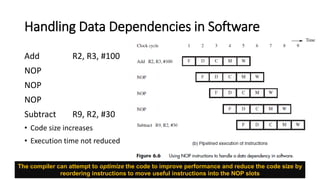
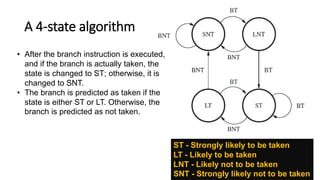
The document discusses the principles and advantages of pipelining in computer architecture, emphasizing how it improves performance by overlapping instruction execution and utilizing faster hardware. It also addresses issues such as hazards that can affect performance, memory delays, and branch penalties, while offering techniques like operand forwarding and dynamic branch prediction to mitigate these challenges. Additionally, it presents the potential for increased instruction throughput in superscalar processors and the role of optimizing compilers in enhancing performance.