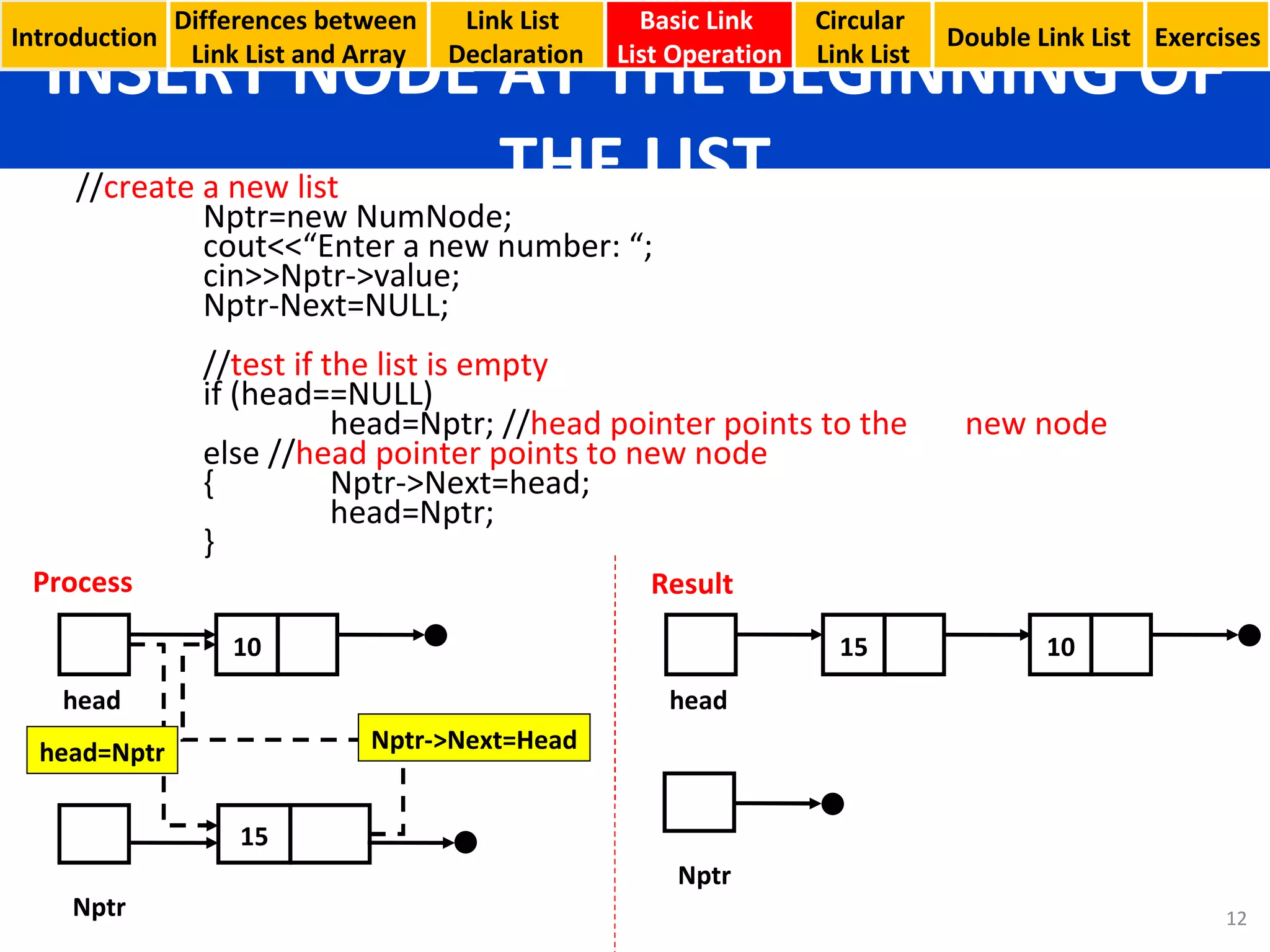
- Examples of inserting a node at the beginning of a linked list
The document contains code examples and diagrams to illustrate key concepts.


![LINK LIST DECLARATION Basic Link List Operation Circular Link List Syntax: struct nodename { variable declarations; nodename *next; }; Example 1: struct Node { int Data; // to store integer value; Node *Next; // a pointer to next node; }; Example 2: A link list node, STUDNODE stores an ID of a student (4 digit characters), name of a student (20 characters) and a floating point CGPA and a pointer to the next node. Write the declaration of the node. struct STUDNODE { char ID [4]; char name [20]; float CGPA; STUDNODE * Next; }; Introduction Link List Declaration Double Link List Exercises Differences between Link List and Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linklist-090914192343-phpapp02/75/Link-List-5-2048.jpg)

![LINK LIST EXTERNAL POINTER Basic Link List Operation Circular Link List Syntax: Nodename *pointer1,*pointer2,..,*pointerN; Example 1: struct Node { int Data; // to store integer value Node *Next; // a pointer to next node }; Node *Head, *Current, *NewNode; Example 2: struct STUDNODE { char ID [4]; char Name [20]; float CGPA; STUDNODE * Next; }; STUDNODE *Firstptr, *CurrPtr, *NewPtr; Introduction Link List Declaration Double Link List Exercises Differences between Link List and Array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linklist-090914192343-phpapp02/75/Link-List-7-2048.jpg)