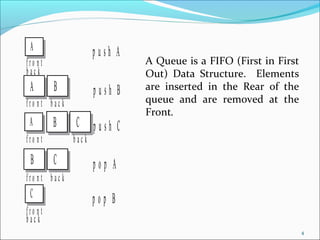
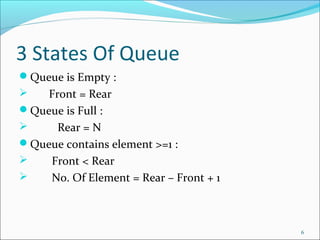
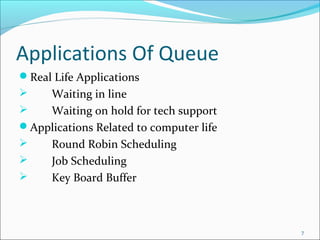
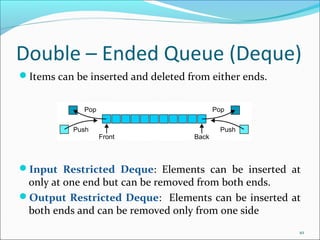
The document provides a comprehensive overview of queues, including their definition as a FIFO data structure where insertion occurs at the rear and deletion at the front. It covers various types of queues such as circular queues, double-ended queues (deques), and priority queues, as well as their applications in both real life and computer science, such as job scheduling and resource management. The document also discusses operations related to each type of queue and their specific functionalities.