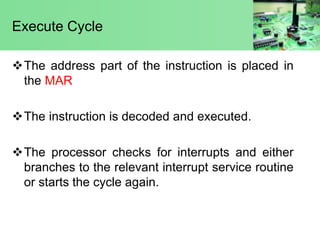
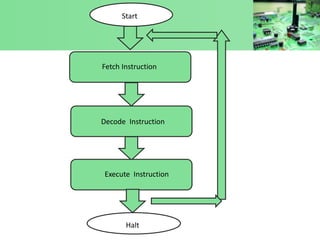
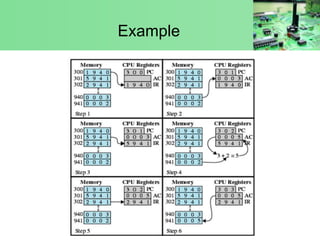
The document discusses instruction execution in a computer processor. It describes how a processor executes instructions by fetching them from memory using the program counter. The instruction is placed in the instruction register and decoded by the control unit. The control unit then selects components like the ALU to carry out operations. Common components involved in instruction execution are the program counter, memory address register, instruction register, memory buffer register, control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and accumulator. The execution cycle involves fetching the instruction from memory address, decoding it, and then executing the instruction.