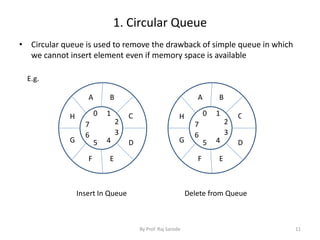
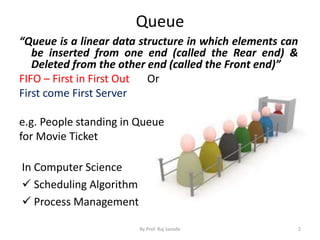
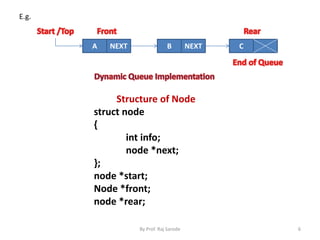
Queue is a linear data structure where elements are inserted at one end called the rear and deleted from the other end called the front. It follows the FIFO (first in, first out) principle. Queues can be implemented using arrays or linked lists. In an array implementation, elements are inserted at the rear and deleted from the front. In a linked list implementation, nodes are added to the rear and removed from the front using front and rear pointers. There are different types of queues including circular queues, double-ended queues, and priority queues.




![Algorithm 1
Q insert (Queue, MAX, FRONT, REAR, Element)
1. Check for Overflow
a. If REAR=MAX-1
or
FRONT = REAR+1 then
b. Print “overflow” & return
2. If FRONT =-1 then
Set FRONT=REAR=0
else if REAR=MAX then
Set REAR=FRONT=0
else Set REAR=REAR+1 //Increment Rear by 1
End if
End if
3. QUEUE [REAR] = Element //Insert the Element at New Location
4. Return.
By Prof. Raj Sarode 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5queue-141014023157-conversion-gate02/85/Queue-8-320.jpg)
![Algorithm 2
Q delete (Queue, MAX, FRONT, REAR, Element)
1. Check for Underflow
a. If FRONT=-1 then
b. Print “underflow” & return
Else
2. Element= Queue[FRONT] //delete element from queue
3. If FRONT=REAR then
Set FRONT=REAR=-1
Else
FRONT=FRONT+1 //Increment the Front by one
End if
4. Return
By Prof. Raj Sarode 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5queue-141014023157-conversion-gate02/85/Queue-9-320.jpg)